The Application Programming Interface (API) in Flow Simulator
- FS_LOAD_MODEL
- FS_RUN_MODEL
- FS_GET
- FS_SET
- FS_END
C, C++, and Fortran programing languages have been tested and examples are supplied with the Flow Simulator installation (<install_directory>/FlowSimulator/Resources/Solver_API_Examples).
The API can be used to couple a Flow Simulator model with another solver. For example, a thermal solver for 2D or 3D parts.
- Run steady-state or transient.
- Allow for exchange of data between multiple Flow Simulator models in co-simulation cases.
- Update model inputs before running. For example, chamber boundary conditions, element geometry, and orifice Cd.
- Extract results after running. For example, internal chamber pressure and temperature and element flow rates.

General Function Information
- FS_LOAD_MODEL_C (model_name)
- Model_name can be absolute or a relative path to the model file (.flo).
- FS_RUN_MODEL_C (coupling_time)
- Runs the Flow Simulator solver
- coupling_time is only needed for transient or quasi steady-state analysis, and it is 0.0 for steady state runs.
- coupling_time is the time step for printing the result file and returning control to the calling program.
- FS_SET_C/GET_C (itemtype_str,
itemnum, locat1_str,
locat2_str, locat3_str,
prop_str, unit_str,
setval, status)
- Uses Flow Simulator controller logic to set or get almost anything in the model.
- These are mainly used for setting boundary conditions or getting results.
- These functions can also be used for data exchange in co-simulation.
- More information on the inputs of these functions can be found in <install_directory>\Resources\misc_solver_files\ FS_coupling.dat
- FS_END_C():
- Clears the data related to the model but does not unload the DLL.
- It releases the Altair license. Therefore, it is very important to call this function before the program is terminated.
Simple API Example

In this example, a C++ main control program is being used. A header file known as DLL_class.h is interfacing with the Flow Simulator DLL and retrieving the address to the functions available in it. The idea is to provide this header file so that you can either create your own interface to the DLL or build on top of this class. This class is just for ease of use and provides a few basic functionalities such as loading/unloading the DLL and calling routines in the DLL.
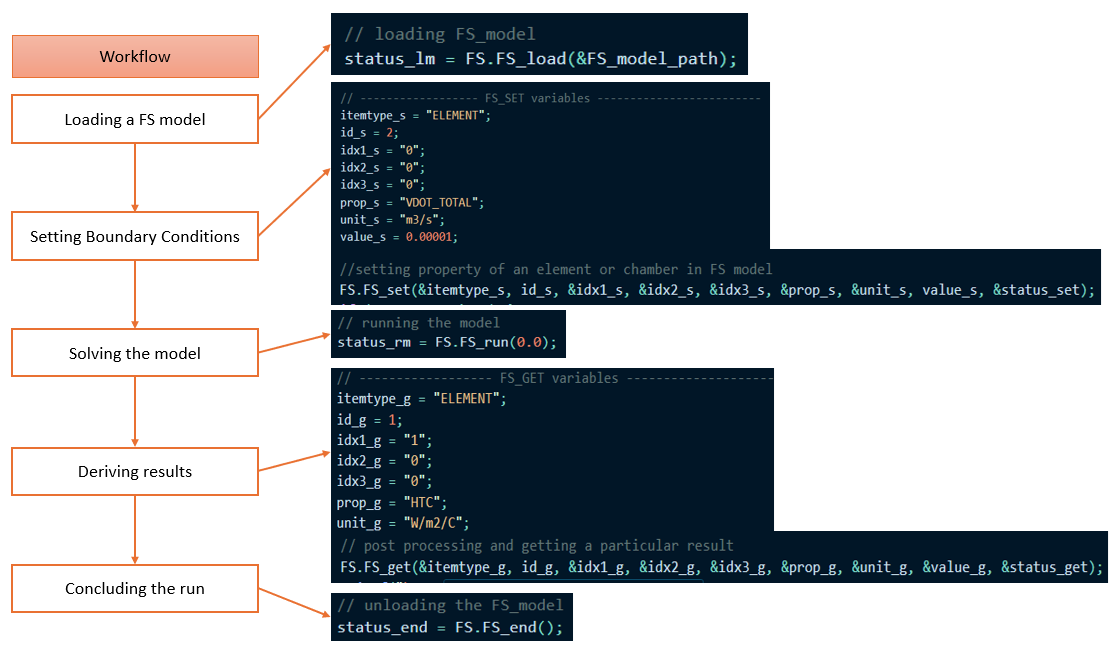
See <install_directory>/FlowSimulator/Resources/Solver_API_Examples/CPP/steady_state/1_w_get_set for this example.