Create OPC-UA Thing Description
See Things documentation on how to manage Things in Altair IoT Studio.
A Thing for this device driver uses a schema as described on this page.
Once it exists in Studio it can be synced to the cluster (asset) as shown on the Sync Things page.
The following is an example of a Thing description to be instantiated by the OPC-UA driver:
{
"@type": [
"swx:opcua,endpoint=opc.tcp://localhost:26543,interval=1000"
],
"id": "<leave blank when creating a thing>",
"title": "My OPCUA Test Device",
"properties": {
"ns=1;s=Temperature": {
"@type": "float64",
"title": "Temperature",
"type": "number",
"readOnly": true
},
}
}
- the "swx:opcua,endpoint=opc.tcp://..." string in the "@type" array
- the "ns=1;s=Temperature" property key
The first item is essential for the OPC-UA driver to recognise this Thing description as a OPC-UA device. Details on how to construct this string can be found in the next section.
@type to configure the OPC-UA
endpoint will be deprecated in the future. It is recommended to configure using the
config property (see subsequent section).The second item is essential for the OPC-UA driver to recognise the node it needs to manage. Details on how to construct property keys and the rest of the property object can be found in a subsequent section.
Configure the OPC-UA Endpoint using the Schema "@type"
The following element in the "@type"` array is required to configure the OPC-UA endpoint. It is comma-separated string of parameters. The element has to start with swx:opcua.
"swx:opcua,endpoint=opc.tcp://localhost:26543,interval=1000"The remaining items in the comma-separated list are key value pairs separated by equal signs. The following keys are allowed:
- endpoint
- required: this is the endpoint of the OPC-UA server
- interval
- optional (default 30000): the subscription interval in milliseconds
It is recommended to only set the basic options and leave the advanced ones to the default values. If the OPC-UA server does not allow self-signed certs to be used by clients then the advanced options can be used.
- intervalData
- optional (default is value of interval): the subscription interval for telemetry data (property values) in milliseconds
- intervalEvent
- optional (default is value of interval): the subscription interval for events in milliseconds
- mode
- optional (default "auto"): the security mode to use, available options "auto", "None", "Sign", "SignAndEncrypt"
- policy
- optional (default "auto"): the security policy to use, available options "auto", "None", "Basic128Rsa15", "Basic256", "Basic256Sha256", "Aes128_Sha256_RsaOaep", "Aes256_Sha256_RsaPss"
- autogencert
- optional (default true): auto generate a self-signed cert if no certfile/keyfile are specified
- certfile
- optional: a public cert to use for communication with the endpoint
- keyfile
- optional: the private key of the public cert
- auth
- optional (default "Anonymous"): the authentication method for the connection to the server. Available options include "Anonymous", "Username", and "Certificate."
- username
- optional: needed when authentication method is set to Username
- password
- optional: needed when authentication method is set to Username
If either mode or policy are set to
None then they will both be treated as set to
None.
If both mode and policy are set to
auto then the highest available security mode and level as
recommended by the server will be used.
If only policy is set to auto then the highest
available security level with the requested mode will be used.
If only mode is set to auto then the highest
available security level with the requested policy will be
used.
If no authentication method is configured, a UserIdentityToken for
anonymous authentication will be set.
Configure the OPC-UA Endpoint Using the "config" Property
Instead of adding the required configuration parameters to the
@type, the configuration can be set using the config property on
the thing schema.
{
"@type": [
"swx:opcua"
],
"properties": {
"config": {
"properties": {
"endpoint": {
"type": "string"
},
"interval": {
"type": "integer"
}
},
"type": "object"
},
"ns=1;s=Temperature": {
"@type": "float64",
"title": "Temperature",
"type": "number",
"readOnly": true
}
}
}The @type itself should now only consist of
swx:opcua and have the configuration parameters removed.
The config property should at least contain the
endpoint; any of the other keys as listed in the previous
section should only be used when required for the specific setup.
Construct a Property
The nodes to report are specified as keys in Properties section. Example below:
"ns=1;s=Temperature": { "@type": "float64", "title": "Temperature", "type": "number", "readOnly": true },
The corresponding section of node discovery report is the following:
"Objects": { "MyDevices": { "Temperature": { "BrowseName": "Temperature", "DataType": "float64", "Description": "", "DisplayName": "Temperature", "NodeID": "ns=1;s=Temperature", "Value": 34.52512524858854, "Writable": false },
The complete NodeID should be used at the property key of the Thing
description.
