ACU-T: 6102 Particle Separation in a Windshifter using AcuSolve - EDEM Bidirectional Coupling
Tutorial Level: Beginner
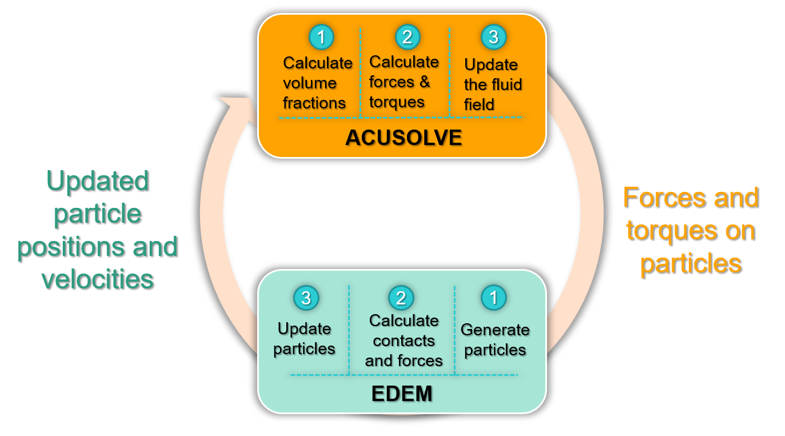
This tutorial introduces you to the workflow for setting up and running a basic bidirectional coupling (two-way) simulation using AcuSolve and EDEM. Prior to starting this tutorial, you should have already run through the introductory tutorial, ACU-T: 1000 Basic Flow Set Up, and ACU-T: 6100 Particle Separation in a Windshifter using Altair EDEM, and have a basic understanding of HyperMesh CFD, AcuSolve, and EDEM. To run this simulation, you will need access to a licensed version of HyperMesh CFD, AcuSolve, and EDEM.
Problem Description
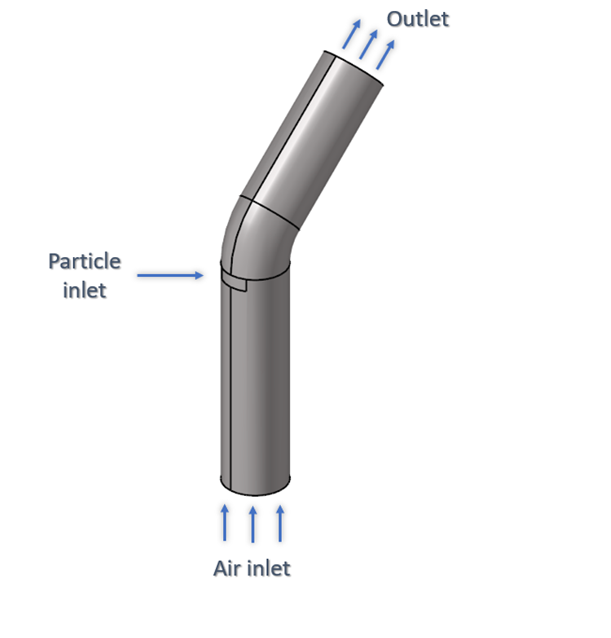
The model consists of a cylindrical pipe with a 45-degree bend. The radius of the pipe is 0.25 m and the particle inlet is located midway through the length of the pipe.
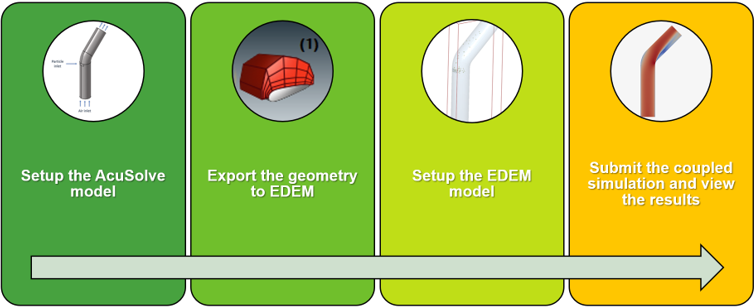
Accordingly, the tutorial consists of two parts:
- AcuSolve setup and geometry export
- EDEM setup and simulation
The AcuSolve model will be set up using HyperMesh CFD. Once the AcuSolve setup is complete, the EDEM deck with the geometry will be exported from HyperMesh CFD. This input deck will be opened in EDEM and will be used to complete the EDEM setup. Once the EDEM deck is set up, you will launch the coupled simulation.
Two different bulk materials used in the EDEM simulation and their properties are listed below:
| Name | Density (kg/m3) | Particle radius (m) | Average weight of individual particle (kg) | Rate of generation (particles per sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy particle | 900 | 0.03 | 0.1 | 100 |
| Light particle | 100 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 100 |
Part 1 - AcuSolve Simulation
Start HyperMesh CFD and Open the HyperMesh Database
- Start HyperMesh CFD from the Windows Start menu by clicking .
-
From the Home tools, Files tool group, click the Open Model tool.
Figure 4. 
The Open File dialog opens. - Browse to the directory where you saved the model file. Select the HyperMesh file ACU-T6102_windshifter.hm and click Open.
- Click .
-
Save the database as windshifter_bidirectional in
the same directory as the other input files.
This will be the working directory and all the files related to the simulation will be stored in this location.
Validate the Geometry
The Validate tool scans through the entire model, performs checks on the surfaces and solids, and flags any defects in the geometry, such as free edges, closed shells, intersections, duplicates, and slivers.

Set Up Flow
Set the General Simulation Parameters
-
From the Flow ribbon, click the Physics tool.
Figure 6. 
The Setup dialog opens. - Under the Physics models setting, select the Multiphase flow radio button.
- Change the Multifluid type to Bidirectional EDEM Coupling.
-
Click the Eulerian material drop-down menu and select Material
Library from the list.
You can create new material models in the Material Library.
-
In the Material Library dialog, select EDEM 2 Way
Multiphase, switch to the My Material
tab, then click
 to add a new material model.
to add a new material model.
- In the microdialog, click EDEM Bidirectional Material in the top-left corner and change the name to Air-Particle.
- Set the Carrier field to Air (if not set already).
-
Set the drag model and the drag coefficients as shown in the figure
below.
Figure 7. 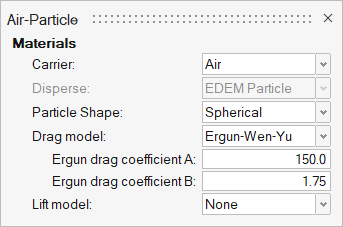
- Close the material model microdialog and then close the Material Library dialog.
- In the Setup dialog, set the Eulerian Material to Air-Particle.
-
Set Time step size and Final time to 0.001 and
1, respectively. Select
Spalart-Allmaras for the Turbulence model. Verify
that Gravity is set to 0, 0, -9.81, as shown below.
Figure 8. 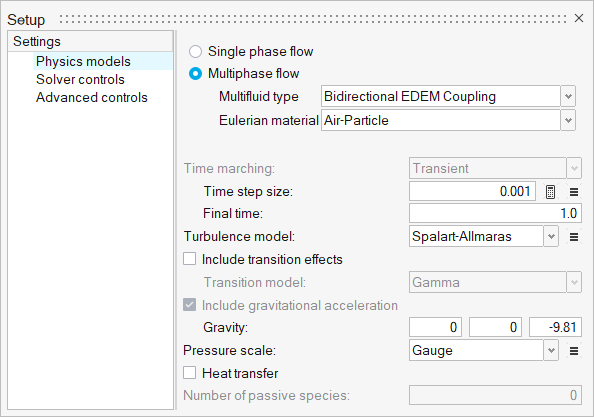
-
Click the Solver controls setting and set the Minimum
and Maximum stagger iterations to 2 and
4, respectively.
