Net to Net
This item checks whether a specified clearance requirement for the net is satisfied.
- Auto Net to Net Combination: Generate combination pair of selected net group.
- Set clearance by thickness: This menu allows you to set the separation distance associated with the Thickness of the Net.
- Item: Input item name.
- 1st Net: specify 1st net (reference).
- 2nd Net: specify 2nd net (target net).
- Exclude Composite: If you select this option, in the case of Composite Net, the Composite will be disassembled and the test will proceed.
- Horizontal Check: Set Horizontal check parameter.
- Outer Layer Net Clearance: Enter trace-to-trace clearance for microstrips (traces on top and bottom layers).
- Inner Layer Net Clearance: Enter trace-to-trace clearance for stripline (traces on inner signal layers).
- Clearance Value Type: Set the Value Type entered above.
(Value/Width).
- Value: The value entered above is used as the separation distance.
- Width: Use the 'value * width' value entered above as the separation distance.
- Height: Use the 'value * net height' value entered above as the separation distance. Here, 'Net Height' refers to the height between the Net and the reference plane.
- Thickness: Use the 'value * net thickness' value entered above as the separation distance.
- Pad/VIA Clearance check: PAD/VIAs connected to the Net are also
included in the inspection target.
- Use Width Value(W): If checked. Use the 'value * width' value entered below as the separation distance.
- Outer Layer Pad/VIA Clearance: Enter clearance for microstrips (traces on top and bottom layers).
- Inner Layer Pad/VIA Clearance: Enter clearance for stripline (traces on inner signal layers).
- Specific area check condition: Option to test with different
separation values within a specific area specified by the user.
- Area Layer: Specify a layer that defines a specific area. PollEx DFE recognizes check areas defined by polygon or polyline.
- Area Clearance: Enter a clearance to the region that is defined in Area Layer.
- Do not check Net segment separation:
- Consider GND Net between Nets: DFE skip to check if ground net is existing between two target nets. Select Ground Net Group.
- Vertical Check: Set Vertical check parameter.
- Use Width Value(W): If checked. Use the 'value * width' value entered below as the separation distance.
- L1 Clearance: Enter clearances from the reference layer to the one layer above and below.
- L2 Clearance: Enter clearances from the reference layer to the two layers above and below.
- All Clearance: Enter clearances from the reference layer to the all layers.
- Include PAD/VIA: When selecting, PAD/VIAs connected to the Net are also included in the test target.
- Options: Set check options.
- Pin Escape: Enter a radius of circular region around pins to be excluded for the rule check.
- Check only parallel segment pair: Only the sections where the target nets are parallel are tested.
- Component Keep IN/OUT: Define the test region. For example, you can test
inside or outside the breakout region of CPU with different test values.
- Component Group: Select the required component group which is used for defining the test region.
- Range (COC+distance): Enter the distance value to define breakout range. The COC (Component Overlap Check) plus this distance value is considered the test range.
- Region: Define the required test region.
- In: Test inside of the breakout region of target component.
- Out: Test outside of the breakout region of target component.
- Different Rule Setup in Specific Region: Specific areas around a component can be assigned different Separation Values.
- Extended Region from COC: Specify a specific region. The area from the COC of the component to 'COC + value' becomes the specific region.
- Allowable Values: Separation Value to be used within the Specific
Region.
- Value: Add additional allowable value.
- Range: Add additional allowable range.
- Deviation: Add additional allowable value with deviation using this option.
- Deviation (%): Add additional allowable value with deviation (%).
- Total Parallel Length Check Only: If selected, DFE does not check the
distance between nets, but checks the maximum allowable length for two nets
to be routed in parallel.
Figure 1. 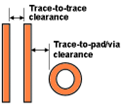
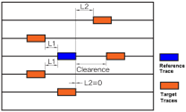
In order to reduce coupling, it is best to make wider clearances for signal. However, clearances are restricted by board size and pin pitch as well as signal characteristics such as voltage or frequency. For example, a clearance among clocks is usually wider than that among normal signal nets. A clearance between clock and normal signal net is also wider than that among normal signal nets.
Clearances among signal nets must be carefully considered on the same layer as well as on adjacent layers.
| Voltage (DC or AC Peak) | Minimum distance (uncoated) | Minimum distance (uncoated) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ~ 15V | 15 mil | 0.4 mil | 5 mil | 0.13 mil |
| 15V ~ 30V | 15 mil | 0.4 mil | 10 mil | 0.25 mil |
| 30V ~ 50V | 15 mil | 0.4 mil | 15 mil | 0.4 mil |
| 50V ~ 100V | 25 mil | 0.6 mil | 20 mil | 0.5 mil |
| 100V ~ 150V | 25 mil | 0.6 mil | 30 mil | 0.8 mil |
| 150V ~ 300V | 50 mil | 1.5 mil | 30 mil | 0.8 mil |
| 300V ~ 500V | 100 mil | 1.5 mil | 60 mil | 1.5 mil |
| 500V ~ | 0.2 mil/volt | 0.005 mil/volt | 0.12 mil/volt | 0.003 mil |
A partial copy of IPC-2221 standard is shown in IPC Material for an additional example.