ACU-T: 2300 Atmospheric Boundary Layer Problem – Flow Over Building
Tutorial Level: Intermediate
Prerequisites
Prior to starting this tutorial, you should have already run through the introductory tutorial, ACU-T: 1000 UI Introduction
- ACU-T2300_Building.hm
Since the HyperMesh CFD database (.hm file) contains meshed geometry, this tutorial does not include steps related to geometry import and mesh generation.
Problem Description
The problem to be addressed in this tutorial is shown schematically in Figure 1. As an example, this problem shows the capability of Atmospheric Boundary Layer modelling in AcuSolve.
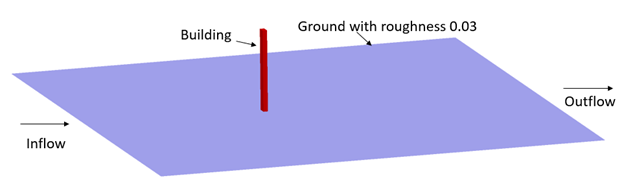
In this tutorial, you will simulate the air flow over a building with a ground roughness of 0.03 m. In this case, User Defined Atmospheric Roughness Type is considered.
Start HyperMesh CFD and Open the HyperMesh Database
- Start HyperMesh CFD from the Windows Start menu by clicking .
-
From the Home tools, Files tool group, click the Open Model tool.
Figure 2. 
The Open File dialog opens. - Browse to the directory where you saved the model file. Select the HyperMesh file ACU-T2300_Building.hm and click Open.
- Click .
-
Create a new directory named Building_ABL and navigate into this directory.
This will be the working directory and all the files related to the simulation will be stored in this location.
- Enter Building as the file name for the database, or choose any name of your preference.
- Click Save to create the database.
Validate the Geometry
The Validate tool scans through the entire model, performs checks on the surfaces and solids, and flags any defects in the geometry, such as free edges, closed shells, intersections, duplicates, and slivers.

Set Up Flow
Set Up the Simulation Parameters and Solver Settings
-
From the Flow ribbon, click the Physics tool.
Figure 4. 
The Setup dialog opens. -
Under the Physics models setting:
Figure 5. 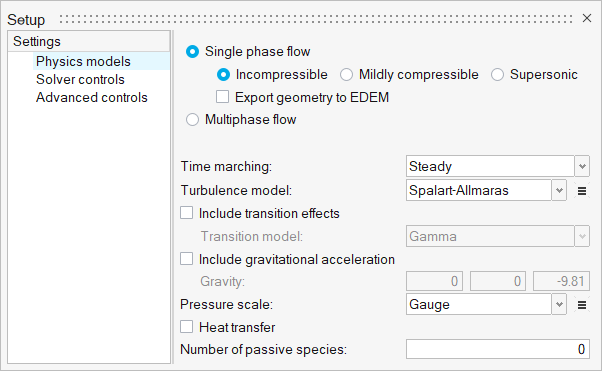
- Click the Solver controls setting.
-
Set the Steady update factor to 0.6 and the Steady
maximum steps to 20.
Figure 6. 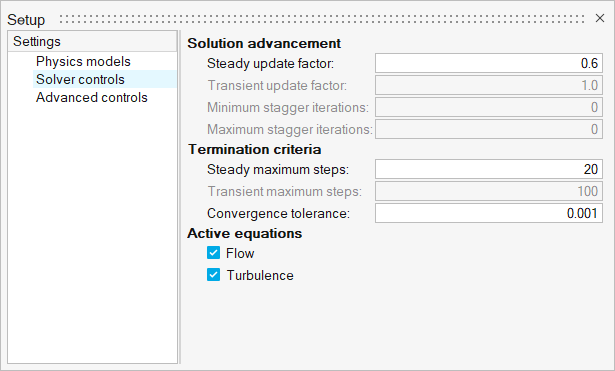
Assign Material Properties
-
From the Flow ribbon, click the Material tool.
Figure 7. 
- Select the solid.
- Select the Air material in the microdialog.
-
Click
 on the guide bar.
on the guide bar.
