Since version 2026, Flux 3D and Flux PEEC are no longer available.
Please use SimLab to create a new 3D project or to import an existing Flux 3D project.
Please use SimLab to create a new PEEC project (not possible to import an existing Flux PEEC project).
/!\ Documentation updates are in progress – some mentions of 3D may still appear.
Explanation of results
Electrostatic energy
The density of the electrostatic energy in a point is expressed by means of the electric field quantities D and E by the relation:
![]()
which can also be written for a linear and isotropic medium as:
The electrostatic energy in a volume region is equal to:
![]()
Electrostatic force and torque
The electrostatic forces and torques are computed by the virtual work method.
The corresponding region should be surrounded by air.
Electric charge on the surface of a conductor
The charge carried by a surface of a conductor is equal to:
![]()
This computation can be carried out on an equipotential surface, i.e.:
- on the surface of a perfect conductor
- on the surface of imposed potential type (with uniform V0)
Capacitance computation
It is possible to compute the capacitance between two conductors in two different ways:
-
by using the expression of electrostatic energy (We):
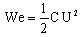 ⇒
⇒ 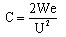
-
by using the expression of electric charge (Q):
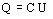 ⇒
⇒ 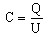
where U represents the potential difference between the conductors.
The second method is more interesting in term of computing time for computation of a matrix of capacitance.