Release Notes: Altair Feko 2023
Altair Feko 2023 is available with new features, corrections and improvements. Altair Feko 2023 is a major release. It can be installed alongside other instances of Altair Feko.
Feko is a powerful and comprehensive 3D simulation package intended for the analysis of a wide range of electromagnetic radiation and scattering problems. Applications include antenna design, antenna placement, microstrip antennas and circuits, dielectric media, scattering analysis, electromagnetic compatibility studies including cable harness modelling and many more.
newFASANT complements Altair’s high frequency electromagnetic software tool (Altair Feko) for general 3D EM field calculations, including, among others, special design tools tailored for specific applications like complex radomes including FSS, automated design of reflectarrays and ultra-conformed reflector antennas, analysis of Doppler effects, ultrasound systems including automotive or complex RCS, and antenna placement problems. Advanced solver technologies like the MoM combined with the characteristic basis functions (CBFS), PO/GO/PTD, GTD/PO and MLFMM parallelised through MPI/OpenMP, being some of them especially efficient for the analysis of electrically very large problems.
WinProp is the most complete suite of tools in the domain of wireless propagation and radio network planning. With applications ranging from satellite to terrestrial, from rural via urban to indoor radio links, WinProp’s innovative wave propagation models combine accuracy with short computation times.
WRAP is a comprehensive tool for electromagnetic propagation, antenna collocation and spectrum management. WRAP combines propagation analysis, often over large areas with many transmitters and receivers, with system analysis to include complex non-linear equipment properties.
Highlights of the 2023 Release
The most notable extensions and improvements to Feko, newFASANT, WinProp and WRAP in the 2023 release.
Salient Features in Feko
- A selection of new components was added to the CADFEKO
component library. Ten new antenna models (including antennas for EMC testing) and four
new platform models were added.
Figure 1. A selection of the new components available in the component library. 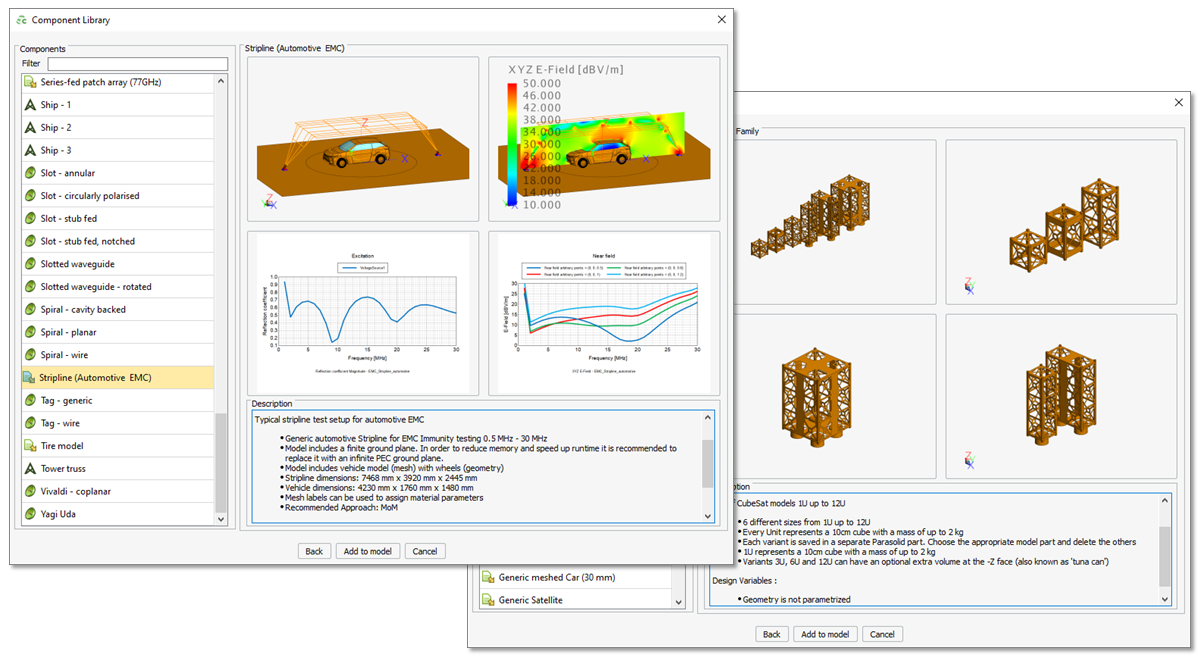
- The Altair Material Data Centre is now populated with media from CADFEKO. Import the media and use in Feko simulations.