The @type is the DataType returned in the
report.
The readOnly should be set to true if Writable is
false (and vice versa).
The type can be determined from the DataType where
available options are number, integer,
string, etc (see the Web-of-Things Modelling section).
If it is desirable to change the subscription interval on-the-fly, then the
opcuaInterval property as shown in the example of the
introduction should be included in the Thing description.
Property Key Mapping
"ns=1;s=Temperature": { "@type": "float64", "title": "Temperature", "type": "number", "readOnly": true },
It is possible to use a form of mapping from the user defined property key to the OPC-UA nodes by overriding the property's "@type". In this case the "@type" has to be defined as an array of strings where the DataType becomes one array item and the node ID another array item. The node ID has to be prefixed with "opcua-node:".
"myUserDefinedKey": { "@type": [ "float64", "node-id:ns=1;s=Temperature" ], "title": "Temperature", "type": "number", "readOnly": true },
Action/Event to Read Node Value
The OPC-UA Thing Description can have an Action and corresponding Event defined to read node values on request. When requesting the action, the result will be published as an event.
"actions": { "readNodeValue": { "input": { "type": "string" }, "title": "Read Node Value" } },
"events": { "readNodeValue": { "data": { "type": "string" }, "description": "", "title": "Read Node Value Result" } },
ns=1;s=Pressure".Action/Event to Read Node History
The OPC-UA Thing description can have an Action and corresponding Event defined to read node values history on request. When requesting the Action, the result will be published as an Event.
To enable this, add the following Action to the Thing description:"readNodeHistoryValues": { "input": { "properties": { "endTime": { "type": "string" }, "nodeId": { "type": "string" }, "startTime": { "type": "string" } }, "type": "object" }, "title": "Read Node History Values" },
"readNodeHistoryValues": { "data": { "type": "array" }, "description": "", "title": "Read Node History Values Result" },
- nodeId (required): this is the OPC-UA node ID
- startTime (required): this needs to be in the ISO8601 (RFC3339) format
- endTime (optional, defaults to now): this needs to be in the ISO8601 (RFC3339) format
Results come up in the event as an array.
[
{
"at": "2024-02-20T14:00:01Z",
"properties": {
"ns=3;i=1005": 0.4158234
}
},
{
"at": "2024-02-20T14:00:02Z",
"properties": {
"ns=3;i=1005": 0.8134732
}
}
] OPC-UA Methods
An OPC-UA Server can have Methods defined on its Nodes.
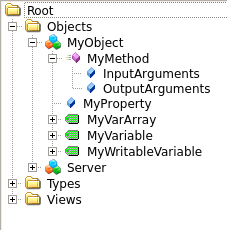
A method called MyMethod exists on the object called
MyObject and has InputArguments as well as
OutputArguments defined.
MyObject: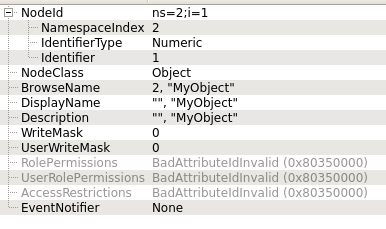
MyMethod: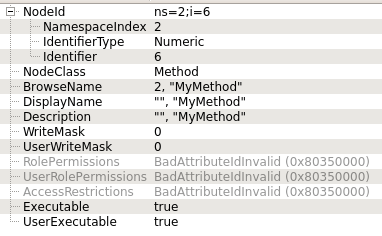
InputArguments: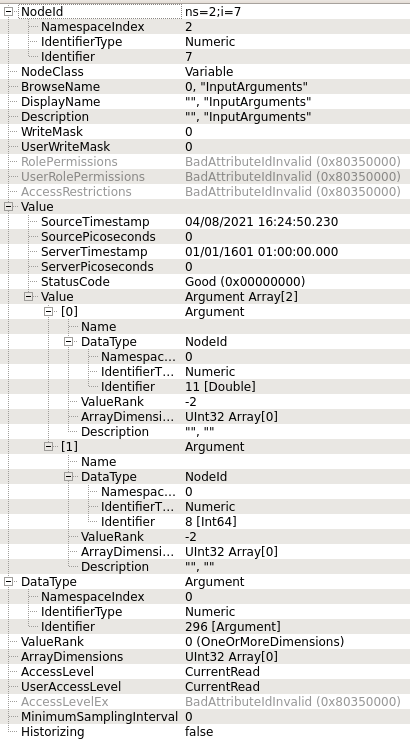
OutputArguments: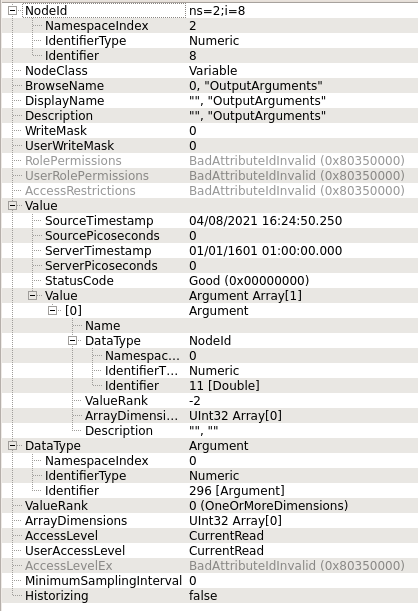
Use these details to configure an Action in the Thing description of the device.
