Since version 2026, Flux 3D and Flux PEEC are no longer available.
Please use SimLab to create a new 3D project or to import an existing Flux 3D project.
Please use SimLab to create a new PEEC project (not possible to import an existing Flux PEEC project).
/!\ Documentation updates are in progress – some mentions of 3D may still appear.
Tools for the creation of the magnetic property B(H): specificities of the numerical models (splines)
Introduction
This section presents the creation of the magnetic property B(H) in the case of numerical models.
The main information refers to:
- the description of the numerical models (standard spline and smoothed spline)
- the operating mode for the creation of a magnetic property B(H) in the case of a numerical model
Two modes of description
It is possible to distinguish between two modes of description for the model:
- the standard spline mode
- the smoothed spline mode
Mode spline standard
In the standard spline mode, the curve B(H) is defined by the assembly of points entered by the user.
The user enters the pair of values B,H observing the following rules:
- the pair of values B,H must respect an increasing sequence and begin with (0,0)
- a sufficient number of points must be given to describe all the curve B(H) up to saturation (the number can vary from 4 to 200)
- the last points must approximate an asymptote having the slope μ0
μincremental(H)
Smoothed spline mode
In the smoothed mode, the definition of the curve B(H) is simplified. This mode of definition requires fewer points than the standard spline mode.
The curve B(H) is divided into three parts:
- the first part is a homographic function passing through zero and describing the bend of the B(H) dependence. It is defined by a pair of values (B,H) provided by the user and it ends at the last pair of values provided by the user
- the second part is a homographic function for tangent connection to the first part and to the last part of the curve B(H)
- the third part is a straight line of slope μ0, which intercepts the vertical axis (H = 0) at an ordinate corresponding to the saturation magnetic polarization Js
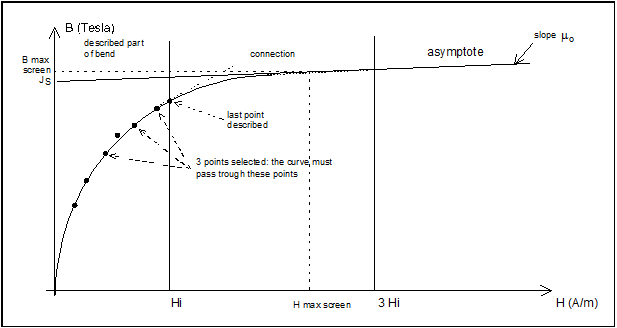
- the pair of values (B,H) must respect an increasing order
- the user must describe the first part of the B(H) curve, up to the bend, with:
- 5 to 8 representative points
- 3 points imposed on this curve
- the user must enter the value of the saturation magnetic polarization Js in order to define the asymptotic part of the B(H) curve
Operating mode
To create a magnetic property B(H) with a numerical model, follow the operating mode below:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 |
In the my_base base of material
|
| 2 |
In the tab B(H)
|
| 3 |
In the zone of the models
|
| 4 |
In the zone for the description of the model
|
| → | Open the assistant … |
| External data / wizard | |
|---|---|
| Step | Action |
| 1. External data |
If the external data exist … If not:
|
| 2. Smoothed spline |
If smoothed spline:
|
| 3. Synthesis | Click on Next |
External data …
The following table resumes what was described before:
| Model | Points (external data) | Points (spline curve) |
|---|---|---|
| Standard spline | The external data correspond to the points of passage of the curve (accessible and modifiable points) | The points of the curve standard spline correspond to the external data (equality) |
| Smoothed spline | The external data correspond to the initial points (accessible and modifiable points) | The points of the smoothed spline curve correspond to the points calculated after the smoothening of the external data |
Advice
If you work in the smoothed mode, you should not forget to tick the box at each modification.