RD-V: 0032 Spring (TYPE8)
Spring force/moment as function of elongation/rotation for different stiffness formulations.
The subject of this study is to verify the behavior of the general spring element using different stiffness formulations with a defined elongation or rotation.
Options and Keywords Used
Input Files
Model Description with Different Translational Stiffness Formulations
Units: Mg, s, mm, MPa
- Elastic linear stiffness
- K=2N/mm
- Nonlinear elastic stiffness
- Force versus displacement function:
- Elongation
- Force
- -20
- -20
- -1
- -10
- 0
- 0
- 1
- 10
- 20
- 20
- Linear stiffness K=50N/mm used for transition
- Force versus displacement function:
- Nonlinear plastic stiffness with isotropic hardening
(H=1)
- Same force versus displacement function and same linear stiffness
- Plastic behavior with H=1
- Linear stiffness K=50N/mm used for transition
- Nonlinear plastic stiffness with uncoupled hardening
(H=2)
- Same force versus displacement function and same linear stiffness
- Plastic behavior with H=2
- Linear stiffness K=50N/mm used for transition
- Nonlinear plastic stiffness with nonlinear unloading
(H=6)
- Same force versus displacement function and same linear stiffness
- Nonlinear unloading force versus displacement:
- Elongation
- Force
- -10
- -20
- -5
- -1
- 0
- 0
- 5
- 1
- 10
- 20
- Plastic behavior with H=6
- Linear stiffness K=50N/mm used for transition
Imposed displacement is defined on one end of the spring element to model tensile and compression (displacement +/- 20mm) with constant velocity of 200mm/s.
The other end of the spring element is clamped.
Results
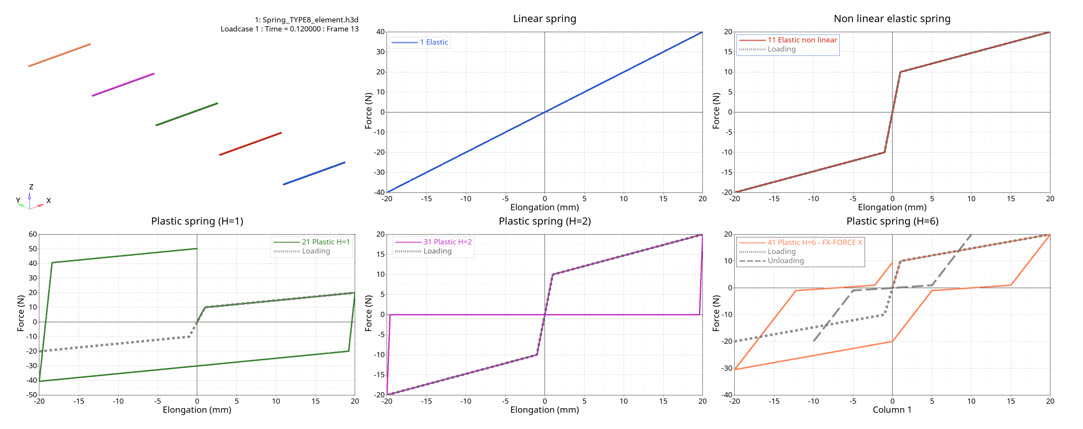
Figure 1. force versus elongation
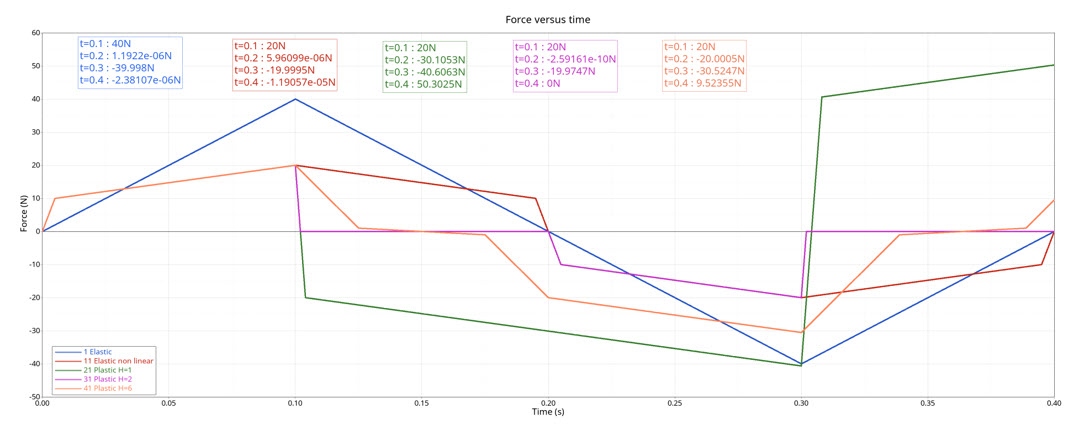
Figure 2. force versus time
| Time | Elastic Linear Stiffness | Nonlinear Elastic | Nonlinear Plastic Stiffness with Isotropic Hardening (H=1) | Nonlinear Plastic Stiffness with Isotropic Hardening (H=2) | Nonlinear Plastic Stiffness with Nonlinear Unloading (H=6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t=0.1s | 40 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| t=0.2s | 0 | 0 | -30.10526316 | 0 | -20 |
