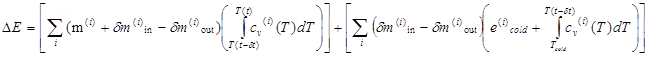Let
the temperature,
the pressure, and
the volume of the airbag at time
, and
the mass of gas
at time
.
,
,
are respectively temperature, pressure and volume of the
airbag at time
, and
the mass of gas
at time
.
Using , the variation of total gas energy can be written as:
(1)
which can be written as:
(2)
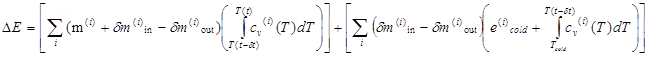
On the other hand, the basic energy equation
Thermodynamical Equations,
Equation 1 of the airbag and the expression of
enthalpy in
Thermodynamical Equations,
Equation 5 gives:
(3)
Where,
and
are characteristics of the inflator and are considered as
input to the problem.
and
can be estimated from the velocity at vent hole
.
is the variation of the external work. This estimation will be
described hereafter.
It comes from
Equation 1 and
Equation 2:
(4)
The variation of the external work can be written as:
(5)
Using
Thermodynamical Equations,
Equation 9, the last expression can be
written as:
(6)
The last equation can be introduced to
Equation 4:
(7)
The first order approximation
for each gas, which allows rewrite
Equation 7 as:
(8)
Which allows to determine the actual temperature
. The actual pressure then computed from the equation of
perfect gas (Thermodynamical Equations, Equation 9).