Nodal Averaging or Aggregation of Elemental Results
- Simple averaging will be referred to as “compute then average”.
- Advanced averaging will be referred to as “average then compute”.
- Averaging mode will be referred to as “Aggregation mode”.
- Averaging across components will be referred to as “Aggregation across components”.
Nodal averaging of elemental results at a node refers to the average of all the element corner results passing through that node.
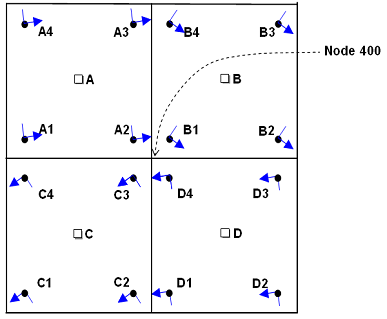
If no corner results are available for an element, centroidal results will be used calculate the nodal average. In the example figure below, four elements are passing through Node 400. The average results at Node 400 is equal to:
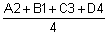 - when Use corner data is turned on.
- when Use corner data is turned on.
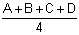 - when Use corner data is turned off.
- when Use corner data is turned off.
- Simple (also known as “compute then average” in the HyperView - MultiCore profile)
- Advanced (also known as “average then compute” in the HyperView - MultiCore profile)
- Difference
- Max of Corner
- Min of Corner
- Extreme of Corner
These methods aggregate the maximum, minimum, or extreme values of all corner values and assign that to the centroid of the element. For example, when using the Max of Corner averaging method on element A: the maximum of A1, A2, A3, A4 is assigned to the element centroid.
- Maximum
- Minimum
In the example figure above, four elements are passing through Node 400. The maximum results at Node 400 is equal to:
max (A2, B1, C3, D4) - when Use corner data is turned on.
max (A, B, C, D) - when Use corner data is turned off.max with min in order to compute the minimum results
at Node 400 (based on the example figure above).