Hybrid Predictions
Ray-optical propagation models consider a maximum number of reflections and diffractions. Use a hybrid approach combining empirical prediction with ray-optical prediction.
Due to the limited number of considered reflections and diffractions, not all prediction points may be reached with the ray-optical algorithms (especially far away from the transmitter). This remaining part of the pixels can be computed with empirical models, based on the direct ray between transmitter and receiver. For urban scenarios, the COST-Walfisch-Ikegami model is implemented.
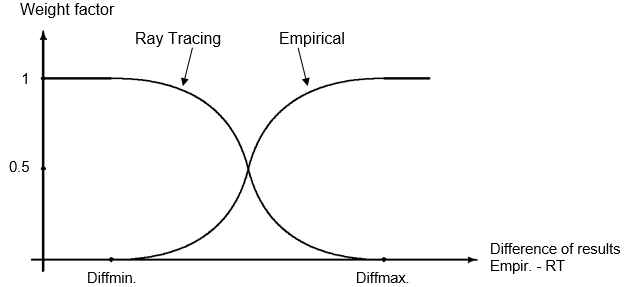
Depending on the difference between the ray-optical and the empirical prediction, a weighted sum of both predictions is computed. The functions for the weight factor are either or . Therefore the sum of both functions is always equal to 1 for all possible values of x.
Investigations have shown that the hybrid prediction reduces the overall prediction error.