- Reduced solution method limitations:
- SEP regions (dielectrics) can be used in the MoM part of the solution for coupled and uncoupled scenarios with RL-GO.
- Lossy dielectrics can be included in characteristic mode analysis calculations.
- Loading restrictions have been relaxed to model direct/strong coupling between the inner and outer regions at the cable terminations in combined MoM/MTL simulations.
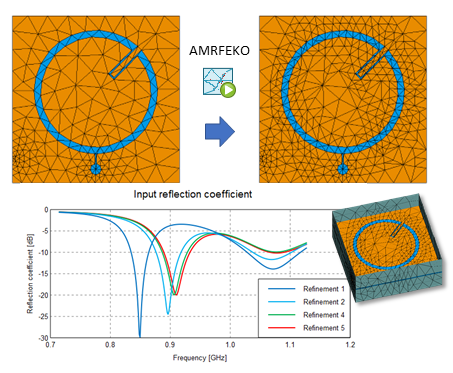
- A new tool (AMRFEKO) is now available, which enables automatic adaptive mesh refinement based on error estimates for FEM and MoM/FEM solutions. The fully-automatic tool can be launched from a command prompt or any of the Feko GUIs and can also be used on HPC resources in a similar fashion to RUNFEKO.
- A new domain connectivity approach allows meshes of specific parts to be treated as if
connected
during MoM and MoM/MLFMM solutions in places where the borders of the meshes are close together, even if the mesh vertices on those borders are not coincident. Domain connectivity can now be configured in CADFEKO (new in 2023) or EDITFEKO (since 2022.3) and visualized in POSTFEKO (new in 2023).Figure 3. A static imported car mesh and a parameterised antenna geometry viewed in POSTFEKO where the Domain Connectivity display tool highlights edges in green that are connected using domain connectivity. 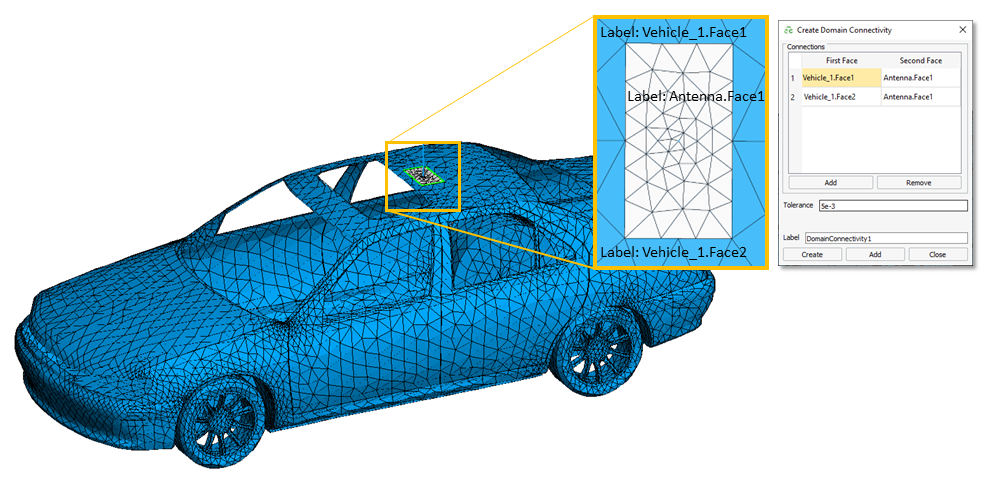
- CBFM is a modification of the conventional method of
moments (MoM) that reduces the number of unknowns using
macro basis functions. This approach could be used with MoM from Feko 2022.3 but is now
available for use with MoM/MLFMM – helping achieve a substantial performance improvement
over MLFMM in some applications such as monostatic RCS
calculations of large objects with similar solution accuracy compared to the default solution.
