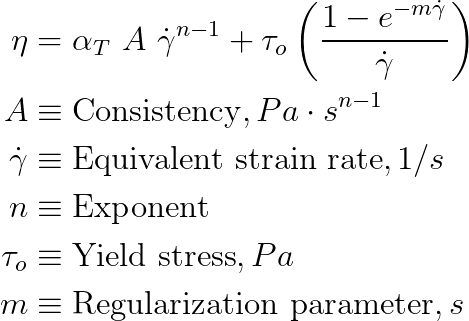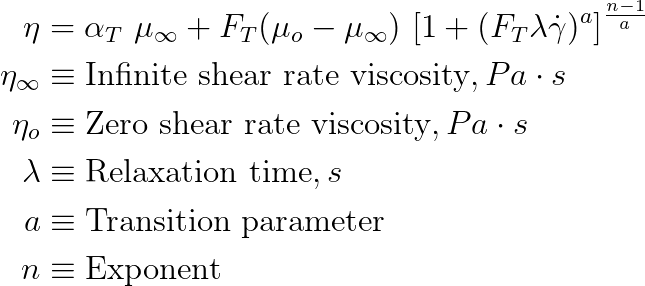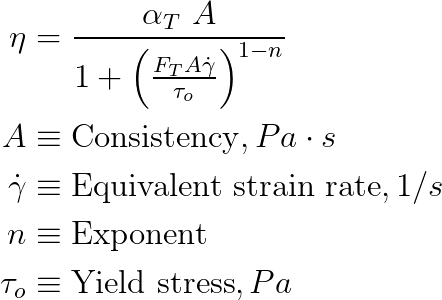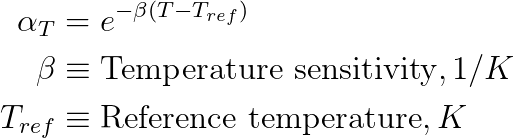Material Properties
View and edit thermal, rheological, mechanical, and PVT properties for materials.
Materials Database
Use the Materials Database tab on the Materials dialog to view the material properties of any material in Inspire Mold. Click Edit to modify a material's properties and save a custom version of the material on the My Materials tab. You can also Import and Export materials to and from the database.
To view a material's properties, select the Material Group and Name at the top of the Materials dialog:
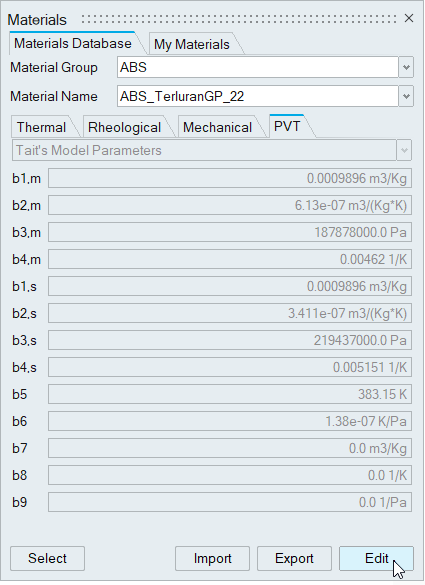
| Material Property | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Material Group | Lists the materials available in the Materials Database. | |
| Material Name | Lists the common polymers available for the specified material group. | |
Description of Material Data
The injection molding solver requires the material properties of the polymer, mold, mold insert, part insert, and fiber to be specified.
- Physical and thermal properties
- Equation of State - PVT data
- Rheological (constitutive) properties
- Mechanical properties
- Additive data
- Physical and thermal properties
- Mechanical properties
Data Format and Units
- The current version of the solver expects the material data in .json format,
- All parameters are input in SI units
Polymer Data
It is assumed that the polymer data is measured with its fillers and other additives.
Physical and Thermal Properties
Each property can be specified as a scalar when considering variations due to temperature changes. Review the properties on the Thermal tab for the specified material:
| Material Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Specific Heat | Specifies the heat energy required to increase the temperature of a unit
quantity J/(Kg-K). Specific heat of the polymer
can be specified as a scalar value or as a function of temperature in the form of a
table. Solver keyword: SPECIFIC_HEAT |
| Conductivity (Thermal Conductivity) | Specifies the heat conductivity of the material
(W/m-K). Thermal conductivity of the polymer
can be specified as a scalar value or as a function of temperature in the form of a
table. Solver keyword: CONDUCTIVITY |
| Density | Specifies the density of the polymer melt at the reference temperature in
(kg/m3). Melt density is assumed
to remain constant during the filling phase. During packing simulation, Tait 2-phase
model for the equation of state is used to compute polymer density. Solver keyword: DENSITY |
Rhealogical Properties
The solver models the rheology of the polymer using generalized Newtonian models. Models currently available in the solver compute viscosity as a function of effective shear rate and temperature. All the constitutive models are set by defining an appropriate combination of : a) an empirical model relating viscosity with shear rate and b) the temperature dependence. Temperature dependence is denoted using the symbol αT.