Define Flow Boundary Conditions
-
From the Flow ribbon, click the
Atmospheric tool.
Figure 8. 
-
Click the inlet face highlighted in the figure below.
Figure 9. 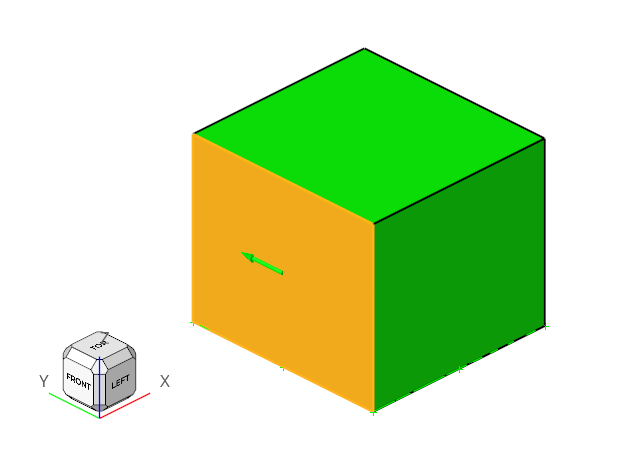
- In the microdialog, select User Value for the Ground roughness type.
-
Set the Friction Velocity to 0.106 m/s.
The atmospheric boundary layer inflow should have a roughness of 0.001 m if the standard turbulence wall function has a roughness of 0.03 m on the ground because the relationship between inflow roughness and standard wall roughness has an empirical ratio of 30.
-
Click the Move tool icon
 .
.
Figure 10. 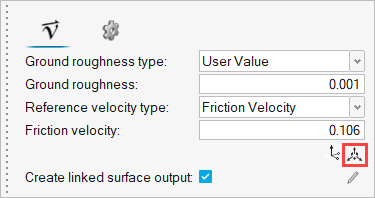
-
Select the z rotation arrow, set it to
-90 degrees, and then press Enter.
Figure 11. 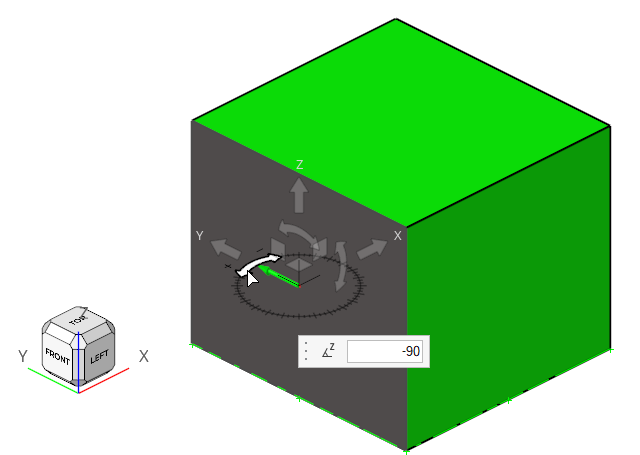
-
Verify the atmospheric flow direction (y) is aligned to the global coordinate
X.
Figure 12. 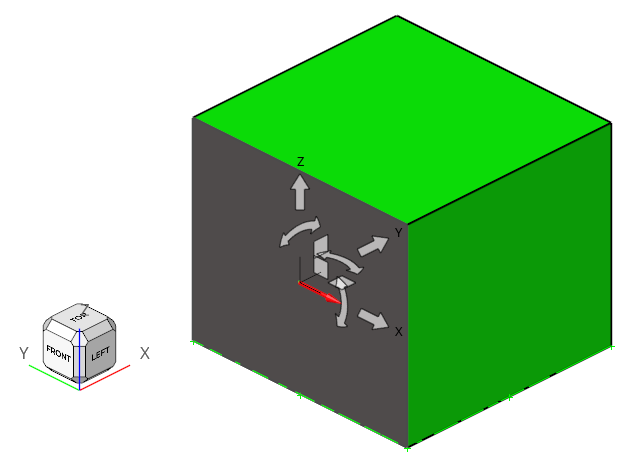
-
Select the y rotation arrow, set it to
-90 degrees, and then press Enter.
