OS-HM-T: 7000 Dynamic Condensation and Residual Analysis using Component Mode Synthesis (CMS) Method
Tutorial Level: Advanced This tutorial demonstrates analysis of reduced structure by the implementation of superelements using Component Mode Synthesis (CMS) method of an airframe section in OptiStruct.
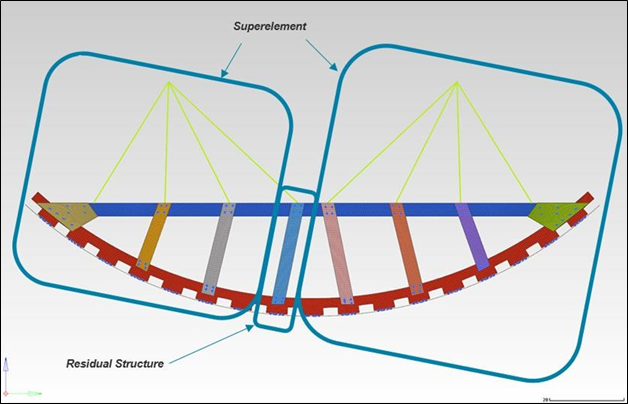
A superelement is a reduced representation of the behavior and performance of a structure or a part of a structure. System equations using these matrices are solved to simulate the structure's behavior. This is referred to as Direct Matrix Input or Superelements. The part of the full model that remains after the superelement has been created is the Residual structure. The reduced loading, mass, stiffness, and damping matrices can be generated using multiple methods. The full model is carefully examined to determine the sections or parts that can be reduced out as superelements. The boundaries between the superelements and the residual structure are identified using connection/interface points. After the identification of interface points, the rest of the structure (residual) is now deleted from the full model. Depending on the superelement creation method selected, the corresponding entries are added (CMSMETH).
- Superelement Generation
- Create ASET boundary constraints
- Delete residual structure
- Request DMIG output
- Residual (Dynamic Condensation)
- Delete superelement
- Create cards to reference DMIG matrices