Vents
Use the Vents icon to define vents that enable gases to escape from the part and mold.
Location: Foaming ribbon, Vents icon
Click the ![]() satellite icon that appears when you hover over the Vents tool to display a table of
all vents in your model.
satellite icon that appears when you hover over the Vents tool to display a table of
all vents in your model.
Add Line Vents
Add line vents to enable gases to travel along the part and escape from the parting line of the mold.
-
Click the Line Vent icon.

-
Click and drag to sketch a line vent on the mold. Click again to end the
vent.
Figure 1. Example of Line Vents on a PolyFoam Model 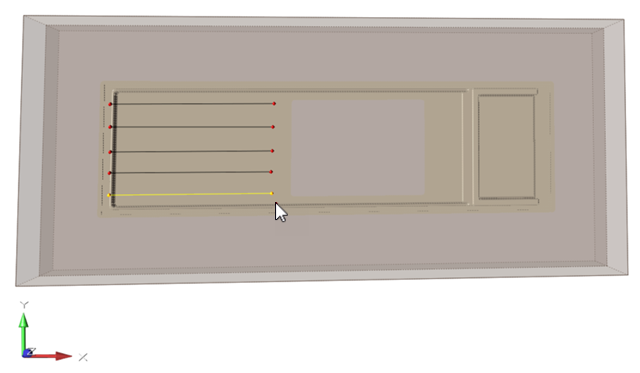
In a PolyFoam model, you sketch vents on the exterior faces of the mold for ease of use. The software projects the vents to the part and runs the simulation on the model as if the vents were located on the part.
In a physical model, line vents are placed along the part to move the air from the part to the partition line.
Figure 2. Example of Line Vents on a Physical Model 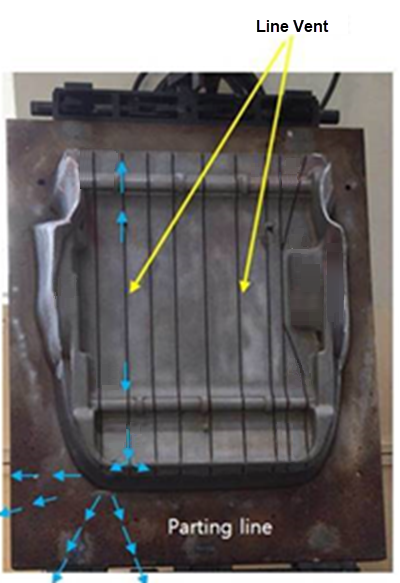
-
Use the microdialog options to define the parameters of the line vent.
Microdialog option Description Note Move Line Vent 
Click the Move tool  to change the location of the
vent.
to change the location of the
vent.Alternatively, enter the X, Y, and Z coordinates for the vent. Thickness 
The thickness accounts for the size of the gap that exists at the parting line of the mold. Enter the gap thickness value. Porosity 
The porosity value controls the vent opening that syphons gas away from the part. Enter a value between 0 and 1, where 0 means the vent is fully closed, and 1 means the vent is fully opened.
Add Point Vents
Add point vents to enable gases to escape from around the part and through the exterior of the mold.
-
Click the Point Vent icon.

-
Click a surface on the part to place a point vent.
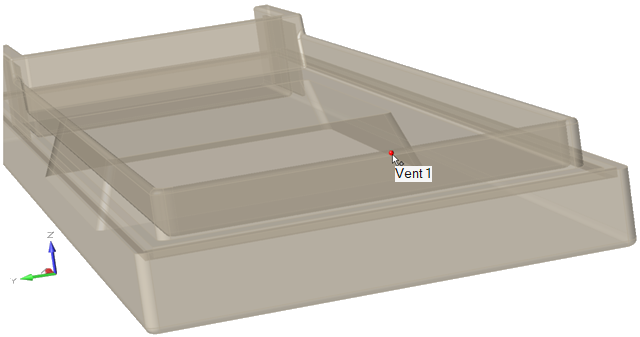
-
Use the microdialog options to define the parameters of the point vent.

