Temperature functions
Electrical resistivity
Note: Only isotropic materials are considered.
Note: Resistivity ρ (rho) is a linear function of
temperature.
The corresponding mathematical formula is:
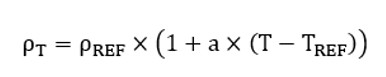
| ρ T | Resistivity to be defined at a temperature T. Linear function of the temperature for an isotropic or anisotropic material. |
| T REF | Reference temperature. |
| T | T is the temperature for which the resistivity must be computed. |
| ρ REF | Resistivity of the material at T REF . |
| a | Temperature coefficient at T REF . |
Thermal conductivity for all materials except gas and liquid
The thermal conductivity is defined at a reference temperature and is considered as constant for all thermal computations.
The reference temperature is then only a memo, to keep in mind the temperature corresponding to the indicated thermal conductivity.
| Symbol | Definition | Unit |
| T ref | Reference temperature (Tref) | °C |
| K ref | Isotropic thermal conductivity at Tref W/K/m) | W/K/m |
Specific heat variation versus temperature – For all material except gas and liquid
The specific heat is defined at a reference temperature and is considered as constant for all thermal computations.
The reference temperature is then only a memo, to keep in mind the temperature corresponding to the indicated specific heat.
| Symbol | Definition | Unit |
| T ref | Reference temperature (Tref) | °C |
| C ref | Specific heat at Tref (J/K/Kg) | J/K/Kg |
Remanent induction of magnets
Note: Only isotropic magnet is considered.
Note: Remanent induction (Br) is a linear function of the
temperature.
The corresponding mathematical formula is:
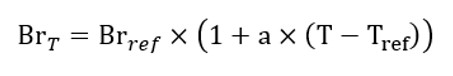
| Br T | Remanent induction to be defined at a temperature T. Linear function of the temperature for an isotropic or anisotropic material. |
| T ref | Reference temperature. |
| T | T is the temperature for which the remanent induction must be computed. |
| Br ref | Remanent induction of the magnet at T REF . |
| a | Reverse temperature coefficient for Br at T REF . |
Intrinsic Coercivity
Note: Only isotropic magnet is considered.
Note: Intrinsic Coercivity (HcJ) is a linear function of the
temperature.
The corresponding mathematical formula is:
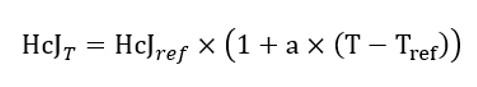
| HcJ T | Intrinsic Coercivity to be defined at a temperature T. Linear function of the temperature for an isotropic or anisotropic material. |
| T ref | Reference temperature. |
| T | T is the magnet temperature for which the Intrinsic Coercivity must be computed. |
| HcJ ref | Intrinsic Coercivity of the magnet at T REF . |
| a | Reverse temperature coefficient for Hcj at T REF . |