| t=0.3s | -40 | -20 | -40.63157895 | -20 | -30.52631579 |
| t=0.4s | 0 | 0 | 50.30249307 | 0 | 9.473684211 |
Model Description with Different Rotational Stiffness Formulations
Units: Mg, s, mm, MPa
- Elastic linear stiffness
- K= 12.73239545 Nmm/rad
- Nonlinear elastic stiffness
- Moment versus rotation function:
- Elongation
- Force
- -3.141592654
- -20
- -.157079633
- -10
- 0
- 0
- .157079633
- 10
- 3.141592654
- 20
- Linear stiffness K=318.3098862 Nmm/rad used for transition
- Moment versus rotation function:
- Nonlinear plastic stiffness with isotropic hardening
(H=1)
- Same moment versus rotation function and same linear stiffness
- Plastic behavior with H=1
- Linear stiffness K= 318.3098862 Nmm/rad used for transition
- Nonlinear plastic stiffness with uncoupled hardening
(H=2)
- Same moment versus rotation function and same linear stiffness
- Plastic behavior with H=2
- Linear stiffness K= 318.3098862 Nmm/rad used for transition
- Nonlinear plastic stiffness with nonlinear unloading
(H=6)
- Same force versus rotation function and same linear stiffness
- Nonlinear unloading force versus rotation:
- Rotation
- Force
- -1.570796327
- -20
- -.785398163
- -1
- 0
- 0
- .785398163
- 1
- 1.570796327
- 20
- Plastic behavior with H=6
- Linear stiffness K= 318.3098862 Nmm/rad used for transition
Imposed displacement is defined on one end of the spring element to model rotation (rotation +/- rad – 180 degrees) with constant velocity of 200mm/s.
The other end of the spring element is clamped.
Results
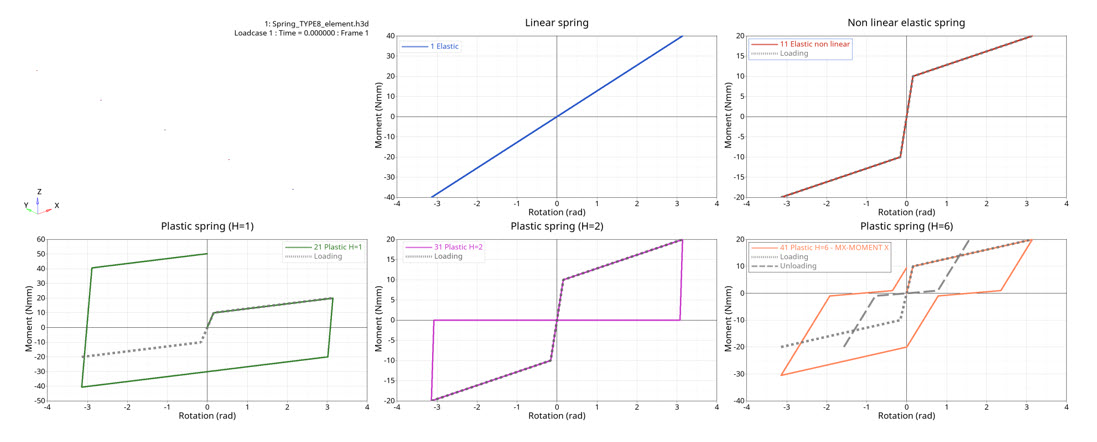
Figure 3. moment versus rotation
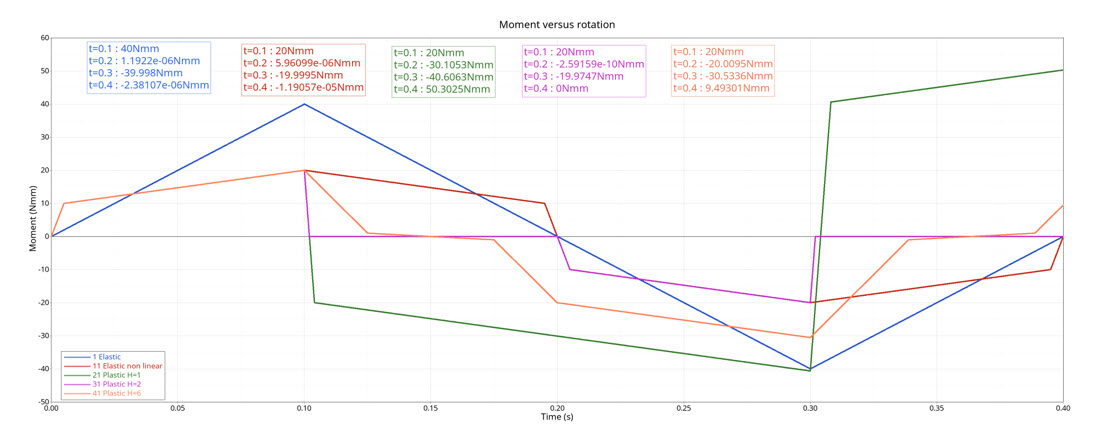
Figure 4. moment versus time
| Time | Elastic Linear Stiffness | Nonlinear Elastic | Nonlinear Plastic Stiffness with Isotropic Hardening (H=1) | Nonlinear Plastic Stiffness with Isotropic Hardening (H=2) | Nonlinear Plastic Stiffness with Nonlinear Unloading (H=6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t=0.1s | 40 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| t=0.2s | 0 | 0 | -30.10526316 | 0 | -20 |