Figure 9. 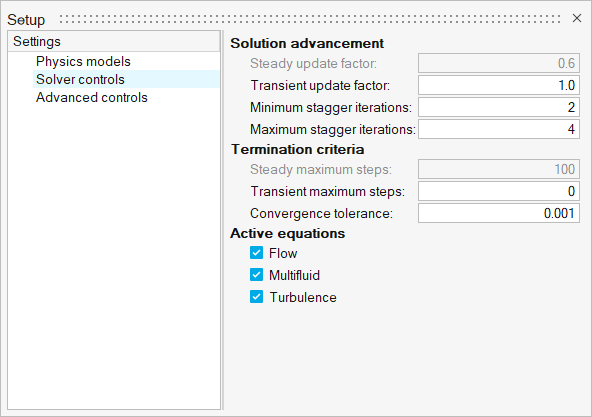
- Close the dialog and save the model.
Assign Material Properties
-
From the Flow ribbon, click the Material tool.
Figure 10. 
- Verify that Air-Particle has been assigned as the material.
-
On the guide bar, click
 to exit
the tool.
to exit
the tool.
Define Flow Boundary Conditions
-
From the Flow ribbon, Profiled
tool group, click the Profiled Inlet tool.
Figure 11. 
-
Click on the inlet face highlighted in the figure below. In the microdialog, enter a value of 20 m/s
for the Average velocity and set the Carrier fluid volume fraction to
1.0.
Figure 12. 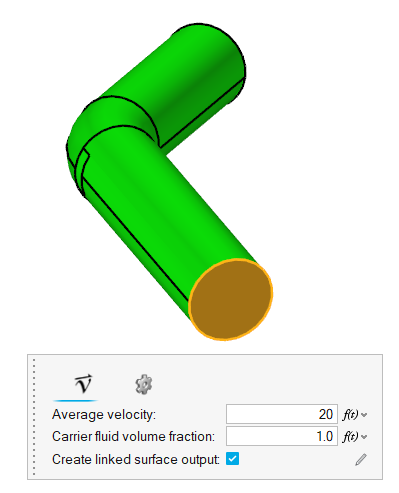
-
On the guide bar, click
 to execute
the command and exit the tool.
to execute
the command and exit the tool.
-
Click the Outlet tool.
Figure 13. 
-
Select the face highlighted in the figure below and then click
 on the
guide bar.
on the
guide bar.
Figure 14. 
-
Click the No Slip tool.
Figure 15. 
-
Select the face highlighted in the figure below.
Figure 16. 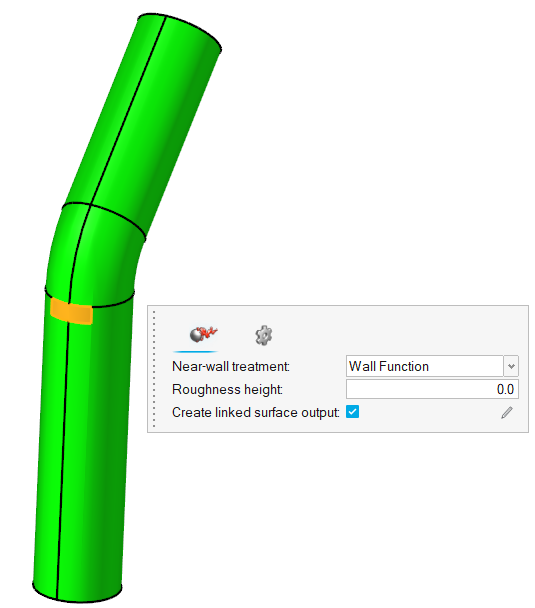
-
In the Boundaries legend, double-click Wall and rename
it to Particle_inlet.
You will use this surface as a reference geometry to create a particle factory in EDEM. Hence, you are placing this surface in a different geometry group.
-
Click
 on the guide bar.
on the guide bar.
- Save the model.
Generate the Mesh
-
From the Mesh ribbon, click the
Volume tool.
Figure 17. 
The Meshing Operations dialog opens. -
Change the Average element size to 0.3.
Figure 18. 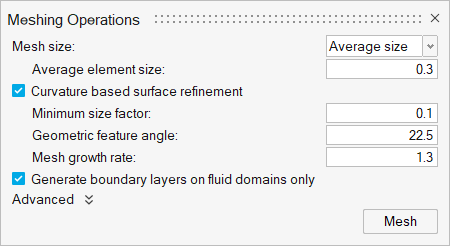
-
Click Mesh.
The Run Status dialog opens. Once the run is complete, the status is updated and you can close the dialog.Tip: Right-click the mesh job and select View log file to view a summary of the meshing process.
- Save the model.
Define Nodal Outputs
Once the meshing is complete, you are automatically taken to the Solution ribbon.
-
From the Solution ribbon, click the Field tool.
Figure 19. 
The Field Output dialog opens. - Check the box for Write Initial Conditions.
-
Set the Time step interval to 10.
Figure 20. 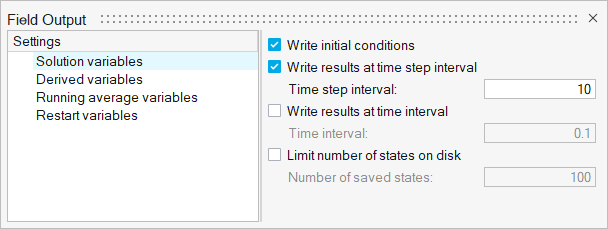
Export the Solver Deck
- From the menu bar, go to .
- Name the file windshifter_bidirectional and make sure that AcuSolve (*.inp) is selected as the file type.
- Click Save.
Part 2 - EDEM Simulation
Start Altair EDEM from the Windows start menu by clicking .
Open the EDEM Input Deck
As mentioned earlier, when the AcuSolve simulation was launched, HyperMesh CFD created a set of EDEM files in the problem directory. You will open that EDEM input deck and setup the DEM simulation.
- In the Creator tab in EDEM, go to .
-
In the dialog, browse to the AcuSolve problem
directory and open the windshifter_bidirectional.dem file located in the EDEM
folder.
The geometry is loaded.
-
Click the Environment tab under the Creator Tree,
uncheck Auto Update from Geometry, and then check the box
again to fit the geometry within the boundary.
Figure 21. 
Figure 22. 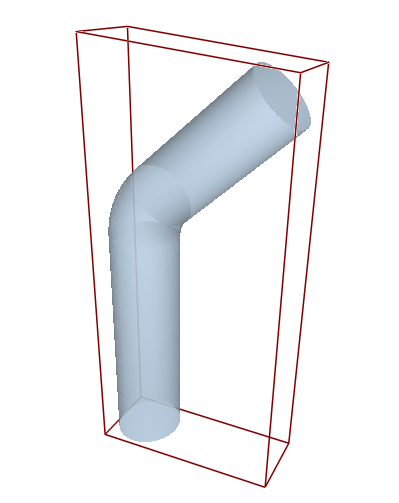
Define the Bulk Materials and Equipment Material
In this step, you will define the material models for the heavy and light bulk material and the equipment material.
- In the Creator Tree, right-click Bulk Material and select Add Bulk Material.
- Rename the material to Heavy.
-
In the Creator Tree, set the Solids Density property to
900 kg/m3.
You will use the default values for other properties for this tutorial.
Figure 23. 
-
Click
 below Interaction to define the
interaction properties for collisions among the heavy particles. In the dialog,
click OK.
below Interaction to define the
interaction properties for collisions among the heavy particles. In the dialog,
click OK.
- In the Creator Tree, right-click Heavy and select .
- Rename the particle to Heavy particle.
- Under Heavy particle, click Properties.