Figure 13. 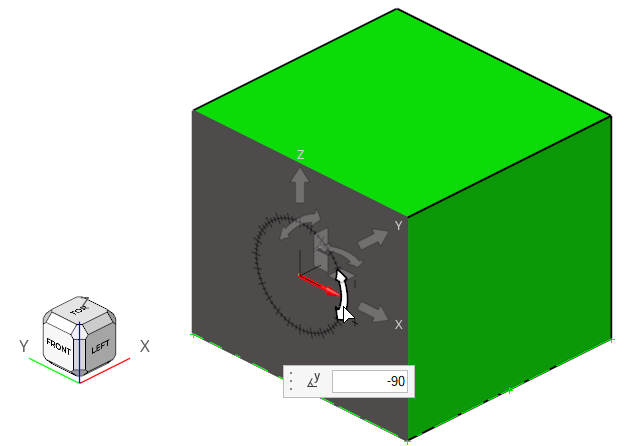
-
Verify the ground normal direction (x) align to the global coordinate Z.
Figure 14. 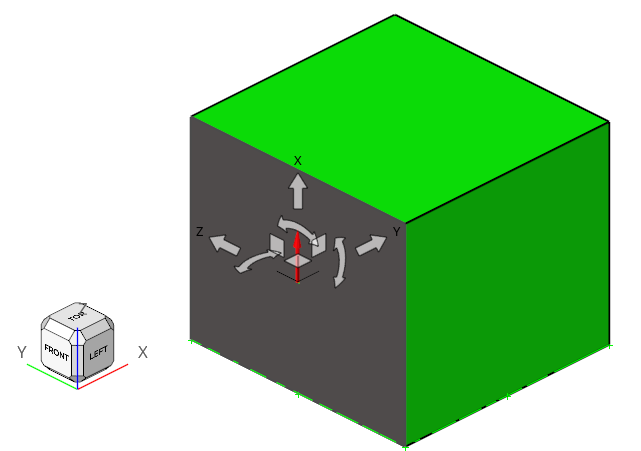
-
Click the origin of the coordinate (marked by the arrow), set the atmospheric
ground origin to (0, 0, 0), and press Enter.
Figure 15. 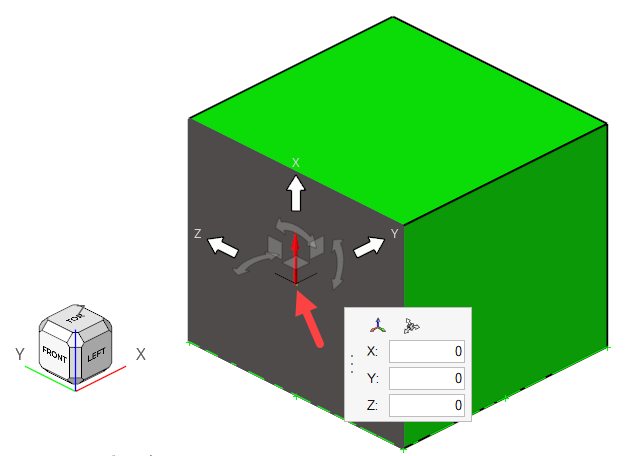
- Press Esc to return from the Move tool.
-
On the guide bar, click
 to execute
the command and exit the tool.
to execute
the command and exit the tool.
-
Click the Outlet tool.
Figure 16. 
-
Select the face highlighted in the figure below, verify that both the static
pressure (Pa) and the pressure loss factor are 0 in the
microdialog, and then click
 on the
guide bar.
on the
guide bar.