| t=0.3s | -40 | -20 | -40.63157895 | -20 | -30.52631579 |
| t=0.4s | 0 | 0 | 50.30249307 | 0 | 9.473684211 |
Model Description for Different Translational Viscous Formulation
Units: Mg, s, mm, MPa
- Nonlinear elastic stiffness
- Force versus displacement function:
- Elongation
- Force
- -5
- -20
- -1
- -10
- 0
- 0
- 1
- 10
- 5
- 20
- Force versus displacement function:
- Elongation rate dependency
- Linear value
- Stiffness scale factor
- Force versus elongation rate scale factor function:
- Elongation
- Force
- -10
- -0.1
- 0
- 0
- 10
- 0.1
- Damping versus elongation rate function:
- Elongation
- Damping
- -10
- -1
- 0
- 0
- 10
- 1
- Damping versus elongation rate function with higher velocity
The imposed displacement function abscissa (time) is scaled by 0.5 to double the constant loading velocity.
Imposed displacement is defined on one end of the spring element to model tension and compression (displacement +/- 5mm) with constant velocity of 50mm/s (with abscissa scale factor 1.0) or1 00mm/s (with abscissa scale factor 0.5). The rotational degrees of freedom at this end of the spring are fixed to see only shear behavior.
The other end of the spring element is clamped.
Results
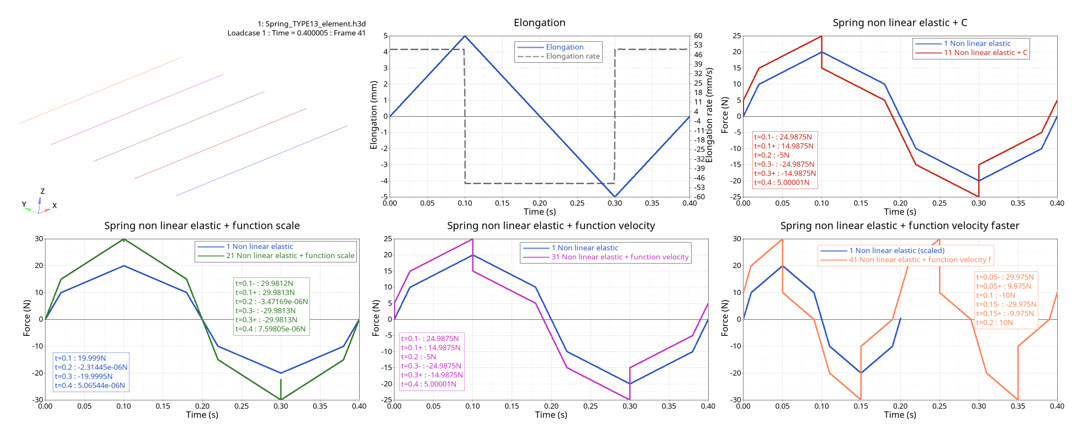
Figure 5. force versus time
| Time | Nonlinear Elastic | Nonlinear Elastic + C | Nonlinear Elastic + Velocity-based Force Function Scale | Nonlinear Elastic + Velocity-based Damping Function (200 mm/s) | Nonlinear Elastic + Velocity-based Damping Function (400 mm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t=0.1s (V+) | 20 | 25 | 30 | 25 | 30 |
| t=0.1s (V-) | 20 | 15 | 30 | 15 | 10 |
| t=0.2s (V-) | 0 | -5 | 0 | -5 | -10 |
| t=0.3s (V-) | -20 | -25 | -30 | -25 | -30 |
| t=0.3s (V+) | -20 | -15 | -30 | -15 | -10 |
| t=0.4s (V+) | 0 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 10 |
