Optimization
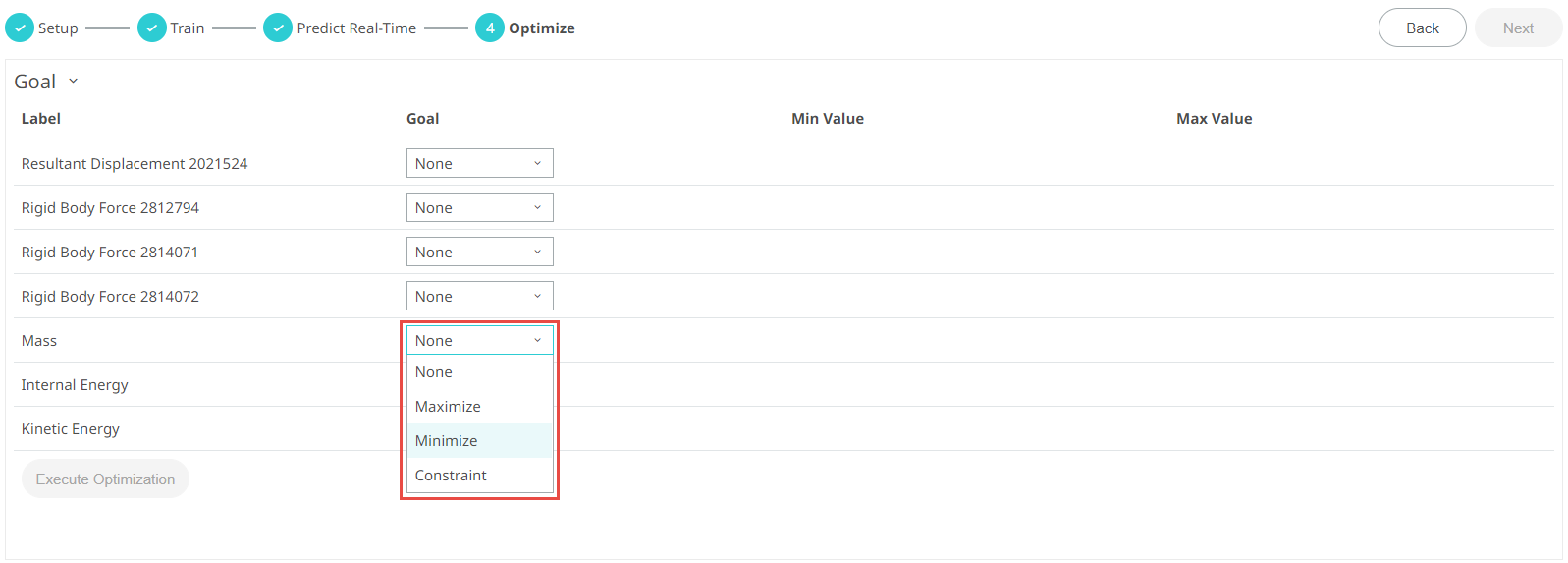
Perform an optimization by updating the input value goals and setting the minimum and maximum values.
An Optimization is a mathematical procedure used to determine the best design for a set of given constraints, by changing the input variables in an automatic manner.
Typically, Optimization can be used to reduce product weight, improve performance, and meet design targets.
Input variables, objectives and constraints need to be defined in order to formulate a design problem as an optimization problem. There can be a single or multiple objectives. Furthermore, problems can be either deterministic or probabilistic, where the objective is to meet a certain reliability and robustness target.