Figure 17. 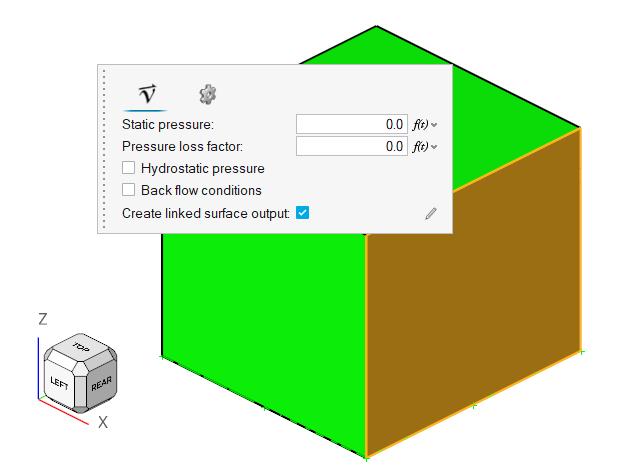
-
Click the Slip tool.
Figure 18. 
- Hide the Atmospheric boundary and the Outlet using the Boundaries legend.
-
Select the top surface and the two sides as shown in the figure below then
click
 on the guide bar.
on the guide bar.
Figure 19. 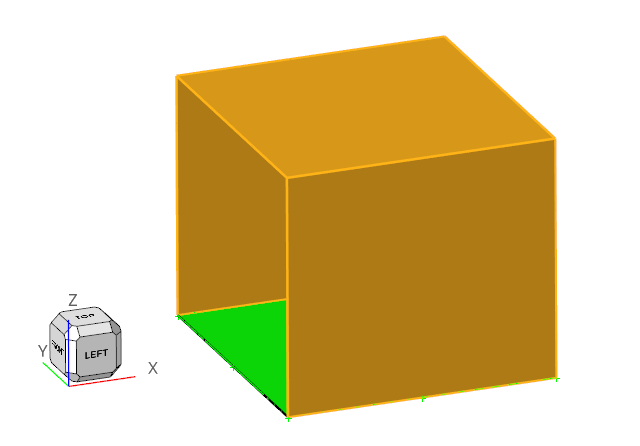
-
Click the No Slip tool.
Figure 20. 
- Hide the Slip surfaces using the Boundaries legend.
- Select the bottom surface as shown in the figure below.
-
Set the Roughness height to 0.03 m.
Figure 21. 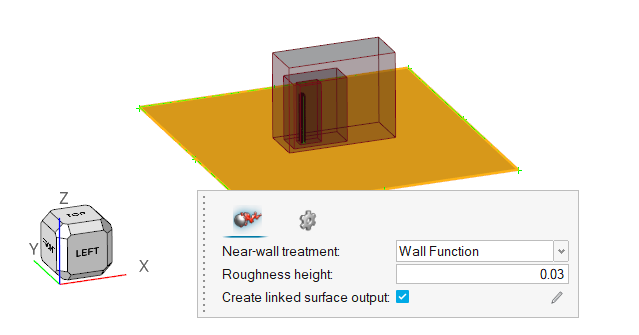
-
On the guide bar, click
 to execute
the command and exit the tool.
to execute
the command and exit the tool.
Run AcuSolve
-
From the Solution ribbon, click the Run tool.
Figure 22. 
- Set the Parallel processing option to Intel MPI.
- Optional: Set the number of processors to 4 or 8 based on availability.
- Uncheck the Automatically define pressure reference option.
- Expand Default initial conditions and uncheck the Pre-compute flow and Pre-compute turbulence options.
- Set all the velocity components to 0 m/s and the eddy viscosity to 0.0001 m2/s.
-
Leave the remaining options as default and click
Run to launch AcuSolve.
Figure 23. 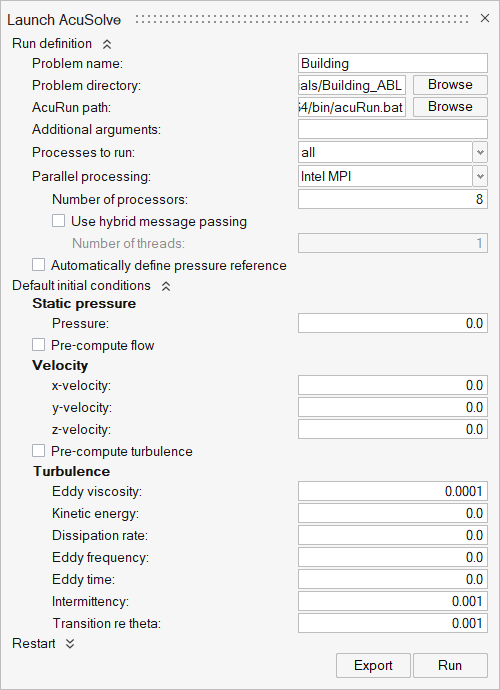
The Run Status dialog opens. Once the run is complete, the status is updated and you can close the dialog.Tip: While AcuSolve is running, right-click the AcuSolve job in the Run Status dialog and select View Log File to monitor the solution process.