-
In the Heavy particle Spheres panel, set the Physical Radius of both the
spheres to 0.03 m and press Enter.
Figure 24. 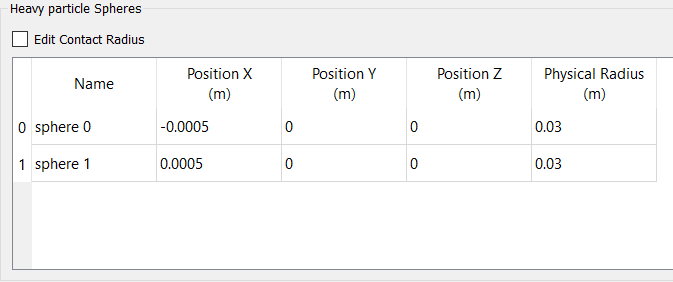
-
In the Creator Tree, click Calculate Properties.
Figure 25. 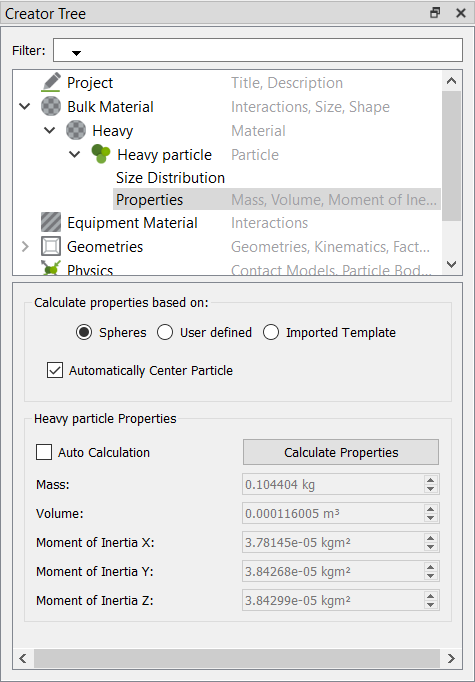
- In the Creator Tree, right-click Bulk Material and select Add Bulk Material.
- Rename the material to Light.
-
In the Creator Tree, set the Solids Density property to
100 kg/m3.
You will use the default values for other properties for this tutorial.
Figure 26. 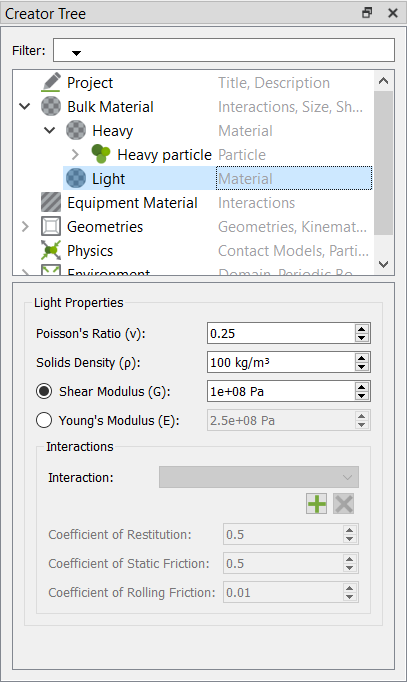
-
Click
 below Interaction to define the
interaction properties for collisions among the heavy particles. In the dialog,
select Heavy and then click OK.
below Interaction to define the
interaction properties for collisions among the heavy particles. In the dialog,
select Heavy and then click OK.
-
Click
 again to define the interaction
properties for collisions among the light particles. In the dialog, select
Light and then click OK.
again to define the interaction
properties for collisions among the light particles. In the dialog, select
Light and then click OK.
- In the Creator Tree, right-click Light and select .
- Rename the particle to Light particle.
- Under Light particle, click Properties.
-
In the Light particle Spheres panel, set the Physical Radius of both the
spheres to 0.03 m and press Enter.
Figure 27. 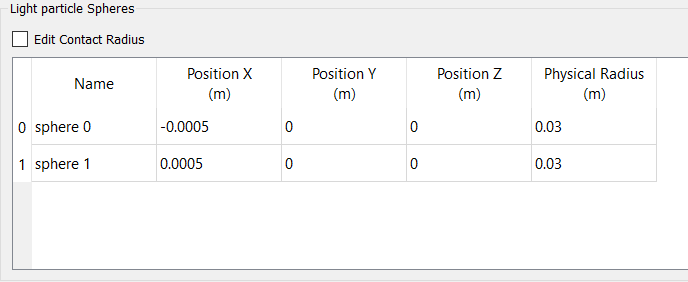
-
In the Creator Tree, click Calculate Properties.
Figure 28. 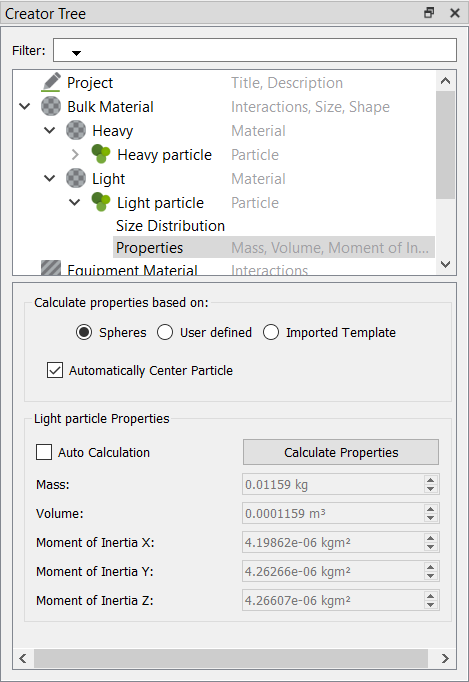
- In the Creator tree, right-click Equipment Material and select Add Equipment Material. Rename it to Steel.
- Set the Density to 7800 kg/m3.
-
Click
 below Interaction to define the
interaction properties for collisions among the heavy particles. In the dialog,
select Heavy and then click OK.
below Interaction to define the
interaction properties for collisions among the heavy particles. In the dialog,
select Heavy and then click OK.
-
Click
 again to define the interaction
properties for collisions among the light particles. In the dialog, select
Light and then click OK.
again to define the interaction
properties for collisions among the light particles. In the dialog, select
Light and then click OK.
- Save the model.
Create the Particle Factory
- Expand Geometries under the Creator Tree tab. Next, right-click the Particle inlet surface group and select .
- Rename the new geometry section to Particle_factory.
- Right-click the Default Wall geometry section in the Creator Tree and select Merge Geometry(s).
- In the Merge Geometry dialog, select the Particle_inlet and then click OK.
-
Click the Default Wall geometry section, set the Type to
Physical, and the Material to
Steel (if not set already).
Figure 29. 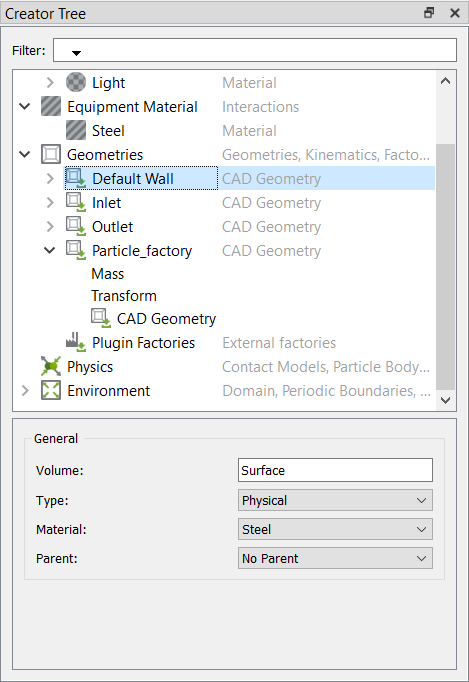
- In the Creator Tree, click the Inlet section and change the Type to Virtual.