Figure 4. An example of a monostatic RCS calculation of an aircraft solved with MLFMM and MoM/MLFMM. 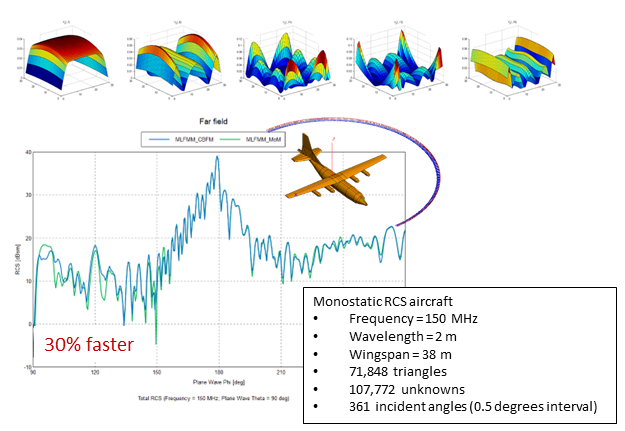
Salient Features in WinProp
- Modified the beam assignment algorithm to use the rays of the receiving pixel leading to
more accurate results.
Figure 5. A before (left) and after (right) example of improved beam assignment algorithm. 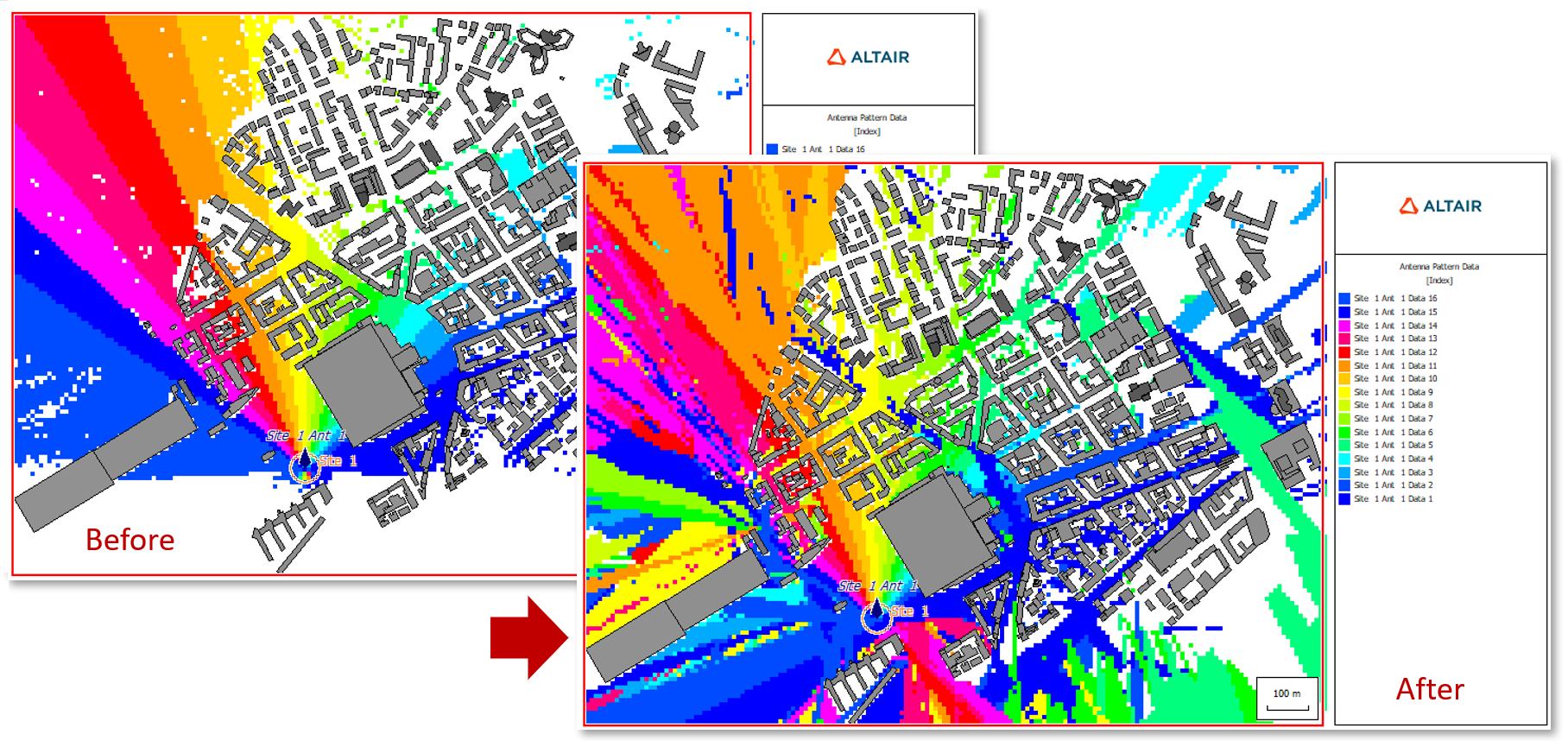
- Arbitrary prediction planes can now be viewed in the 2D view by selecting the plane from
the prediction plane drop-down list. In the past, arbitrary prediction
planes could only be viewed in the 3D view. This option is useful when viewing vertical
planes of the Parabolic Equation (PE) model.
