Project Parameters: Main Tab
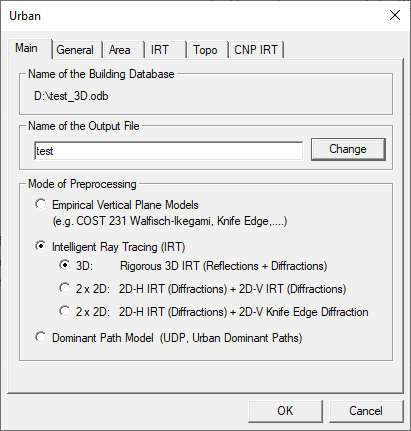
- Name of the Output File
- This name defines the file name and folder of the files generated as the output of
the pre-processing.CAUTION: Do not use the same name as the input database file name, as it would be overwritten.
- Mode of Preprocessing
- Depending on which prediction model should be used in the predictions within
ProMan, the corresponding model must be chosen for
the pre-processing.
- Empirical Vertical Plane Models
- For these wave propagation models (COST 231 Walfisch-Ikegami, Knife-Edge Diffraction, ...) the pre-processing is not required, but can be used to combine the building and topographical layers and to compute the prediction grid (which pixels are outside and which ones are inside the buildings) in advance.
- Intelligent Ray Tracing (IRT)
-
- 3D: Rigorous 3D IRT (Reflections + Diffractions)
- The 3D Intelligent Ray Tracing technique computes the propagation path in three dimensions including reflections at building walls and diffractions around building wedges (horizontal and vertical). To accelerate the path finding the model is based on the pre-processed building data. In addition to the rigorous 3D ray-tracing, there are two different other ray-optical modes available.
- 2 x 2D: 2D-H IRT (Diffractions) + 2D-V IRT (Diffractions)
-
The pre-processing and as a follow-on also the determination of propagation paths is done in two perpendicular planes: one horizontal plane (for the wave-guiding, including the vertical wedges) and one vertical plane (for the over rooftop propagation including the horizontal wedges). In both planes, the propagation paths are determined similarly to the 3D-IRT method by using ray optical methods.
- 2 x 2D: 2D-H IRT (Diffractions) + 2D-V Knife Edge Diffraction
- This model treats the propagation in the horizontal plane in the same way as the previously described model, by using ray optical methods (for the wave-guiding, including the vertical wedges). The over-rooftop propagation (vertical plane) is considered by evaluating the knife edge diffraction model.
- Dominant Path Model (UDP, Urban Dominant Paths)
- For the urban dominant path model the pre-processing is not required but can be used to combine the building and topographical layers and to compute the prediction grid (which pixels are outside and which ones are inside the buildings) in advance.