- Similarly, change the Type to Virtual for the Outlet and Particle_factory sections.
-
Under Particle_factory, click Transform. Set the
X-Position to 0.035 m.
Figure 30. 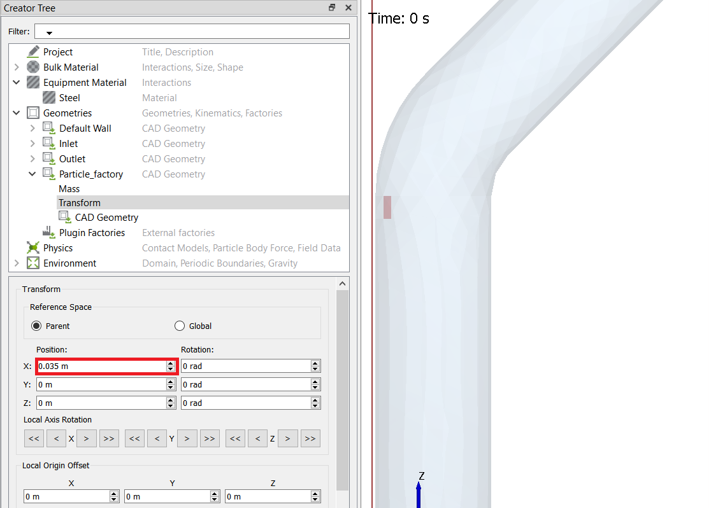
Note: Set the Opacity value to 0.2 to see the transformed surface location inside the pipe geometry.This is done to make sure that the particles are generated inside the fluid domain.
Define the Particle Factory
Now that the bulk material, geometry sections, and equipment materials are defined, you need to create a particle factory to generate the particles. You will create one factory for each bulk material.
- In the Creator Tree, right-click Particle_factory and select Add Factory.
- Rename the new factory to Heavy factory.
-
Set the particle generation parameters as shown in the figure below.
Figure 31. 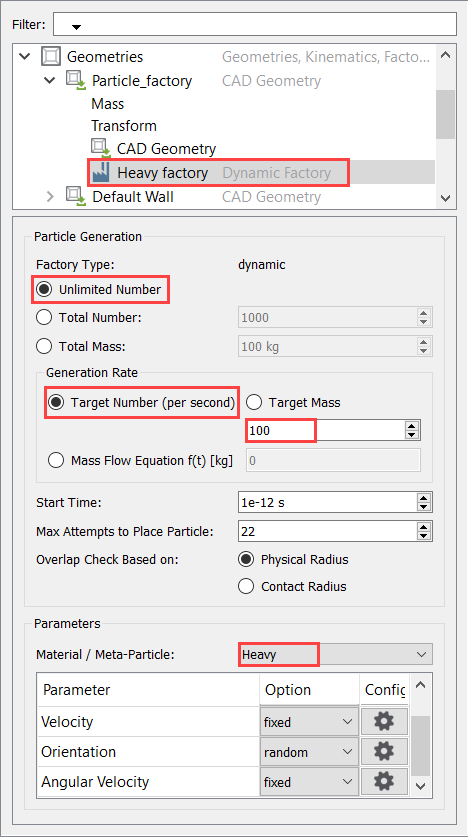
-
Click
 besides Velocity, set the
X-velocity to 1 m/s, and then click OK.
besides Velocity, set the
X-velocity to 1 m/s, and then click OK.
- Repeat steps 1-4 to create another factory named Light factory using the same parameters but with Light as the Material.
Define the Environment
In this step, you will define the extents of the domain for the EDEM simulation and the direction of gravitational acceleration.
- In the Creator Tree, click Environment.
-
Activate the checkbox for Auto Update from Geometry (if
not already selected).
When a moving particle touches the bounding faces of the domain (environment), it will be removed from the simulation.
- Activate Gravity and set the z-value to -9.81 m/s2.
- Save the EDEM deck.
Define the Simulation Settings
-
Click
 in the top-left corner to go to
the EDEM Simulator tab.
in the top-left corner to go to
the EDEM Simulator tab.
-
In the Simulator Settings tab, set the Time Integration scheme to
Euler and deactivate the Auto Time
Step checkbox.
Note: The Auto time step should never be used for AS-EDEM bidirectional coupled simulations.
-
Enter a value of 2e-5 for Fixed Time Step.
When setting the time step for the DEM model, make sure that the CFD time step is an integer multiple of DEM time step. In this case, the CFD time step is 1e-3, which is 50 times the DEM time step. This ensures that the physical time in both the solvers match at the end of each data exchange interval. Also, the recommended range for the CFD-to-DEM time step ratio is 50-200 for most cases.
- Set the Total Time to 1 s and the Target Save Interval to 0.01 s.
-
Set the Cell Size to 4 R min.
Generally, a value in the range of 3-6 Rmin is recommended as the optimum cell size. The cell size in EDEM does not have any impact on the accuracy of the simulation and affects only the run time.
-
Set the Selected Engine to CPU Solver and set the Number
of CPU Cores based on availability.
Figure 32. 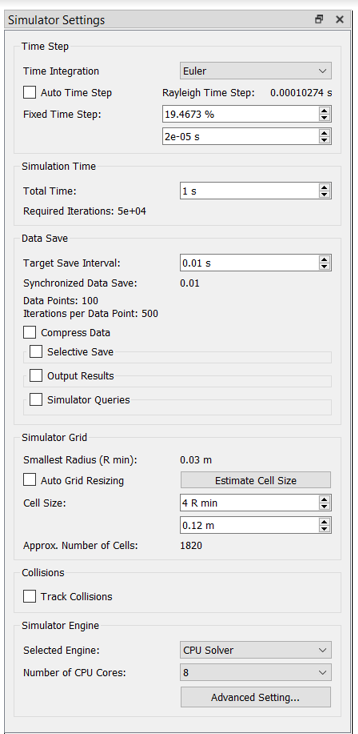
- Once the simulation settings have been defined, save the model.
Submit the Coupled Simulation
-
Start the coupling server by clicking Coupling Server in
EDEM.
Figure 33. 
Once the Coupling server is activated, the icon changes.Figure 34. 
- Return to HyperMesh CFD.
-
From the Solution ribbon, click the Run tool.
Figure 35. 
The Launch AcuSolve dialog opens. - Set the Parallel processing option to Intel MPI.
- Optional: Set the number of processors to 4 or 8 based on availability.
- Expand Default initial conditions, uncheck Pre-compute flow and set the velocity values to 0. Uncheck Pre-compute Turbulence.
-
Click Run to launch AcuSolve.
Figure 36. 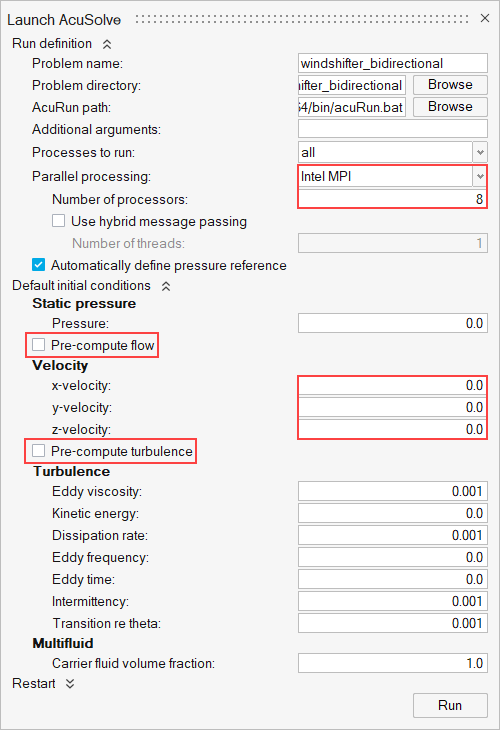
If the coupling between AcuSolve and EDEM is successful, a message will be printed in the AcuSolve Log file before the first time step.Figure 37. 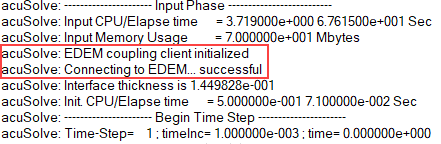
Analyze the Results
AcuSolve Post-Processing
- Once the solution is completed, navigate to the Post ribbon.