Figure 6. Examples of arbitrary prediction planes that are now available in the prediction plane drop-down list. Left: Arbitrary plane in an indoor scenario in the 3D view and new 2D view; Right: A vertical prediction plane used in the PE model. 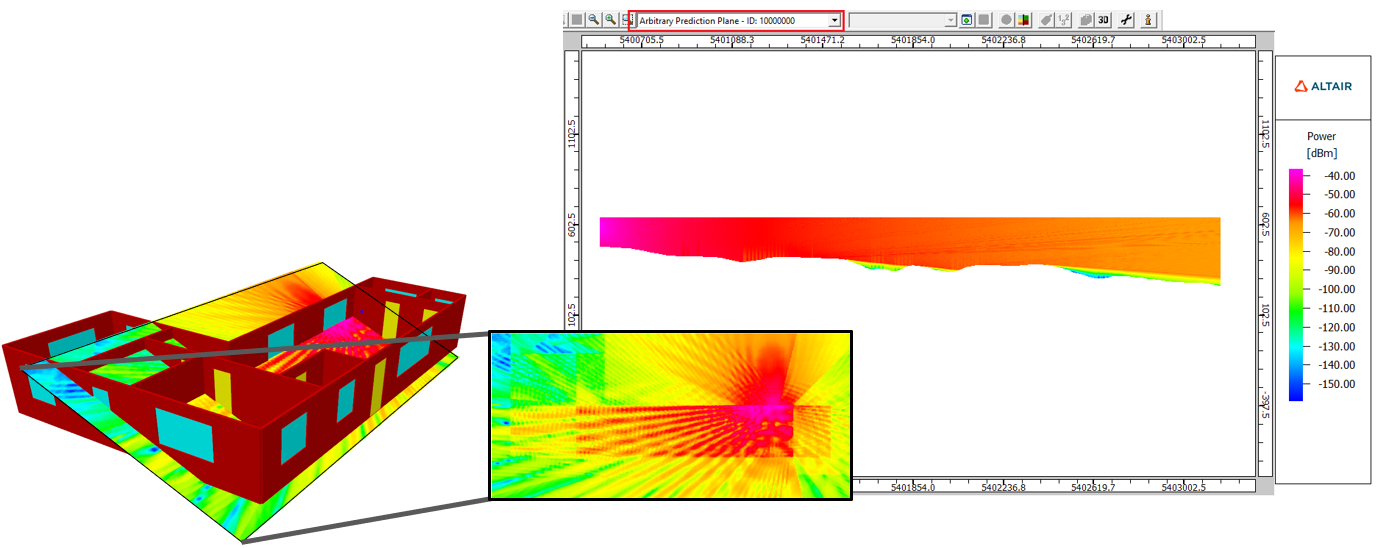
- The pixel center and pixel grid can be enabled on the Default
Settings dialog.
