/LOAD/PFLUID
Block Format Keyword This entry provides a simple way to simulate hydrodynamic fluid pressure on a structure. The fluid pressure is calculated according to the specified fluid velocity, orientation of the structural surface against the fluid vector and the height of the fluid column above the surface of the structure.
Format
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /LOAD/PFLUID/load_ID/unit_ID | |||||||||
| load_title | |||||||||
| surf_ID | sens_ID | ||||||||
| fct_hsp | Ascalex_hsp | Fscaley_hsp | |||||||
| Dir_hsp | frahsp_ID | ||||||||
| fct_pc | Ascalex_pc | Fscaley_pc | |||||||
| fct_vel | Ascalex_vel | Fscaley_vel | |||||||
| Dir_vel | fravel_ID | ||||||||
Definition
| Field | Contents | SI Unit Example |
|---|---|---|
| load_ID | Load block
identifier. (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| unit_ID | Unit Identifier. (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| load_title | Load block title. (Character, maximum 100 characters) |
|
| surf_ID | Surface
identifier. (Integer) |
|
| sens_ID | Sensor
identifier. (Integer) |
|
| fct_hsp | Hydro-static pressure as a
function of the fluid column height above the structural
surface. (Integer) |
|
| Ascalex_hsp | Abscissa scale factor for
fct_hsp. Default = 1.0 (Real) |
|
| Fscaley_hsp | Ordinate scale factor for
fct_hsp. Default = 1.0 (Real) |
|
| Dir_hsp | Vertical (gravitational)
direction of the water column above the structural surface (input X, Y or
Z). (Text) |
|
| frahsp_ID | Frame identifier for the vertical
(gravitational) direction of the water column above the structural
surface. (Integer) |
|
| fct_pc | Hydrodynamic drag coefficient as
a function of time. 4 (Integer) |
|
| Ascalex_pc | Abscissa scale factor for
fct_pc. Default = 1.0 (Real) |
|
| Fscaley_pc | Ordinate scale factor for
fct_pc. Default = 1.0 (Real) |
|
| fct_vel | Fluid velocity as a function of
time. (Integer) |
|
| Ascalex_vel | Abscissa scale factor for
fct_vel. Default = 1.0 (Real) |
|
| Fscaley_vel | Ordinate scale factor for
fct_vel. Default = 1.0 (Real) |
|
| Dir_vel | Direction of fluid velocity
(input X, Y or Z). (Text) |
|
| fravel_ID | Frame identifier for the fluid
velocity direction. (Integer) |
Example (Wind Effect)
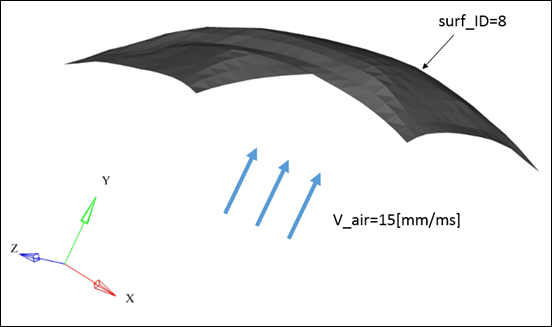
Figure 1.
#RADIOSS STARTER
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
/UNIT/1
unit for load
# MUNIT LUNIT TUNIT
kg mm ms
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
/LOAD/PFLUID/1/1
Wind effect
# surf_ID sens_ID
8 0
# fct_hsp Ascalex_hsp Fscaley_hsp
0 0 0
# Dir_hsp frahsp_ID
0
# fct_pc Ascalex_pc Fscaley_pc
2 0 2
# fct_vel Ascalex_vel Fscaley_vel
3 0 15
# Dir_vel fravel_ID
Y 0
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
/FUNCT/2
Air density
# X Y
0 1.2E-9
1000 1.2E-9
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
/FUNCT/3
Air velocity
# X Y
0 1
1000 1
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
#ENDDATAComments
- The fluid pressure applied to each
element of the structural surface is computed as:
(1) Where,- Fluid density
- Acceleration due to gravity
- Height of the water column above an element of the structural surface
- Relative fluid velocity which is normal to the element of the structural surface
- Drag coefficient for complete structural surface
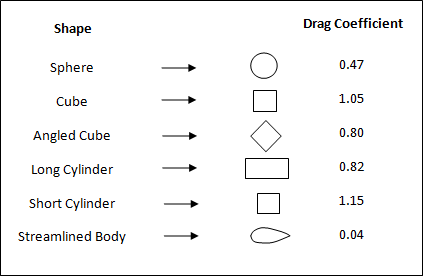
Figure 2. Drag Coefficient Values for Different Shapes - The value of hydrostatic pressure ( ) as a function of fluid column height ( ) above the structural surface is stated using the function fct_hsp. If this is not defined (=0), the effect is not accounted for (fct_hsp(altitude)=0).
- Hydrodynamic pressure is calculated
with respect to the relative orientation of the fluid vector and the element
normal.
(2) Where,- Specified fluid velocity (fct_vel(t)). If not defined (=0), the effect of fluid velocity is not accounted for ( = 0)
- Element velocity
- Element normal
- fct_pc defines the value of as a function of time. If this is not defined, the effect of fluid velocity is not accounted for.