- From the menu bar, click .
-
Select the AcuSolve
.log file in your problem
directory to load the results for post-processing.
The solid and all the surfaces are loaded in the Post Browser.
-
Select the Left face on the view cube to align the model
to the x-z plane.
Figure 38. 
-
In the Post Browser, turn off the display of the boundary
surfaces by clicking the icon next to Flow Boundaries.
Figure 39. 
-
Click the Slice Planes tool.
Figure 40. 
- In the modeling window, click the plane that is parallel to the screen (the x-z plane).
-
In the slice plane microdialog, click
 to
create the slice plane.
to
create the slice plane.
- In the display properties microdialog, set the display to velocity and activate the Legend toggle.
- Change the upper bound of the legend to 36.
-
Click
 and set the Colormap name to Rainbow
Uniform.
and set the Colormap name to Rainbow
Uniform.
Figure 41. 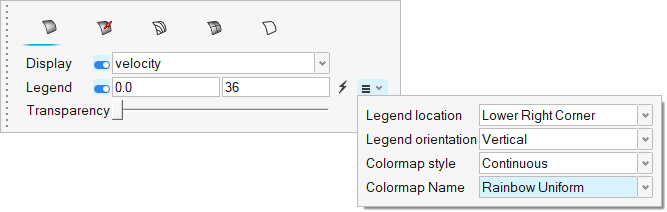
-
Click
 on the guide bar.
The velocity contour should look like the one shown below at the beginning of the simulation.