The actionKey needs to be
"<ObjectNodeID>,<MethodNodeID>" which in this case is
"ns=2;i=1,ns=2;i=6".
This particular method has two input arguments; one with the type of 'double' and one with the type of 'int64'. They are defined as input properties for the action with property keys of your choice and types "number" and "integer", respectively.
This method has one output argument of type "double". Define an event on the Thing Description with eventKey the same as the before-mentioned actionKey. Data for this event is defined as type "number".
{
"@type": [
"swx:opcua"
],
"properties": {
"config": {
"properties": {
"endpoint": {
"type": "string"
},
"interval": {
"type": "integer"
}
},
"type": "object"
}
},
"actions": {
"ns=2;i=1,ns=2;i=6": {
"title": "MyMethod",
"input": {
"title": "Input for Method",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"argument1": {
"title": "Input type double",
"type": "number"
},
"argument2": {
"title": "Input type int64",
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
},
"events": {
"ns=2;i=1,ns=2;i=6": {
"title": "MyMethodEvent",
"data": {
"title": "Output of Method",
"type": "number"
}
}
}
}POST /things/<thing-id>/actions/ns=2;i=1,ns=2;i=6{
"ns=2;i=1,ns=2;i=6": {
"input": {
"argument1": 25.73,
"argument2": 873
}
}
}{"messageType":"actionStatus","thingId":"01FCE7WVXN1E6WCTS7JBWXGNF7","timestamp":1628597874,"data":{"ns=2;i=1,ns=2;i=6":{"href":"/things/01FCE7WVXN1E6WCTS7JBWXGNF7/actions/ns=2;i=1,ns=2;i=6/01FCQZYW6HCQ5HVZMC0AGD4WFZ","input":{"argument1":25.73,"argument2":873},"status":"received","timeRequested":"2021-08-10T14:17:54+02:00"}}}
{"messageType":"event","thingId":"01FCE7WVXN1E6WCTS7JBWXGNF7","timestamp":1628597875,"data":{"ns=2;i=1,ns=2;i=6":{"data":22462.29}}}
{"messageType":"actionStatus","thingId":"01FCE7WVXN1E6WCTS7JBWXGNF7","timestamp":1628597875,"data":{"ns=2;i=1,ns=2;i=6":{"href":"/things/01FCE7WVXN1E6WCTS7JBWXGNF7/actions/ns=2;i=1,ns=2;i=6/01FCQZYW6HCQ5HVZMC0AGD4WFZ","input":{"argument1":25.73,"argument2":873},"status":"completed","timeCompleted":"2021-08-10T14:17:55+02:00","timeRequested":"2021-08-10T14:17:54+02:00"}}}OPC-UA Events
"ns=1;i=1465": {
"data": {
"type": "object"
},
"description": "",
"title": "Tank"
}, The underlying mechanism uses OPC-UA subscriptions, just like the mechanism used for property value publishing.
The OPC-UA Endpoint Configuration section describes a parameter to set the general subscription interval. This parameter is called "interval". This parameter applies to both the Data (property values) and the Events.
New parameters for use in the configuration of the OPC-UA endpoint have been added to independently set the intervals for Data and Events: "intervalData" and "intervalEvent".