Model Description for Different Rotational Viscous Formulation
Units: Mg, s, mm, MPa
- Nonlinear elastic stiffness
- Moment versus rotation function:
- Rotation
- Moment
- -3.141592654
- -20
- -.157079633
- -10
- 0
- 0
- .157079633
- 10
- 3.141592654
- 20
- Moment versus rotation function:
- Elongation rate dependency
- Linear value
- Stiffness scale factor
- Force versus rotation rate scale factor function:
- Elongation
- Force
- -10
- .636619772
- 0
- 0
- 10
- .636619772
- Damping versus rotation rate function:
- Elongation
- Damping
- -10
- -6.366197724
- 0
- 0
- 10
- 6.366197724
- Damping versus rotation rate function with higher velocity
The imposed displacement function abscissa (time) is scaled by 0.5 to double the constant loading velocity.
Imposed rotation is defined on one end of the spring element to model rotation (displacement +/- rd) with constant velocity of 10. rd/s (with abscissa scale factor 1.0) or 20. rd/s (with abscissa scale factor 0.5). The displacement Y and Z at this end of the spring are fixed to avoid shear deformation and see only bending.
The other end of the spring element is clamped.
Results
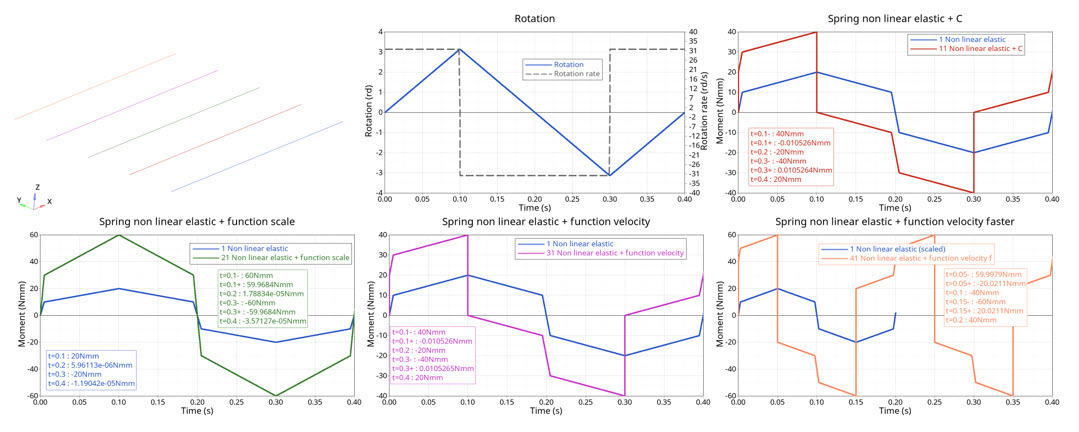
Figure 6. moment versus time
| Time | Nonlinear Elastic | Nonlinear Elastic + C | Nonlinear Elastic + Rotational Velocity-based Force Function Scale | Nonlinear Elastic + Rotational Velocity-based Damping Function (200 mm/s) | Nonlinear Elastic + Velocity-based Damping Function (400 mm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t=0.1s (V+) | 20 | 40 | 60 | 40 | 60 |
| t=0.1s (V-) | 20 | 0 | 60 | 0 | -20 |
| t=0.2s (V-) | 0 | -20 | 0 | -20 | -40 |
| t=0.3s (V-) | -20 | -40 | 60 | -40 | -60 |
| t=0.3s (V+) | -20 | 0 | 60 | 0 | 20 |
| t=0.4s (V+) | 0 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 40 |
Conclusion
The Radioss computations returns results very close to the theoretical values with the expected behavior for the elastic or plastic behavior.
The different options to model the translation or rotation rate effect returns the expected results