on the guide bar.
The velocity contour should look like the one shown below at the beginning of the simulation.Figure 42. 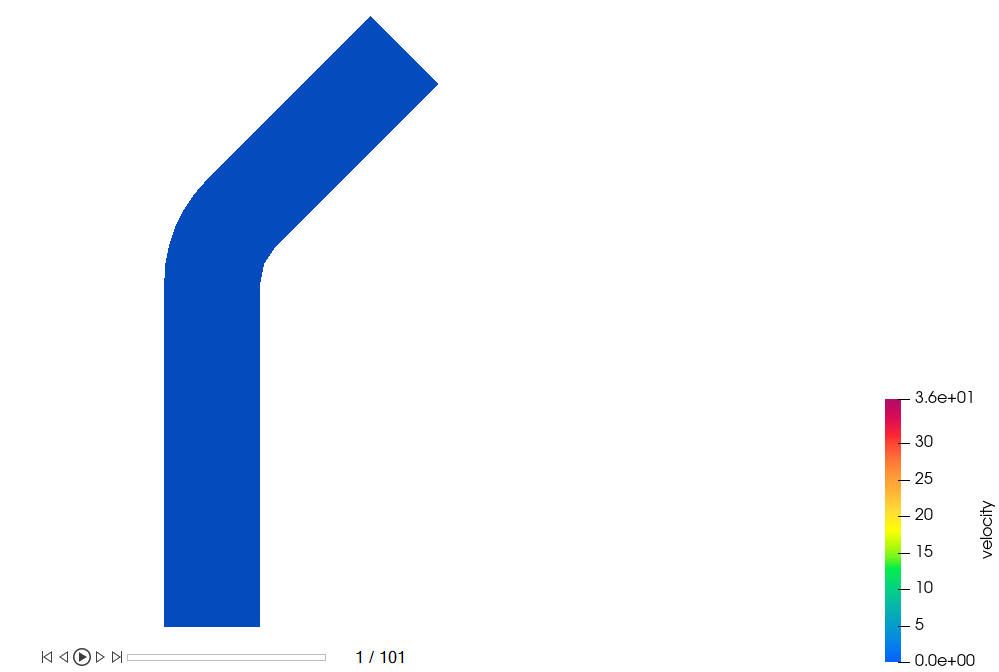
-
Plot the contours at 0.25s, 0.5s, 0.75s, and 1.0s by dragging the slider on the
bottom to the 26th, 51th, 76th, and
101st frames.
Figure 43. 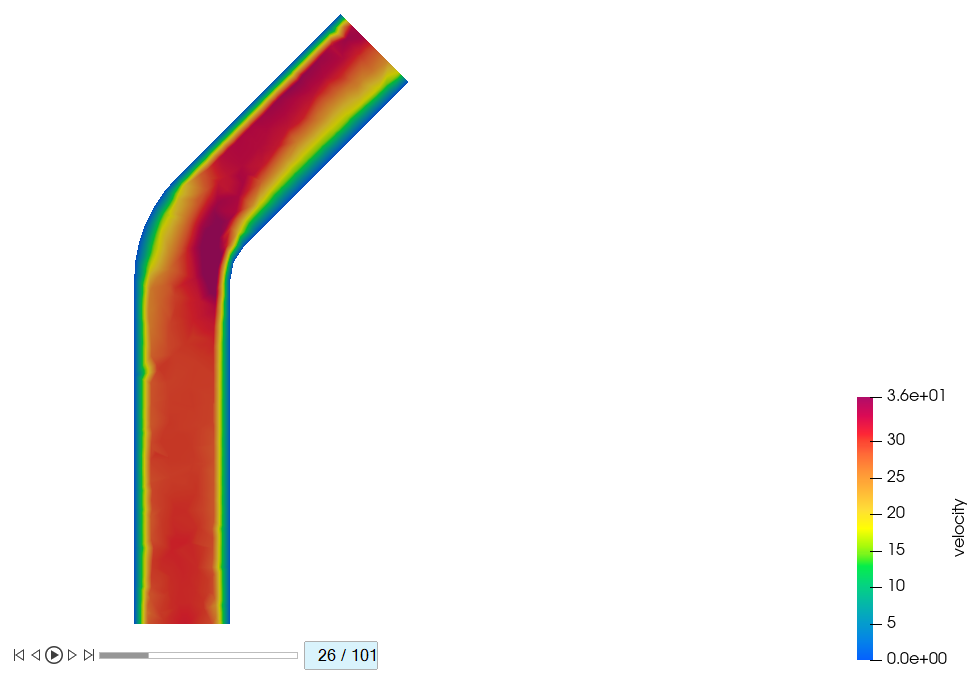
Figure 44. 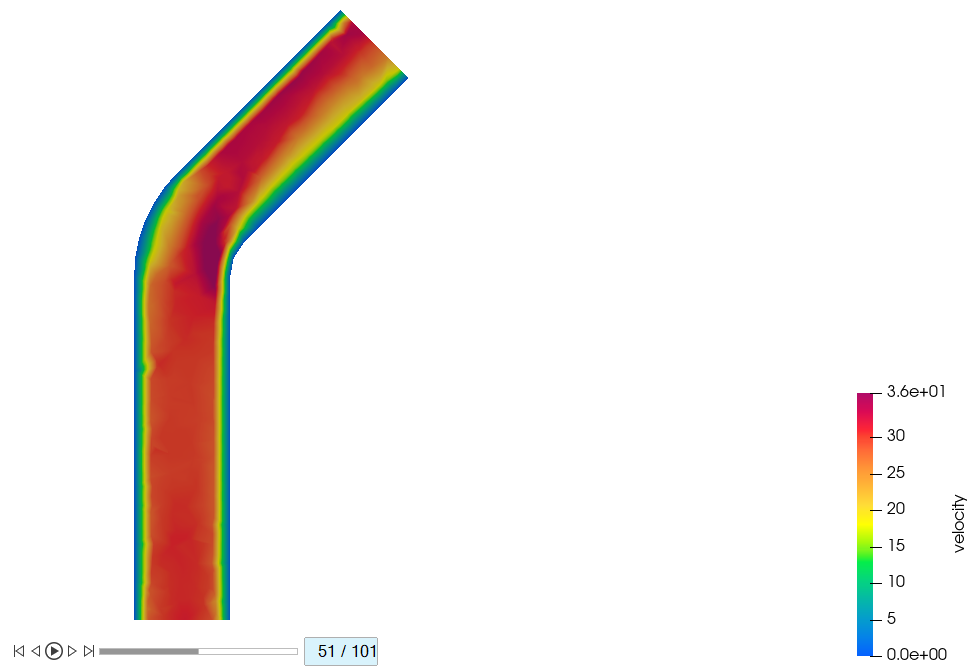
Figure 45. 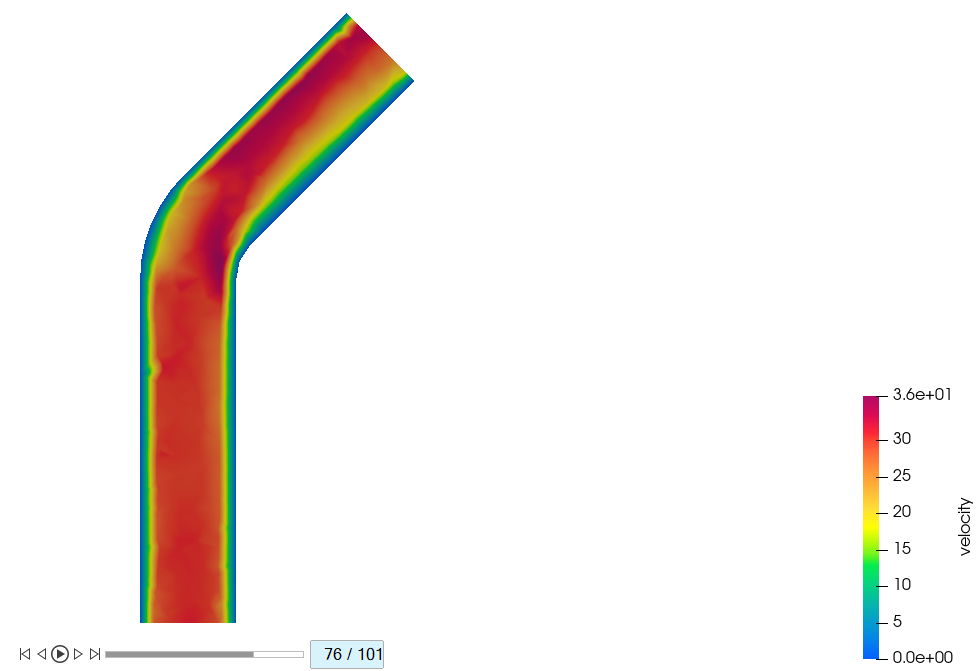
Figure 46. 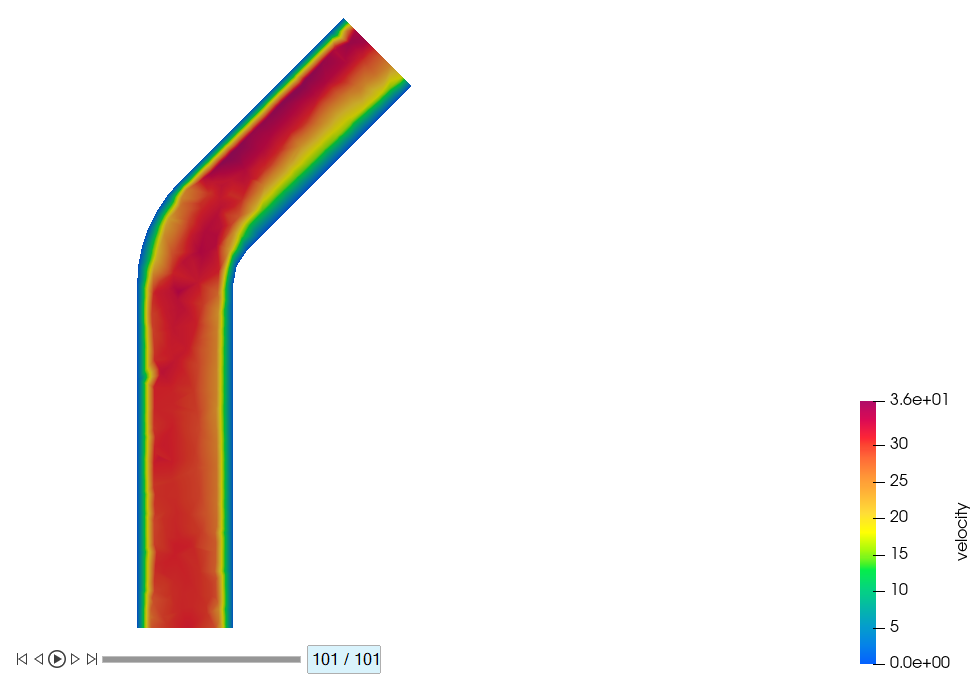
- Right-click Slice Plane 1 in the Post Browser and select Edit.
- In the microdialog, change the Display variable from velocity to volume fraction edem particle and set the upper bound of the legend to 0.186.
-
Click
 on the guide bar.
on the guide bar.
Figure 47. 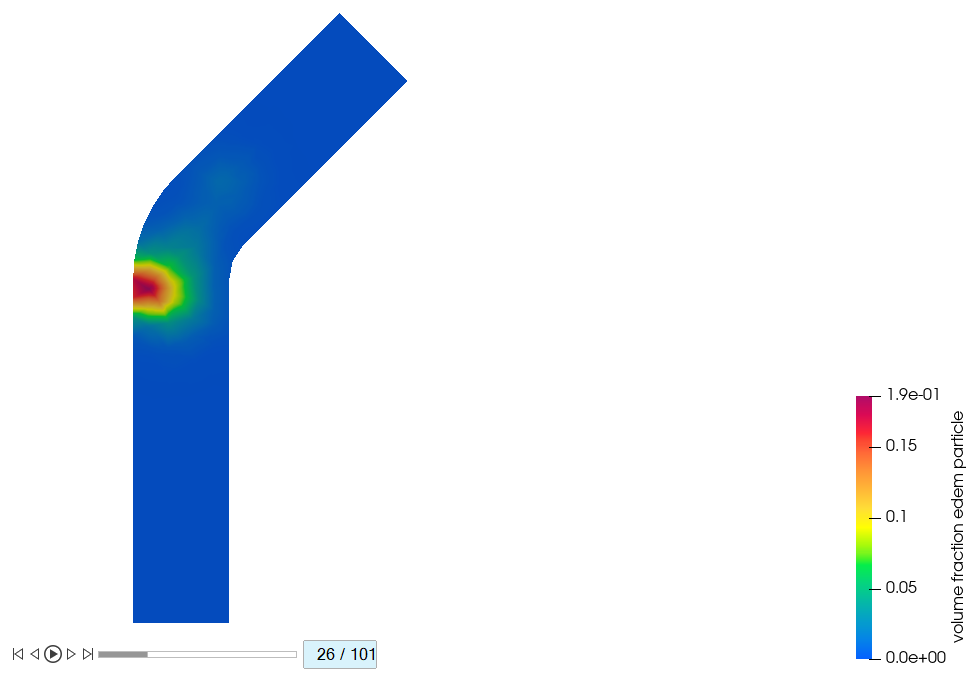
-
Plot the contours at 0.5s (step=51/101), 0.75s (step=76/101), and 1.0s (step =
101/101) to see the volume fraction edem particle distribution inside the fluid
domain.