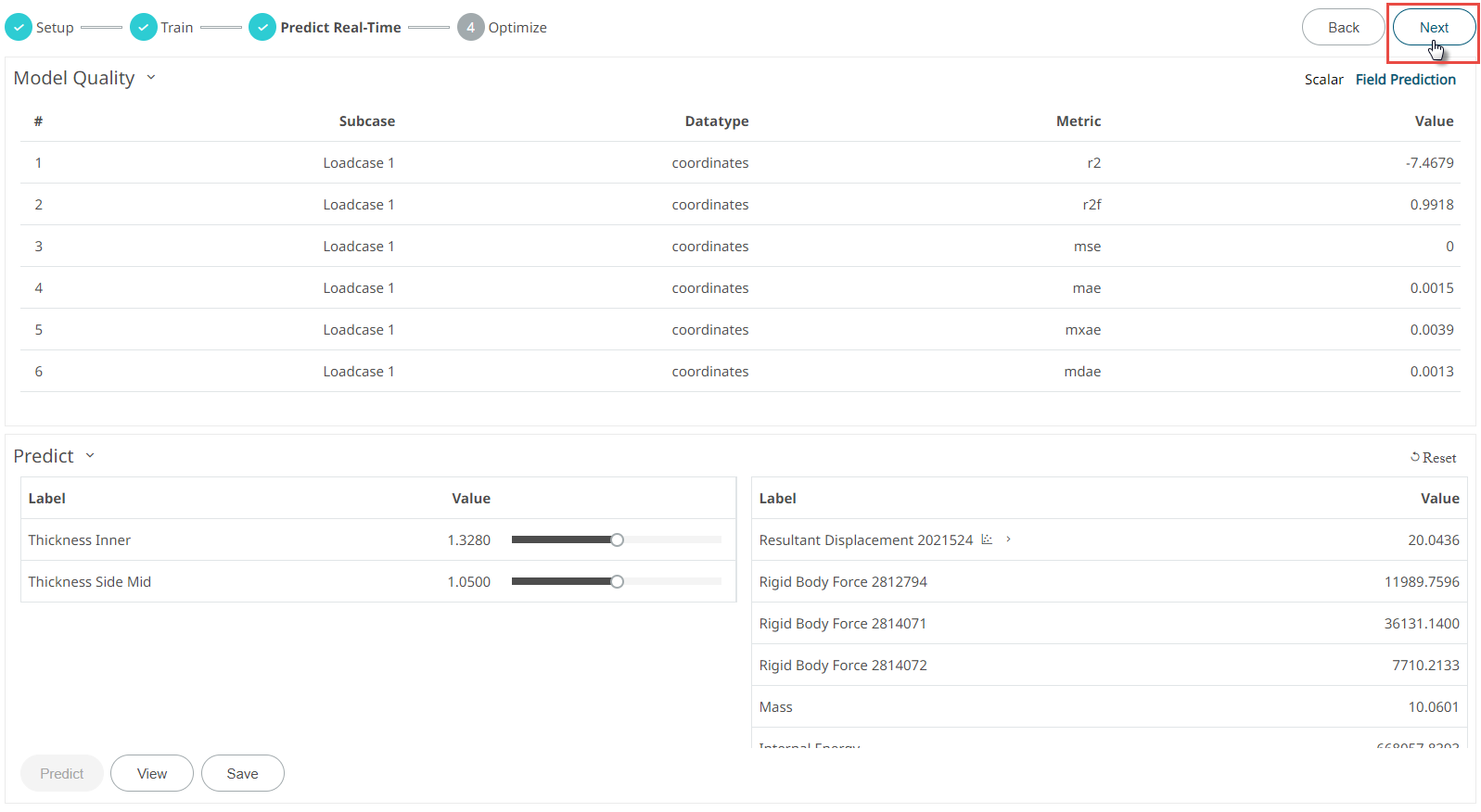
Optimization uses the predicted model values. In Predict Real-Time, you set the design variables to get the responses. In Optimization, you set the requirements for the responses to get the design variable values that will meet that.
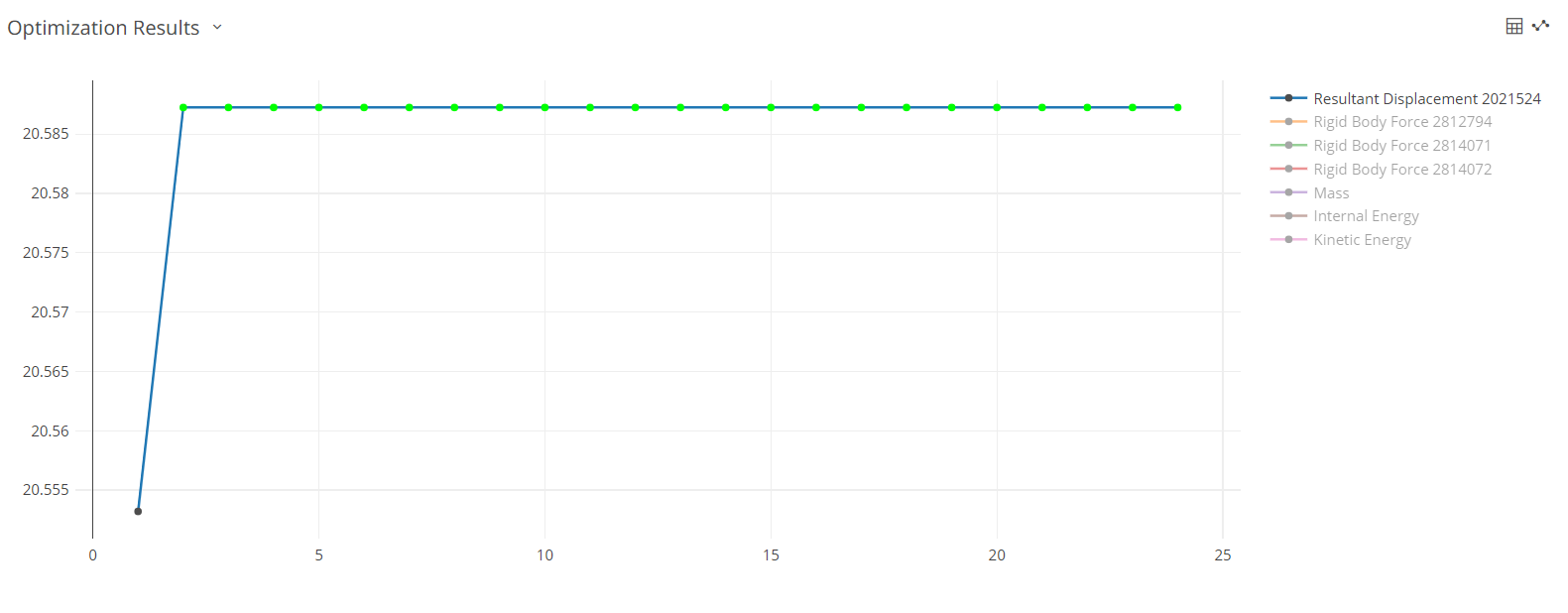
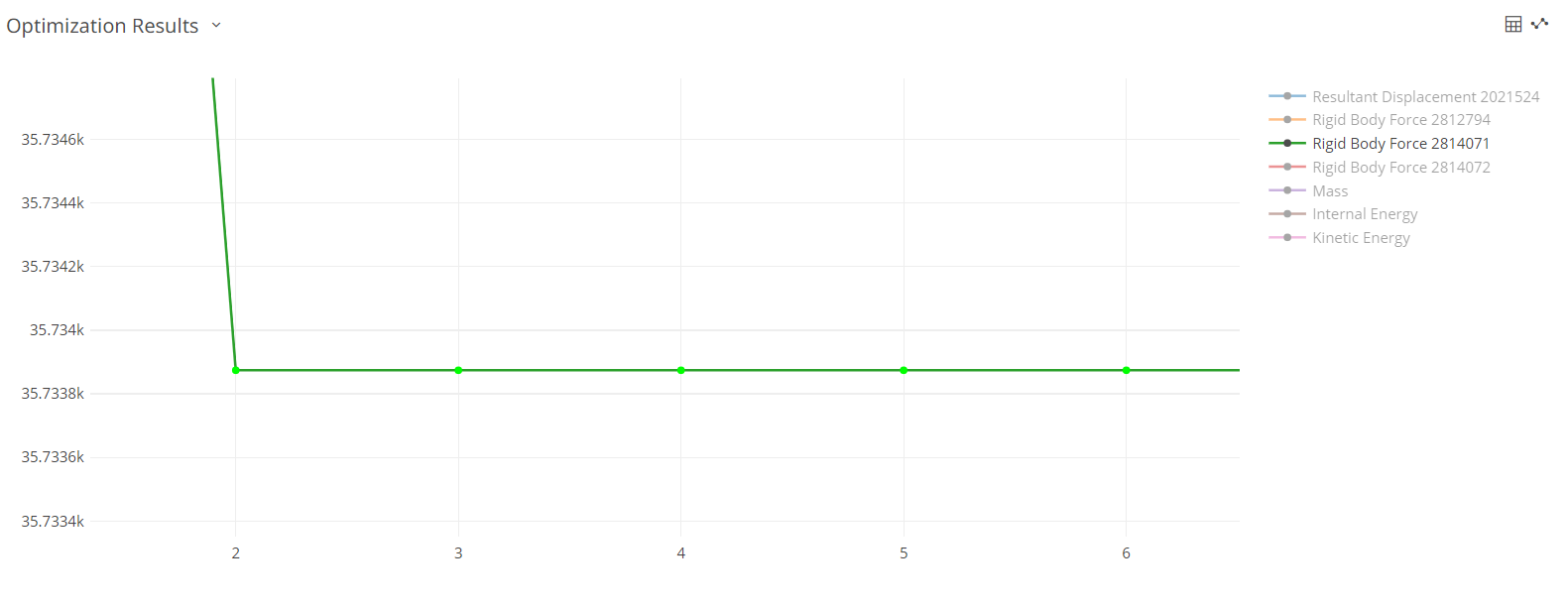
If the optimization does not meet your expectations, then change the requirements of the response and run the optimization to get the optimal values.
- Optimum - The point or design that minimized (maximized) the objective function and at the same time satisfy all the constraints.
- Violated - Constraint that is not satisfied.
- Active - Constraint that is satisfied exactly; equality constraints are active for feasible designs.
- Inactive - Constraint that satisfied but not on the bound.
- Feasible - A point or a design that satisfies all the constraints.
- Infeasible - A design that violates one or more constraints.