Post-Process the Results with HM-CFD Post
- Once the solution is completed, navigate to the Post ribbon.
- From the menu bar, click .
-
Select the AcuSolve
.log file in your problem
directory to load the results for post-processing.
The solid and all the surfaces are loaded in the Post Browser.
-
Click the Slice Planes tool.
Figure 24. 
-
Select the slice plane shown below.
Figure 25. 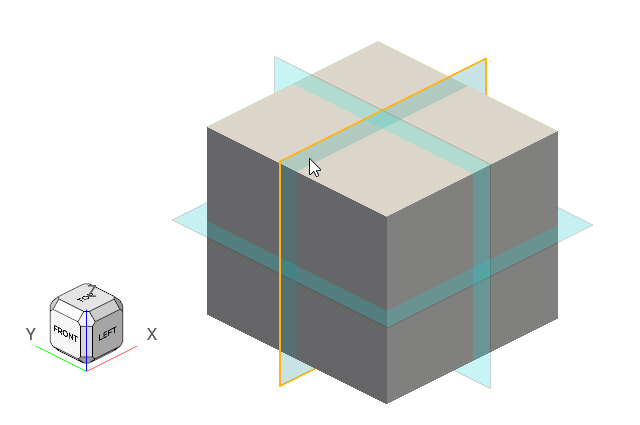
-
In the slice plane microdialog, click
 to
create the slice plane.
to
create the slice plane.
- In the display properties microdialog, set the display to velocity and activate the Legend toggle.
-
Click
 and set the Colormap name to Rainbow
Uniform.
and set the Colormap name to Rainbow
Uniform.
Figure 26. 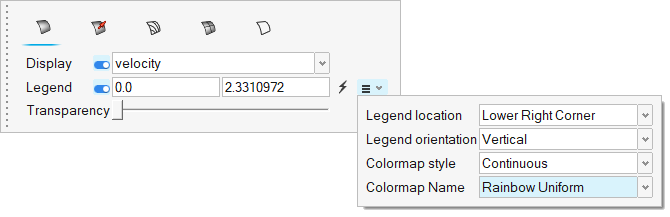
- Isolate Slice Plane 1.
- Click the Left face on the View Cube to orient the slice plane.
-
Click
 on the guide bar to show the velocity (m/s)
contours.
on the guide bar to show the velocity (m/s)
contours.
Figure 27. 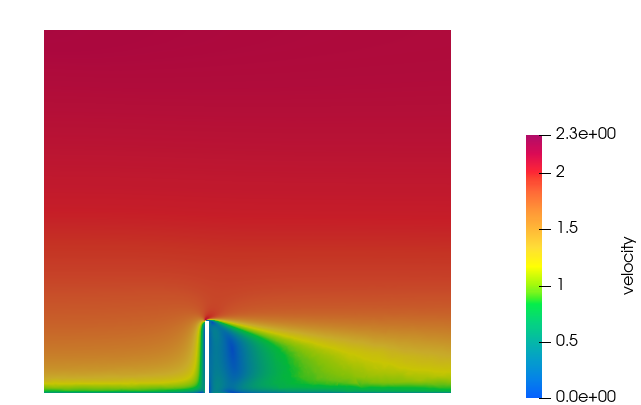
Summary
In this tutorial, you successfully learned how to set up and solve a simulation involving an atmospheric boundary condition using HyperMesh CFD. You started by opening the HyperMesh CFD input file with the geometry and then defined the simulation parameters, fluid material, and boundary conditions. Once the solution was computed, you visualized the results of the velocity magnitude on a plane.