Figure 7. An example of an indoor database where the pixel center and pixel grid were enabled on the Default Settings dialog. For a large database, zoom-in to view the pixel center and pixel grid. 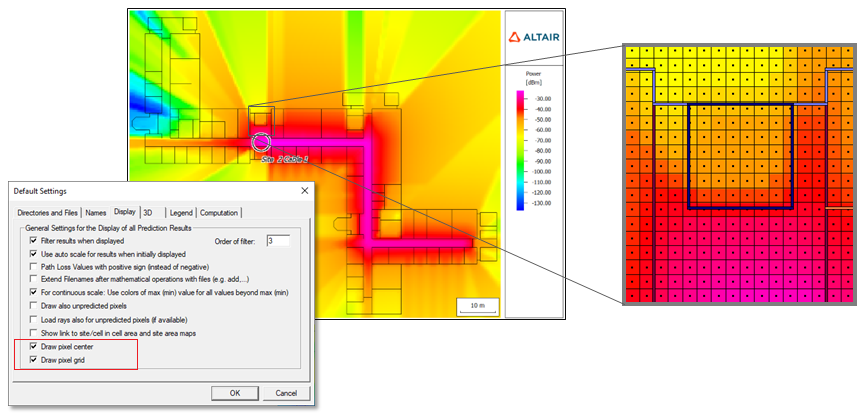
- Added the new wireless standard definition files (.wst1) for WiFi 7 (802.11be) and updated WiFi 6 (802.11ax). ProMan was extended to support the new 4096-QAM transmission modes for WiFi 7 (802.11be).
Salient Features in WRAP
- Added a new and improved format for height and landcover maps to WRAP and MapDataManager that have non-integer resolutions and are backwards compatible with the old format. To support coordinates and resolutions with non-integer arc second values, modifications were made to MapData Manager and height/clutter data reader functions. For this new format, WRAP supports horizontal resolution in micrometers, and vertical resolution in mm. This will assist detailed prediction and planning, involving maps with finer vertical and horizontal details of height and clutter (land use) data.
- The ITU-R P. 1409 propagation model was added to WRAP, which
provides propagation predictions for radio communication systems or networks using
high-altitude platform stations (HAPS) or other elevated stations in the stratosphere. The
model is valid from 1 GHz and above.
Figure 8. Propagation paths for high-altitude station.
- Added support to calculate the LTE sub-carrier interference between neighbouring
co-channel LTE base stations. The user has the option to select the strongest co-channel
interference only, or all interference, in addition to defining the cell load. The option
is used when LTE transmitters exist in coverage calculations that make use of
interference, for example, RSSI, RSRQ, Data rate, Throughput, SINR.
Figure 9. The SINR LTE Base station settings dialog where you can select the strongest co-channel interference only, or all interference, in addition to defining the cell load. 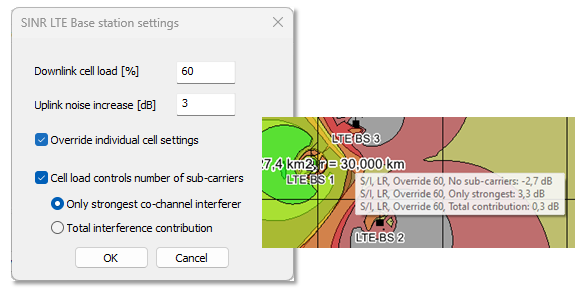
Feko 2023 Release Notes
The most notable extensions and improvements to Feko are listed by component.
CADFEKO
Features
- Added the Find Cable tool.
- Antenna arrays are now supported when importing a .cfx file.
- Extended the waveguide mesh port to support curvilinear faces.
- Added auto-delete of the waveguide mesh port when the referenced mesh topology is deleted with vertex definition (for both normal and curvilinear faces).
- Implemented unlinking of waveguide mesh ports (for both normal and curvilinear faces).
- The Adaptive Refinement mesh refinement rule option was renamed to Error Estimate Refinement. The old API (MeshRefinementRules:AddAdaptiveRefinement) is still supported.
- Model mesh boundary edges and boundary faces are exposed on the details tree. This change allows visualisation of these model mesh boundary faces and boundary edges in the 3D view.
- Added support to group mesh refinement rules.
- Added support for adding edge mesh refinements. This allows mesh refinement of geometry or model mesh edges.
- Improved application startup behaviour by showing the splash screen earlier during startup. This provides more immediate feedback to the user that the application had been launched.
- Enable the combination of CBFM and MLFMM.
- Added support to configure domain connectivity.
- Added missing Matrix Lua bindings.
- Added the ability to export the mesh outline to a .dxf file as two-dimensional data by projecting it onto the XY plane.
