Since version 2026, Flux 3D and Flux PEEC are no longer available.
Please use SimLab to create a new 3D project or to import an existing Flux 3D project.
Please use SimLab to create a new PEEC project (not possible to import an existing Flux PEEC project).
/!\ Documentation updates are in progress – some mentions of 3D may still appear.
Example of a capacitor
Capacitor with dielectric
Let us consider a Steady state AC Electric problem comprising a real capacitor and a voltage source applied at its terminals. The problem does not contain another voltage supply.
With:
- Veff, the rms value of the voltage applied to the capacitor, and ω the pulsation,
- the resistance R (in Ω) and the capacitance C (in F) of the equivalent RC parallel circuit of the capacitor. The dielectric material of the capacitor is supposed to be linear in order to enable the definition of the capacitance C.
Capacitance and resistance of the capacitor
The complex apparent power S (in VA) of the capacitor has the expression: S = P + j Q
where:
- P is the active power (in W):
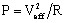
- Q is the reactive power (in VAr):
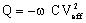
From the active power of the capacitor we can compute the equivalent resistance: ![]()
From the active power of the capacitor we can compute the equivalent capacitance:
![]()