Figure 48. 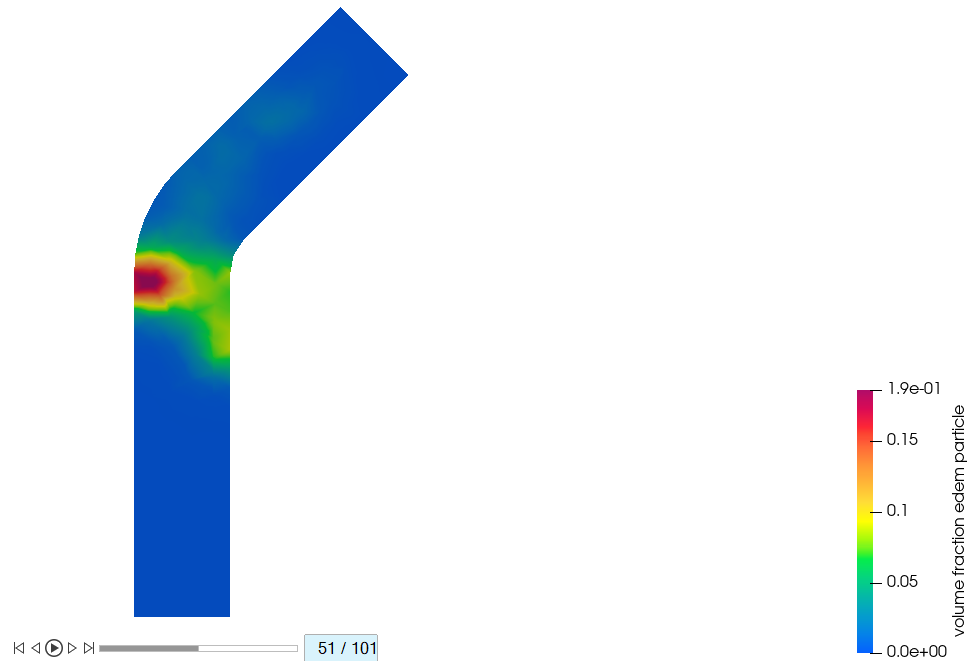
Figure 49. 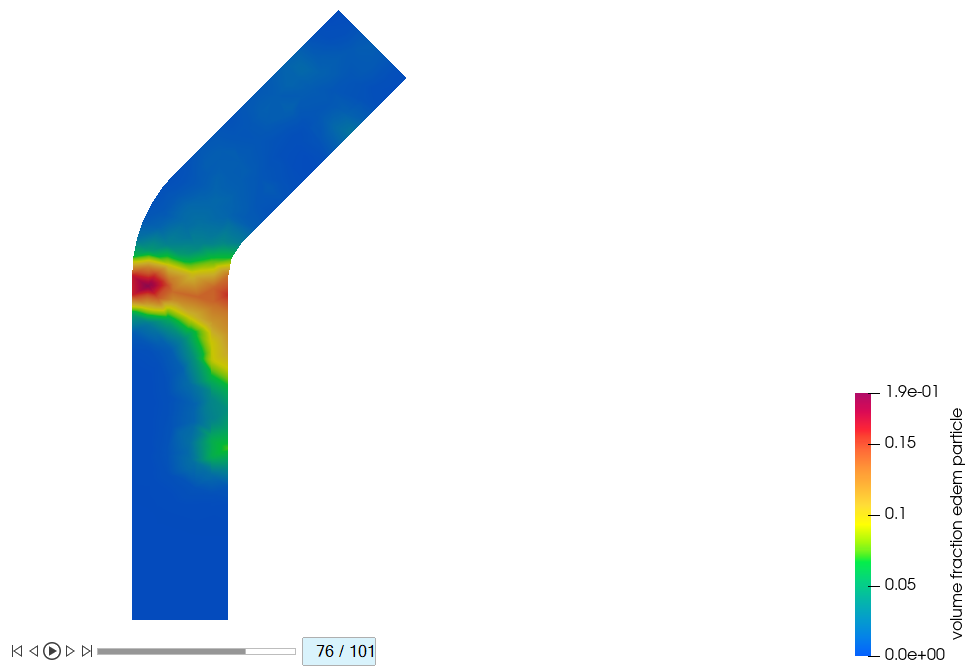
Figure 50. 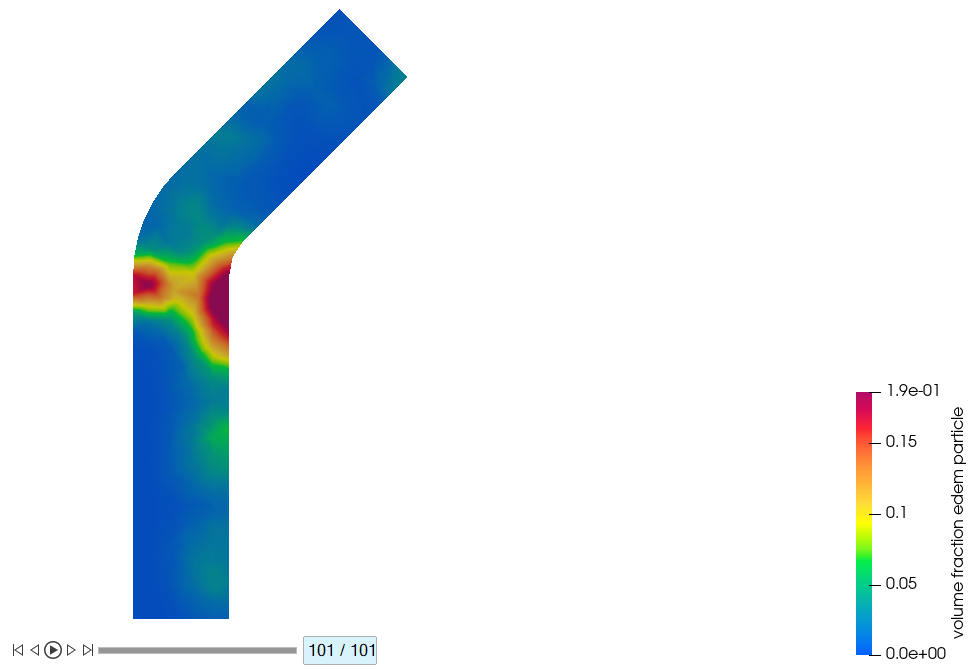
EDEM Post-Processing
-
Once the EDEM simulation is complete, click
 in the top-left corner to go to
the EDEM Analyst tab.
in the top-left corner to go to
the EDEM Analyst tab.
- In the Analyst Tree, expand and then click Default Wall.
-
Verify that the Display Mode is set to Filled and set
the Opacity to 0.2.
Figure 51. 
- In the Analyst Tree, expand Particles and click Heavy particle.
-
Change the display color to Magenta.
Figure 52. 
-
Click Light particle and set the display color to
Green.
Figure 53. 
-
On the menu bar, set the time to
0 by clicking:
Figure 54. 
-
Set the View plane to + Y.
Figure 55. 
-
In the Viewer window, set the Playback Speed to 0.1x and
then click the play icon to play the particle flow animation.
Figure 56. 
-
You can also plot the results at different timesteps by clicking the drop-down
menu.
Figure 57. 
