CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL
Specifies a thermal conductivity model for the temperature equation.
Type
AcuSolve Command
Syntax
CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL("name") {parameters...}
Qualifier
User-given name.
Parameters
- type (enumerated) [=none]
- Type of the thermal conductivity.
- constant or const
- Constant isotropic conductivity. Requires conductivity.
- constant_prandtl_number or const_pr
- Constant Prandtl number isotropic conductivity. Requires prandtl_number.
- ramped or ramp
- Ramp the isotropic conductivity to a constant value. Requires conductivity.
- piecewise_linear or linear
- Piecewise linear curve fit. Requires curve_fit_values and curve_fit_variable.
- cubic_spline or spline
- Cubic spline curve fit isotropic conductivity. Requires curve_fit_values and curve_fit_variable.
- user_function or user
- User-defined function. Requires user_function, user_values and user_strings.
- constant_anisotropic or const_aniso
- Constant anisotropic conductivity. Requires anisotropic_conductivity.
- piecewise_linear_anisotropic
- Piecewise linear curve fit anisotropic conductivity. Requires anisotropic_curve_fit_values and anisotropic_curve_fit_variable.
- cubic_spline_anisotropic
- Cubic spline curve fit anisotropic conductivity. Requires anisotropic_curve_fit_values and anisotropic_curve_fit_variable.
- user_function_anisotropic
- User-defined function anisotropic conductivity. Requires anisotropic_user_function, anisotropic_user_values and anisotropic_user_strings.
- cylindrical_anisotropic
- Anisotropic conductivity in a cylindrical system. Requires cylindrical_center, cylindrical_axis, anisotropic_conductivity.
- sutherland
- Sutherland temperature dependent conductivity. Requires sutherland_reference_conductivity, sutherland_reference_temperature, sutherland_constant.
- gas_kinetic
- Gas kinetic conductivity model for gases only. Requires GAS_KINETIC_MODEL.
- conductivity or cond (real) >=0 [=0]
- Constant value of the isotropic thermal conductivity. Used with constant and ramped types.
- prandtl_number or pr (real) >=0 [=0.71]
- Prandtl number value. Used with constant_prandtl_number type.
- curve_fit_values or curve_values (array) [={0,0}]
- A two-column array of independent-variable/isotropic conductivity data values. Used with piecewise_linear and cubic_spline types.
- curve_fit_variable or curve_var (enumerated) [=temperature]
- Independent variable of the curve fit for isotropic conductivity. Used with
piecewise_linear and cubic_spline types.
- x_coordinate or xcrd
- X-component of coordinates.
- y_coordinate or ycrd
- Y-component of coordinates.
- z_coordinate or zcrd
- Z-component of coordinates.
- x_reference_coordinate or xrefcrd
- X-component of reference coordinates.
- y_reference_coordinate or yrefcrd
- Y-component of reference coordinates.
- z_reference_coordinate or zrefcrd
- Z-component of reference coordinates.
- temperature or temp
- Temperature.
- species_1 or spec1
- Species 1.
- species_2 or spec2
- Species 2.
- species_3 or spec3
- Species 3.
- species_4 or spec4
- Species 4.
- species_5 or spec5
- Species 5.
- species_6 or spec6
- Species 6.
- species_7 or spec7
- Species 7.
- species_8 or spec8
- Species 8.
- species_9 or spec9
- Species 9.
- sutherland_reference_conductivity (real) >= 0 [=0.0241]
- Sutherland model reference conductivity at sutherland_reference_temperature. Used with sutherland type.
- sutherland_reference_temperature (real) > 0 [=273]
- Sutherland model reference temperature corresponding to sutherland_reference_conductivity. Used with sutherland type.
- sutherland_constant (real) > 0 [=194]
- Sutherland model constant. Used with sutherland type.
- user_function or user (string) [no default]
- Name of the user-defined function. Used with user_function type.
- user_values (array) [={}]
- Array of values to be passed to the user-defined function. Used with user_function type.
- user_strings (list) [={}]
- Array of strings to be passed to the user-defined function. Used with user_function type.