- Added a histogram to the Mesh Info dialog for a visual representation of the distribution of simulation mesh edge lengths.
- Extended FEM line ports to cause mesh refinement around the port.
- New instances of CADFEKO will have default tree branches expanded by default. An application session will remember the tree expansion setting as new models are created or loaded. Details trees will remember collapsed states of the collection when swapping between entities.
- Added support to hide individual cable paths by clicking on the related icon in the model tree.
- Improved the Mesh Info dialog to indicate whether a specific part or all parts are considered in the calculation of the displayed mesh information.
- Added the same limits of student licences in legacy CADFEKO to new CADFEKO.
- Added support to hide individual named points by clicking on the icon for that named point in the model tree.
- Various models have been added to the component library. When using these components, design or configuration options that are available with other component library models are not shown, but rather a preconfigured model is imported into the open project. The user may then adjust variables and settings as needed.
- A model of a biconical/log hybrid (bilog) antenna for EMC immunity testing was added to the component library.
- A model of a horn antenna for EMC immunity testing was added to the component library.
- A model of a log periodic antenna for EMC immunity testing was added to the component library.
- A model of a stripline antenna for EMC immunity testing was added to the component library.
- A model of a reflectarray was added to the component library.
- A model of a generic satellite was added to the component library.
- A model of an open boundary quad-ridged horn antenna was added to the component library.
- A model of a two-by-two corporate feed patch antenna array at 5.7 GHz was added to the component library.
- A model of a square-shaped miniature satellite (CubeSat) was added to the component library.
- A model of a base station sector antenna was added to the component library.
- A model of a series-fed patch array for 77 GHz advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) radar was added to the component library.
- Models of a generic car and tyres were added to the component library.
Resolved Issues
- Resolved an issue where face media properties were not considered for FDTD meshing.
- Resolved an assertion that failed with the message Assertion failed: Geometry could not be transformed correctly for combining when creating a union of geometry parts. This assert prevented the import of certain legacy CADFEKO models.
- Resolved an assertion failure that could be triggered when saving a model with defined coatings.
- Resolved a crash when opening repair and sew faces operator properties.
- Resolved an issue where the mesh size setting was scaled with mesh parts resulting in meshes that were not the correct size. The correct mesh size is now applied when re-meshing scaled mesh parts.
- Reversing normals now works correctly on all mesh face types.
- Component launch options, which could have been modified in another Feko component, for example, in POSTFEKO, are loaded when opening the component launch options tool. The options are also stored when applying changes, making it available to other Feko components while the current instance of CADFEKO is still running.
- Improved geometric region symmetry calculations by introducing a tolerance.
- Fixed a symmetric meshing problem that resulted in a verification error containing SimulationMeshRegionEntity.cpp (614): Assertion failed: It should have 1 region.
- Resolved an issue where reversing the model mesh element normals had no effect in the 3D view.
- Resolved an issue when exporting mesh to I-DEAS mesh (.unv) file format that resulted in reversed element normals.
- Added support to allow vertical resizing of dialogs containing tables.
- Show a warning instead of an error when face normals point in the wrong direction for the faces to be considered symmetric around a plane of symmetry.
- Symmetrical geometric entities which have a scale transform applied to them will now be correctly assessed according to the symmetry setting specified.
- Improved erratic tree behaviour. The scroll bar position no longer jumps to the previously selected item.
- Improved legacy script error feedback in the script editor so that the line at which the error occurred is reported.
- Cable dialogs now all have correct Escape and Enter key behaviour to close the dialog or accept changes without first having to change focus away from the image to another field by pressing Tab or through clicking.
- Resolved an issue where excluding a group did not exclude the entities inside of the group.
- Improved the Save As dialog to use the current project name (instead of the name of a previously imported file) as the suggested file name.
- Validation hierarchy notifications no longer appear as message dialogs but are shown as verification messages in the model status panel.
- Resolved an issue where the Show Only tool was not working as intended.
- Improved selection behaviour using the Rectangle Select tool.
- Point entry widgets refresh their styling when focusing into the widget.
- Fixed missing API documentation on some objects for LocalWorkplane.