For the current case, the results are plotted at 0.25s, 0.5s, 0.75s, and 0.98s to see the particle distribution inside the fluid domain at both inlet and outlet.Figure 58. 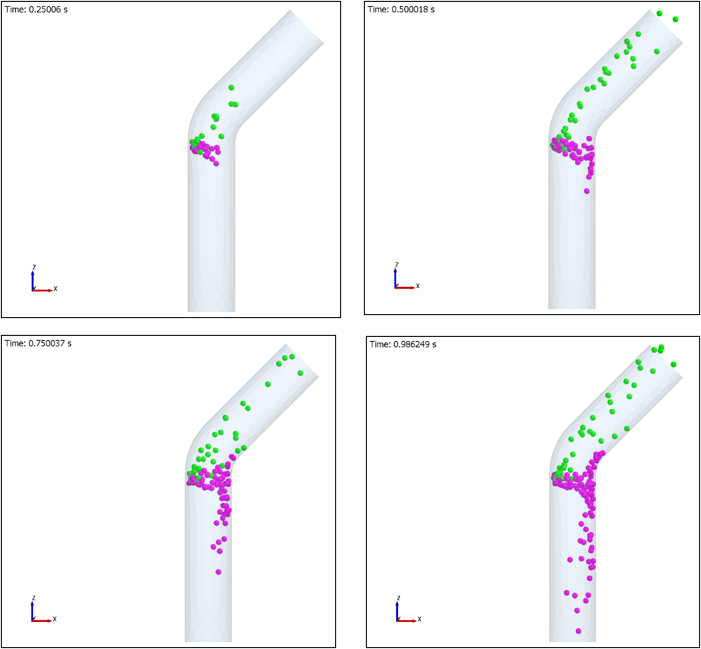
Observe that the lighter particles (green) get carried by the fluid and escape the domain through the outlet at the top and the heavier particles (magenta) stay inside the domain for a longer time while some of them fall through the bottom of the pipe.
-
On the menu bar, click the Create
Graph icon
 .
.
-
In the Analyst Tree, change the plot type to Line by clicking
 .
.
-
Click the X-axis tab and verify that the values are set
as shown in the figure below.
Figure 59. 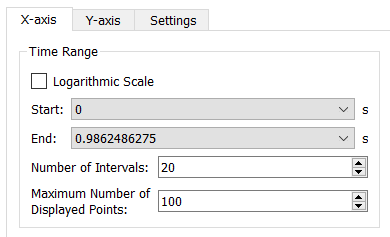
-
Click the Y-axis tab. Create a plot of average residence
time of the heavy particle over the simulation time by setting the values as
shown in the figure below.
Figure 60. 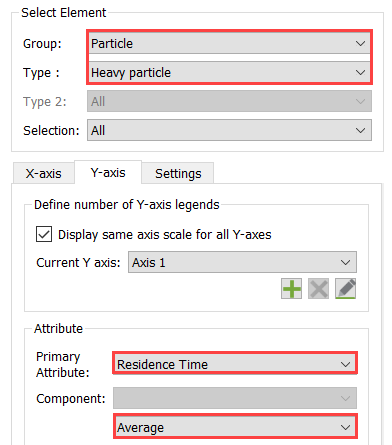
-
Click
 to add another Y-axis and set
the Type to Light particle.
to add another Y-axis and set
the Type to Light particle.
Figure 61. 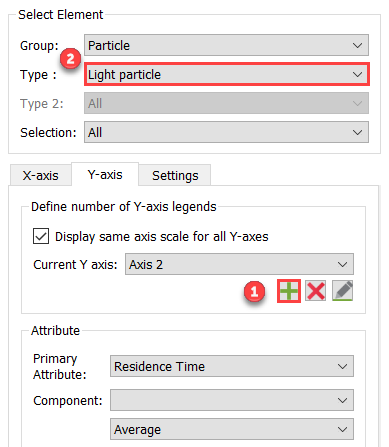
-
Leave all the other options unchanged and then click Create
Graph to create a plot of average residence time of both the
particles.
Figure 62. 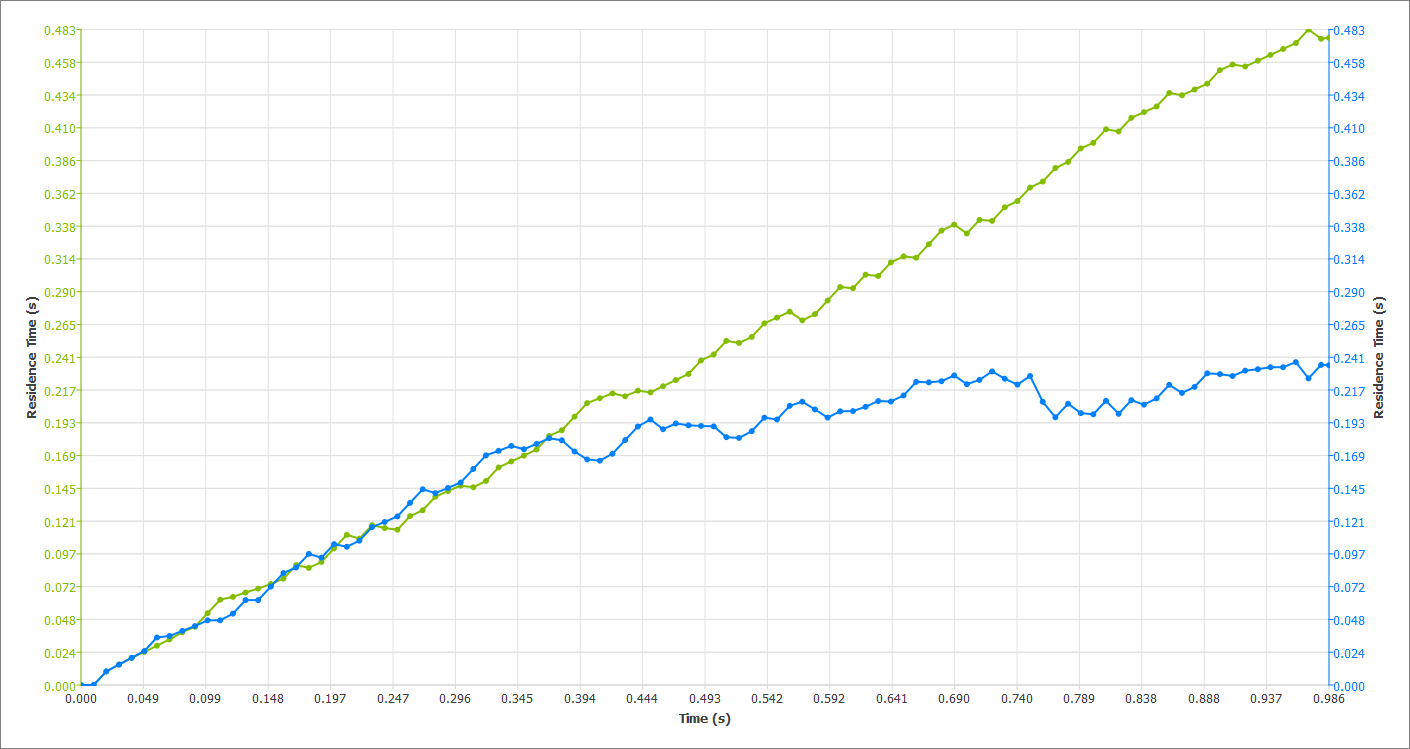
The plot in green is for the heavier particles and it can be observed that the average residence time is higher for the heavier particles compared to the lighter particles (blue).
Summary
In this tutorial, you learned how to setup and run a basic AcuSolve-EDEM bidirectional (two-way) coupling problem. In the first part, you set up the AcuSolve model in HyperMesh CFD and exported the geometry. Next, you imported the EDEM input files created by HyperMesh CFD, set up the EDEM model, and ran the coupled simulation. Once the coupled simulation was completed, you have learned how to create animations and plots in both HyperMesh CFD Post and EDEM Analyst.