Microdialog option Description Note Move Line Vent 
Click the Move tool  to change the location of the
vent.
to change the location of the
vent.Alternatively, enter the X, Y, and Z coordinates for the vent. Vent Shape 
Circular: Circular vents release gasses through the exterior of the mold.
Square: Square vents enable air to escape from around the part in the mold.Select a shape for the vent. For circular, enter the radius of the vent. For square, enter the X, Y and Z dimensions of the vent. Porosity 
The porosity value is the filtering capacity of the vent to siphon gases away from the part. Enter a value between 0 and 1, where 0 means no gases can escape and 1 means gases can fully escape. Variable Porosity 
Variable porosity defines a venting system with time-dependent changes to vent porosity. You can apply variable porosity to individual point vents to siphon gases away from the part. Select the check box to enable variable porosity. To define the porosity properties, click the variable porosity button  and enter the porosity over
time in the dialog:
and enter the porosity over
time in the dialog: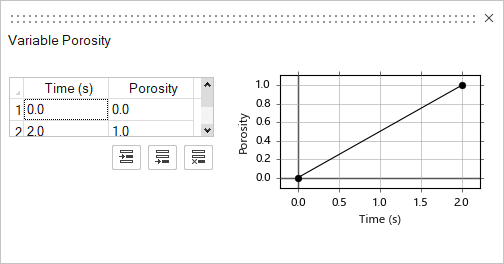
Variable Pressure 
Variable pressure defines a venting system with time-dependent changes to pressure, including vacuum conditions. You can apply variable pressure to circular point vents to siphon gases away from the part. Select the check box if your model includes a pressure system. To define the pressure properties, click the variable pressure button  and enter the pressure over
time in the dialog:
and enter the pressure over
time in the dialog: 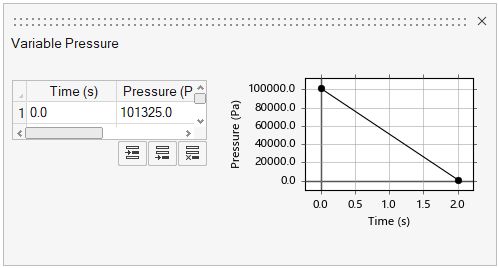
Vents Table
You can review, modify, and work with point vents in the Vents table.
Click the ![]() satellite icon on the Vents tool to display the table.
satellite icon on the Vents tool to display the table.
The table shows the current coordinates and radius or dimensions for each vent. Use the dropdown menu to select squared vents or circular vents.
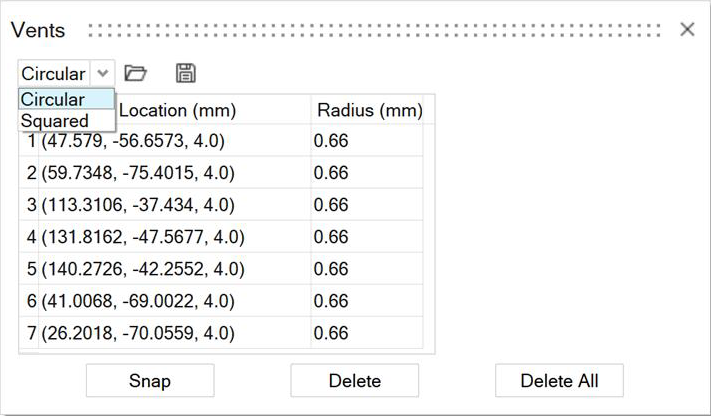
Column 1 numbers the vents in the order that you added them. The Location column pinpoints the vent at X, Y, and Z coordinates. For round vents, the Radius column displays the vents' radii. For squared vents, the X, Y, and Z columns display the vents' dimensions. When a row is selected, you can use the microdialog to edit the corresponding vent.
Click the ![]() icon to export vents to a .csv or .txt file.
icon to export vents to a .csv or .txt file.
Click the ![]() icon to import vents from a .csv or .txt file.
icon to import vents from a .csv or .txt file.