Since version 2026, Flux 3D and Flux PEEC are no longer available.
Please use SimLab to create a new 3D project or to import an existing Flux 3D project.
Please use SimLab to create a new PEEC project (not possible to import an existing Flux PEEC project).
/!\ Documentation updates are in progress – some mentions of 3D may still appear.
Post-processing quantities: translation motion)
Introduction
This paragraph deals with physical quantities computed for translating motion.
Kinematic variables
The list of kinematic variables used for solving and the names of the corresponding Flux parameters are given in the table below; in this table MS indicates the concerned mechanical set.
| Kinematic variable | Name | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Linear position: y | LinPos(MS) | m |
| Linear speed: |
LinSpeed(MS) | m/s |
| Linear acceleration: |
LinAcc(MS) | m/s² |
Physical quantities
The list of physical quantities computed in the post-processing module and the names of the corresponding Flux parameters are given in the table below; in this table MS indicates the concerned mechanical set.
| Force | Name | Unit | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic force: F em | ForceElecMag(MS) | N | |
| Internal system | |||
| Friction force: |
ForceFrInt(MS) | N |
|
| Spring return force: |
ForceSpInt(MS) | N |
|
| Inertia force: |
ForceInInt(MS) | N |
|
| Resistant force*: |
ForceReInt(MS) | N |
|
| External system | |||
| Friction force: |
ForceFrExt(MS) | N |
|
| Spring return force: |
ForceSpExt(MS) | N |
|
| Inertia force: |
ForceInExt(MS) | N |
|
| Resistant force * : |
ForceReExt(MS) | N |
|
- either the sum of the friction force + the spring return force
- or the resistant force defined using a formula
Reminder of the solved mechanical equation
The solved mechanical equation for translating motion is: ![]()
where:
- m is the mass
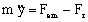
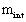 is the mass of the
moving mechanical set (internal system)
is the mass of the
moving mechanical set (internal system)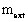 is the mass of the
external load (external system)
is the mass of the
external load (external system)
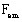 is the
electromagnetic force
is the
electromagnetic force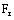 is the resistant
force
is the resistant
force 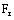
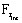 is the resistant
force acting on the moving mechanical set (internal system)
is the resistant
force acting on the moving mechanical set (internal system)
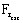 is the resistant
force acting on the external load (external system)
is the resistant
force acting on the external load (external system)
Important note
When there are symmetries and periodicities, the forces are computed for the entire device.