Since version 2026, Flux 3D and Flux PEEC are no longer available.
Please use SimLab to create a new 3D project or to import an existing Flux 3D project.
Please use SimLab to create a new PEEC project (not possible to import an existing Flux PEEC project).
/!\ Documentation updates are in progress – some mentions of 3D may still appear.
Describing material media
Introduction
For all that concerns the describing of the material media:
-
for the magnetic aspects: see chapter Steady State AC Magnetic application: principles
-
for the thermal aspects: see chapter Thermal applications: principles
Specificities connected with the coupling
Generally speaking, for each modeled area the following should be achieved:
- a magnetic definition
- a thermal definition
The table below summarizes the main conceivable situations for different parts of the studied device.
| The regions belonging to the study domain… | are defined by... | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) |
Magnetic and thermal (ex: heated piece or pieces “important” from the thermal point of view) |
a magnetic type:
|
a thermal type:
|
| (2) |
only magnetic (ex: surrounding pieces without influence from the thermal point of view) |
a magnetic type:
|
a thermal type:
|
| The regions belonging to the study domain… | are defined by... | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (3) |
only thermal (ex: thermal exchange surface with the surrounding air) |
a magnetic type:
|
a thermal type:
|
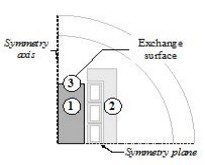
Example
In the previously presented example…
- the steel billet is defined from the magnetic and thermal points of view (1)
- the inductor and the magnetic core are defined only from the magnetic point of view (2)
- the thermal exchanges surface is defined only from the thermal point of view
(3)