CADFEKO [LEGACY]
Features
- When importing Cartesian boundary near field data from files, the option to ignore a face of the near field boundary is now available in both CADFEKO and legacy CADFEKO. This option should be used to achieve accurate simulation results for Cartesian boundary near field data that was computed with one face of the Cartesian boundary coincident with a conductive plane.
EDITFEKO
Features
- Enable the selection of CBFM with MLFMM at the FM card.
POSTFEKO
Features
- Added the functionality to POSTFEKO to plot complex eigenvalues.
- Added rendering support for domain connectivity.
Resolved Issues
- Resolved an assertion failure in POSTFEKO that occurred when importing a large .fek file.
- Implemented a correction to prevent a crash during .fek file updating.
- Added support to display error estimates on curved triangles (order 0.5 only) and segments.
Solver
Features
- Extended the combined MoM/MTL method to relax the loading restrictions at terminations, allowing for direct/strong coupling between the inner MTL and outer MoM regions.
- Added support for CFIE in the characteristic basis function method (CBFM).
- The characteristic basis function method (CBFM) can now be used with MoM in the Feko Solver. This implementation will be extended to support MoM/MLFMM in future releases to improve impact for a wider range of practical problems for applications such as scattering analysis.
- Added a utility for de-embedding S-parameters.
- Add support for MoM-SEP (dielectric materials) hybridized with RL-GO for both coupled and uncoupled cases.
- The calculation of FEM error indicators at metallic surfaces (infinitely thin sheets) within a FEM region has been improved. The error indicator levels are now comparable to the indicator levels in other regions of the model, impacting positively on all workflows relying on these error indicator values. The error indicator calculation phase has also been parallelized.
Shared Interface Changes
Support Components
Features
- Removed the CoMan and OptMan examples from the installation and documentation. Users are encouraged to use HyperStudy for optimisation studies.
- Added a table of supported media types for each solution method to the Feko User Guide.
- Extended the Feko User Guide to include a list of solution methods supported with a multilayer substrate.
- After running a set of simulations prepared using the Create Frequency Ranges macro in CADFEKO, the Combine Results macro will automatically be launched in POSTFEKO to process and display the combined results.
- Converted the Create Impedance Sheet for Layered Metals application macro from the CADFEKO [LEGACY] API to the new CADFEKO API.
WinProp 2023 Release Notes
The most notable extensions and improvements to WinProp are listed by component.
General
Features
- Added new wireless standard definition files for WiFi 7 (802.11be) and updated ones for WiFi 6 (802.11ax).
- OptMan is deprecated and removed from the installation.
- CoMan is deprecated and removed from the installation.
- Upgraded the CityGML converter and corrected an issue where buildings were added multiple times.
ProMan
Features
- Added support to view arbitrary prediction planes in the 2D view. The display of the pixel center and pixel grid can be enabled on the Default Settings dialog (Display tab).
- Modified the beam assignment algorithm to use the rays of the receiving pixel leading to more accurate results.
WallMan
Features
- Added an error message that urban preprocessing with negative coordinates is not possible.
Resolved Issues
- Resolved an issue when saving an indoor database (.idb) as an outdoor database (.odb).
WRAP 2023 Release Notes
The most notable extensions and improvements to WRAP are listed by component.
General
Features
- Add three options (best-case, worst-case, and mean) for methods to combine multiple coverage results in the composite function.
- Added support to define a threshold in the coverage comparison tool.
- The demo database shipped with WRAP now contains LTE Base Station Template, Mobile Station, Transmitter and Receiver (for LTE Band1) for LTE Coverage Calculations.
- The size of the icons in WRAP Toolbar has been modified to adapt to the display resolution.
- Added support for calculating LTE sub-carrier interference between neighbouring co-channel LTE base stations in the Coverage tool.
- Implemented the ITU-R P. 1409 propagation model, which provides propagation predictions for systems using high-altitude platform stations or other elevated stations in the stratosphere.
- Added support for the ITU-R P.617 model in the API with the Link Performance Tool.
Resolved Issues
- Fixed error with ObsMan Method 2 considering out of range radars, when search sector was not specified.
- Corrected some of the warnings about valid ranges in the Radio Link Performance tool.
WRAP MapDataManager
Features
- Added support for map data with non-integer and sub-integer resolutions to support high resolution maps with resolutions below 1 arcsec or below 1 m.
