Project Parameters: IRT Tab
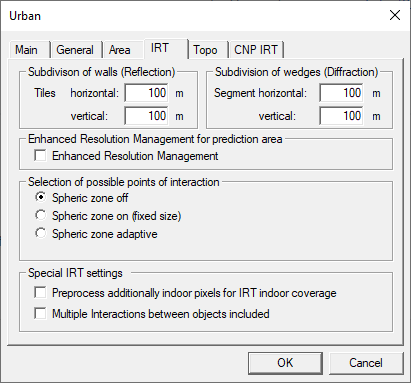
- Subdivision of Walls
-
This option defines the maximum size of the tiles the walls are divided into. The horizontal and vertical value can be defined separately.
If a wall is smaller than the values given (in both horizontal and vertical direction) it is not divided but handled as the whole wall.
The smaller the values are chosen, the longer the computation time and the larger the database size gets, because the visibility relations for more tiles must be computed. Suggested values are between 40 – 100 meters, a typical value is 60 meters.
- Subdivision of Wedges
-
This option defines the maximum size of the horizontal and vertical segments the wedges are divided into. The horizontal and vertical value can be defined separately. If in a scenario the diffraction at the roof wedges is important (if the over-rooftop propagation is dominant), then a smaller value for the horizontal segments should be used. If a wedge is smaller than the values given it is not divided but handled as the whole wedge. The smaller the values are chosen, the longer the computation time and the larger the database size gets, because the visibility relations for more segments must be computed.
Suggested values are between 40 – 100 meters, a typical value is 60 meters.
- Enhanced Resolution Management
- This option defines the factor for the Adaptive Resolution Management. Suggested values are 2 or 3.
- Selection of Possible Points of Interaction (Spheric Zone)
-
This option (if enabled) defines the maximum radius (distance) up to which the visibility relations between the elements are considered. The value must be specified in meters.
Suggested values are from 600 – 1000 meters, depending on the database structure. A typical value is 800 meters for the fixed size. In
Auto
mode the size of the spheric zone depends on the height of the individual element (tile or segment), for higher elements automatically a larger radius is considered. Therefore, the maximum distance (= radius of the spheric zone) up to which visibility relations are considered is determined according to the settings of the basic radius and the radius increment.This acceleration method puts only limitations on the range between the different interaction points (reflection, diffraction) and the pixels of the prediction grid. There is no limitation for the distance between the transmitter and the first interaction point by this procedure!
- Multiple Interactions between objects included
-
This acceleration method can be combined with all three IRT modes included in WallMan, 3D-IRT, 2x2D (2D-H IRT + 2D-V IRT) and 2x2D (2D-H IRT + 2D-V Knife Edge Diffraction). The following paragraphs describe the approach in more detail.
The pre-processing of the building data is a prerequisite for the ray-optical modeling of the wave propagation based on the IRT algorithm. The IRT approach allows ray-optical predictions over large urban areas which are not possible using conventional ray-optical algorithms.
In this pre-processing, in a first step, the building walls are subdivided into tiles and the building wedges are subdivided into segments (vertical and horizontal ones). After this segmentation the mutual visibility relations between the numerous elements (walls, segments and pixels) of the building database are determined.- Multiple Interactions check box enabled
- Usually the pre-processing in WallMan includes both the determination of visibility relations between tiles and tiles (segments and segments) as well as between tiles and pixels (segments and pixels). This allows then coverage predictions including multiple interactions (reflections, diffractions) which guarantee a high accuracy. However, due to the high number of visibility relations, which must be determined, the pre-processing of large urban areas (larger than 10 km2) might take a long time.
- Multiple Interactions check box disabled
- The new
Interaction Control
feature implemented in the IRT algorithm provides a better opportunity for such large urban areas. This approach focuses on the determination of the visibilities between tiles and pixels (segments and pixels) and requires, therefore, a reduced pre-processing time. So, it is possible to pre-process even larger areas. However, the ray-optical prediction is limited to the computation of a single diffraction on the building wedges and a single reflection on the building walls, while for the over rooftop propagation the knife-edge diffraction model is used.
- Pre-process additionally indoor pixels for IRT indoor coverage
-
The ray-optical wave propagation modeling is based on the building database (in vector format, each building is described as a polygonal cylinder) and the underlying terrain data (if available).
The ray-tracing algorithm has been extended so that not only the rays to outdoor pixels are calculated but also the rays to pixels inside the buildings. This has been achieved by subsequent modifications to the algorithms which are in charge of the ray determination. However, the effort for the pre-processing is increased (computation time as well as the size of the pre-processing file) if this feature is activated.