- anisotropic_conductivity or aniso_cond (array) [={0,0,0,0,0,0}]
- A six-element array of the form {k11, k22, k33, k12, k23, k31} for the anisotropic conductivity. Used with constant_anisotropic type.
- anisotropic_curve_fit_values or aniso_curve_values (array) [={0,0,0,0,0,0,0}]
- A seven-column array of independent-variable/anisotropic conductivity data values, in the order variable, k11, k22, k33, k12, k23, k31. Used with piecewise_linear_anisotropic and cubic_spline_anisotropic types.
- anisotropic_curve_fit_variable or aniso_curve_var (enumerated) [=temperature]
- Independent variable of the curve fit for anisotropic conductivity. Used with
piecewise_linear_anisotropic and
cubic_spline_anisotropic types.
- x_coordinate or xcrd
- X-component of coordinates.
- y_coordinate or ycrd
- Y-component of coordinates.
- z_coordinate or zcrd
- Z-component of coordinates.
- x_reference_coordinate or xrefcrd
- X-component of reference coordinates.
- y_reference_coordinate or yrefcrd
- Y-component of reference coordinates.
- z_reference_coordinate or zrefcrd
- Z-component of reference coordinates.
- temperature or temp
- Temperature.
- species_1 or spec1
- Species 1.
- species_2 or spec2
- Species 2.
- species_3 or spec3
- Species 3.
- species_4 or spec4
- Species 4.
- species_5 or spec5
- Species 5.
- species_6 or spec6
- Species 6.
- species_7 or spec7
- Species 7.
- species_8 or spec8
- Species 8.
- species_9 or spec9
- Species 9.
- anisotropic_user_function or aniso_user (string) [no default]
- Name of the user-defined function for anisotropic conductivity. Used with user_function_anisotropic type.
- anisotropic_user_values (array) [={}]
- Array of values to be passed to the user-defined function for anisotropic conductivity. Used with user_function_anisotropic type.
- anisotropic_user_strings (list) [={}]
- Array of strings to be passed to the user-defined function for anisotropic conductivity. Used with user_function_anisotropic type.
- cylindrical_center (array) [={0,0,0}]
- Array of the origin of a local cylindrical coordinate system. Used with cylindrical_anisotropic type and cylindrical_axis.
- cylindrical_axis (array) [={0,0,1}]
- Array of the longitudinal axis of a local cylindrical coordinate system. Used with cylindrical_anisotropic type and cylindrical_center.
- multiplier_function (string) [=none]
- User-given name of the multiplier function for scaling the conductivity. If none, no scaling is performed.
- turbulent_prandtl_number_type (enumerated) [=constant]
- Used with turbulence models.
- constant
- User-specified turbulent Prandtl number. Requires turbulent_prandtl_number.
- auto
- Turbulent Prandtl number is computed based on local flow and material properties.
- turbulent_prandtl_number or turb_pr (real) >0 [=0.91]
- Value of the turbulent Prandtl number. Used when turbulent_prandtl_number_type = constant.
Description
This command specifies a thermal conductivity model for the temperature (energy) equation. This model is applicable to fluid, solid, and shell element sets.
CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL( "my conductivity model" ) {
type = constant
conductivity = 2.521e-2
}
MATERIAL_MODEL( "my material model" ) {
conductivity_model = "my conductivity model"
...
}
ELEMENT_SET( "fluid elements" ) {
material_model = "my material model"
...
}The heat flux vector q is given by either:
where κ is an isotropic thermal conductivity, or by:
where K is an anisotropic thermal conductivity.
CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL( "my anisotropic conductivity model" ) {
type = constant_anisotropic
anisotropic_conductivity = { 0.02, 0.03, 0.04, 0, 0, 0 }
}The elements of the anisotropic conductivity tensor are always specified in the order k11, k22, k33, k12, k23, k31.
CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL( "MyCylindricalConductivity" ) {
type = cylindrical_anisotropic
cylindrical_center = { 0.0, 0.0, 0.0; }
cylindrical_axis = { 0.785, 0.0, 0.785; }
anisotropic_conductivity = { 1.0, 50.0, 50.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0; }
}A constant_prandtl_number conductivity model computes the isotropic thermal conductivity from the specific heat at constant pressure and the viscosity:
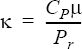
SPECIFIC_HEAT_MODEL( "air" ) {
type = constant
specific_heat = 1005
}
VISCOSITY_MODEL( "air" ) {
type = constant
viscosity = 1.781e-5
}
CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL( "air" ) {
type = constant_prandtl_number
prandtl_number = 0.71
}
MATERIAL_MODEL( "air" ) {
specific_heat_model = "air"
viscosity_model = "air"
conductivity_model = "air"
}yields a thermal conductivity of 2.521e-2.
CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL( "ramped conductivity model" ) {
type = ramped
conductivity = 2.521e-2
}starts at conductivity of 2.521e+1 at time step one and reduces the conductivity until time step 10, at which time a conductivity of 2.521e-2 is used.
CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL( "curve fit conductivity model" ) {
type = piecewise_linear
curve_fit_values = { 273, 2.42e-2 ;
323, 2.76e-2 ;
373, 3.10e-2 ;
423, 3.44e-2 ; }
curve_fit_variable = temperature
}defines the conductivity as a function of temperature. The curve_fit_values parameter is a two-column array corresponding to the independent variable and the conductivity values. The independent variable values must be in ascending order. The limit point values of the curve fit are used when curve_fit_variable falls outside of the curve fit limits.
273 2.42e-2
323 2.76e-2
373 3.10e-2
423 3.44e-2CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL( "curve fit conductivity model" ) {
type = piecewise_linear
curve_fit_values = Read( "conductivity.fit" )
curve_fit_variable = temperature
}CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL( "curve fit anisotropic conductivity model" ) {
type = piecewise_linear_anisotropic
anisotropic_curve_fit_values = { 273, 2.42e-2, 3.42e-2, 4.42e-2, 0, 0, 0 ;
323, 2.76e-2, 3.76e-2, 4.76e-2, 0, 0, 0 ;
373, 3.10e-2, 4.10e-2, 5.10e-2, 0, 0, 0 ;
423, 3.44e-2, 4.44e-2, 5.44e-2, 0, 0, 0 ; }
anisotropic_curve_fit_variable = temperature
}defines the anisotropic conductivity as a function of temperature. The anisotropic_curve_fit_values parameter is a seven-column array corresponding to the independent variable and the component values of the conductivity tensor. The independent variable values must be in ascending order. The limit point values of the curve fit are used when anisotropic_curve_fit_variable falls outside of the curve fit limits.
273 2.42e-2 3.42e-2 4.42e-2 0 0 0
323 2.76e-2 3.76e-2 4.76e-2 0 0 0
373 3.10e-2 4.10e-2 5.10e-2 0 0 0
423 3.44e-2 4.44e-2 5.44e-2 0 0 0CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL( "curve fit anisotropic conductivity model" ) {
type = piecewise_linear_anisotropic
anisotropic_curve_fit_values = Read( "anisotropic_conductivity.fit" )
anisotropic_curve_fit_variable = temperature
}The sutherland type defines a temperature dependent conductivity model according to the following equation:
where is the sutherland_reference_conductivity at the specified sutherland_reference_temperature ( ), is the model temperature and is the sutherland_constant.
VISCOSITY_MODEL( "Sutherland Model" ) {
type = sutherland
sutherland_reference_conductivity = 2.41e-2
sutherland_reference_temperature = 273.0
sutherland_constant = 194
}Conductivity types user_function and user_function_anisotropic may be used to model more complex behaviors; see the AcuSolve User-Defined Functions Manual for a detailed description of user defined functions.
CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL( "UDF conductivity model" ) {
type = user_function
user_function = "usrConductivityExample"
user_values = { 0.02, # constant value
1.e-3, # temperature scale
1.e-3 } # species scale
}#include "acusim.h"
#include "udf.h"
UDF_PROTOTYPE( usrConductivityExample ) ; /* function prototype */
Void usrConductivityExample (
UdfHd udfHd, /* Opaque handle for accessing data */
Real* outVec, /* Output vector */
Integer nItems, /* Number of elements */
Integer vecDim /* = 1 */
) {
Integer elem ; /* an element counter */
Real cond0 ; /* reference conductivity */
Real sScale ; /* species scale */
Real tScale ; /* temperature scale */
Real* spec ; /* species field */
Real* temp ; /* temperature field */
Real* usrVals ; /* user values */
udfCheckNumUsrVals( udfHd, 3 ) ; /* check for error */
usrVals = udfGetUsrVals( udfHd ) ; /* get the user vals */
cond0 = usrVals[0] ; /* reference cond. */
tScale = usrVals[1] ; /* temp. scale */
sScale = usrVals[2] ; /* spec. scale */
temp = udfGetElmData( udfHd, UDF_ELM_TEMPERATURE ) ; /* get temperature */
spec = udfGetElmData( udfHd, UDF_ELM_SPECIES ) ; /* get species */
for ( elem = 0 ; elem < nItems ; elem++ ) {
outVec[elem] = cond0
+ tScale * temp[elem]
+ sScale * spec[elem] ;
}
} /* end of usrConductivityExample() */CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL( "UDF anisotropic conductivity model" ) {
type = user_function_anisotropic
anisotropic_user_function = "usrAnisoConductivityExample"
anisotropic_user_values = { 0.02, # constant value
1.e-3, # temperature scale
1.e-3 } # species scale
}#include "acusim.h"
#include "udf.h"
UDF_PROTOTYPE( usrAnisoConductivityExample ) ; /* function prototype */
Void usrAnisoConductivityExample (
UdfHd udfHd, /* Opaque handle for accessing data */
Real* outVec, /* Output vector */
Integer nItems, /* Number of elements */
Integer vecDim /* = 6 */
) {
Integer elem ; /* an element counter */
Real cond ; /* conductivity */
Real cond0 ; /* reference conductivity */
Real sScale ; /* species scale */
Real* tScale ; /* temperature scale */
Real* spec ; /* species field */
Real* temp ; /* temperature field */
Real* usrVals ; /* user values */
udfCheckNumUsrVals( udfHd, 3 ) ; /* check for error */
usrVals udfGetUsrVals( udfHd ) ; /* get the user vals */
cond0 = usrVals[0] ; /* reference cond. */
tScale = usrVals[1] ; /* temp. scale */
sScale = usrVals[2] ; /* spec. scale */
temp = udfGetElmData( udfHd, UDF_ELM_TEMPERATURE ) ; /* get temperature */
spec = udfGetElmData( udfHd, UDF_ELM_SPECIES ) ; /* get species */
for ( elem = 0 ; elem < nItems ; elem++ ) {
cond = cond0 + tScale * temp[elem] + sScale * spec[elem] ;
outVec[0*nItems+elem] = cond ;
outVec[1*nItems+elem] = cond ;
outVec[2*nItems+elem] = cond ;
outVec[3*nItems+elem] = 0 ;
outVec[4*nItems+elem] = 0 ;
outVec[5*nItems+elem] = 0 ;
}
} /* end of usrAnisoConductivityExample() */The dimension of the returned conductivity vector, outVec, is the number of elements times six.
CONDUCTIVITY_MODEL( "similar to ramped conductivity model" ) {
type = constant
conductivity = 2.521e-2
multiplier_function = "ramped"
}
MULTIPLIER_FUNCTION( "ramped" ) {
type = piecewise_log_linear
curve_fit_values = { 1, 1000 ; 10, 1 }
curve_fit_variable = time_step
}In areas of turbulent flow the molecular conductivity κ or K is replaced by the total conductivity κ + κt or K+ κtI(where I is the identity matrix) in the definition of the heat flux vector for the isotropic or anisotropic cases respectively. The turbulent conductivity κt is defined by
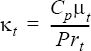
where t is the turbulent viscosity, given by the turbulence model in use; and Prt is the turbulent Prandtl number, given by turbulent_prandtl_number.