Review the properties on the Rhealogical tab for the specified material:
| Material Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Constitutive Model | Five models are included in the Materials Database. Select the model
appropriate for your material choice. Review the Exponent, Consistency and Relative
Shear Stress for your chosen model.
|
| Temperature Dependence | Temperature dependency of the viscosity can be modeled through one of the
following ways. The chosen model is specified with the temperature dependence
parameter, which is set with an integer value from 0 to 3:
|
| Miscellaneous | Review these parameters:
|
| Fiber Info | Inlet fiber distribution is assumed to be random. Review the fiber content for
the specified material including:
Note: Some materials do not include fiber orientation data. To add this data,
edit an existing material and save it as a new material in the My Materials
tab. |
Mechanical Properties
The solver uses Young's modulus, Poisson's ratio, and the thermal expansion coefficient to perform warpage calculations of the solidified part. Review the properties on the Mechanical tab for the specified material:
| Material Property-Isotropic Model | Description |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus | Young's modulus of a material is a measure of the resistance of the material to deformation when subjected to stress. It is a measure of stiffness of the material. Units: Pa Solver keyword: YOUNG_MODULUS. |
| Poisson Ratio | Poisson's ratio is the ratio of lateral and longitudinal strain when subjected to uniaxial stress. Solver keyword: POISSON_RATIO |
| Yield Stress |
Specifies the stress point at which the material deformation changes from elastic to plastic. Units: Pa |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion |
The thermal expansion coefficient describes the extent of changes in the size of the object due to variation in temperature: Units: 1/K Solver keyword: COEFFICIENT_THERMAL_EXPANSION |
Equation of State - PVT Data
The pressure-volume-temperature (PVT) relationship is modeled using Tait's two-phase equation of state. The PVT behavior of the polymer in both solid and melt state is described using 14 parameters. These parameters are indicated with letter b and with a numerical subscript (1-9) and a letter subscript (m=melt, s=solid). The following equations describe the equation of state and its parameters.

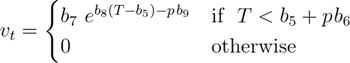
Parameters b5 to b9 are identical for both melt and solid. They are repeated for simplicity of the data file and structure of the code.
TAIT_PARAMETERS_MOLTEN_STATE = [b1m , b2m, b3m, b4m, b5, b6, b7, b8, b9]
TAIT_PARAMETERS_SOLID_STATE = [b1s, b2s, b3s, b4s, b5, b6, b7, b8, b9]
Database keywords: TAIT_PARAMETERS_MOLTEN_STATE, TAIT_PARAMETERS_SOLID_STATEProcessing Data
- Valid for semi-crystalline materials
- The temperature at which the crystalline structures melt
- The solver does not use this. Will become useful when we implement crystallization kinetics
- Solver keyword: MELTING_TEMPERATURE
- The temperature at which material ceases to flow
- It is greater than Glass Transition Temperature
- Solver keyword: NO_FLOW_TEMPERATURE
- The temperature at which the part can be safely ejected
- Solver keyword: EJECTION_TEMPERATURE
- Recommended minimum mold temperature
- Solver keyword: MINIMUM_MOLD_TEMPERATURE
- Recommended maximum mold temperature
- Solver keyword: MAXIMUM_MOLD_TEMPERATURE
- Recommended minimum melt temperature
- Solver keyword: MINIMUM_MELT_TEMPERATURE
- Recommended maximum melt temperature
- Solver keyword: MAXIMUM_MELT_TEMPERATURE
- The absolute maximum allowed for the melt temperature at the inlet
- Solver keyword: ABSOLUTE_MAXIMUM_MELT_TEMPERATURE
Mold / Mold Insert / Part Insert Data
Reference Temperature:- Reference Temperature at which the data is measured. Units: K
-
Solver keyword: REFERENCE_TEMPERATURE
- Density of the material at reference temperature. Solver will also support a temperature dependent table in the place of a single value at the reference temperature. Units: kg/m3
- Solver keyword: DENSITY
- Specific heat of the material at reference temperature. Solver will also support a temperature dependent table in the place of a single value at the reference temperature. Units: J/(kg-K)
- Solver keyword: SPECIFIC_HEAT
- Thermal conductivity of the material at reference temperature. Solver will also support a temperature dependent table in the place of a single value at the reference temperature. Units: W/(m-K)
- Solver keyword: CONDUCTIVITY
- Young's modulus of the material. Units: Pa
- Solver keyword: YOUNG_MODULUS
- Poisson's ratio of the material.
- Solver keyword: POISSON_RATIO
- The thermal expansion coefficient of the material. Units: 1/K
- Solver keyword: COEFFICIENT_THERMAL_EXPANSION
Fiber Material data - For Stress Analysis of the Molded Part
This data is independent of the polymer or the percentage of weight in the mix. This is the basic fiber material data.
- Reference Temperature at which the data is measured. Ideally it should be temperature at which the test is performed. Units: K
-
Solver keyword: REFERENCE_TEMPERARTURE
- Density of the fiber at reference temperature. Solver will also support a temperature dependent table in the place of a single value at the reference temperature. Units: kg/m3
- Solver keyword: DENSITY
- Specific heat of the fiber at reference temperature. Solver will also support a temperature dependent table in the place of a single value at the reference temperature. Units: J/(kg-K)
- Solver keyword: SPECIFIC_HEAT
- Thermal conductivity of the fiber at reference temperature. Solver will also support a temperature dependent table in the place of a single value at the reference temperature. Units: W/(m-K)
- Solver keyword: CONDUCTIVITY
- Young's modulus of the fiber. Units: Pa
- Solver keyword: YOUNG_MODULUS
- Poisson's ratio of the fiber.
- Solver keyword: POISSON_RATIO
- The thermal expansion coefficient of the fiber. Units: 1/K
- Solver keyword: COEFFICIENT_THERMAL_EXPANSION
Base Polymer Data For Stress Analysis of the Molded Part
- Reference Temperature at which the data is measured. Units: K
- Solver keyword: REFERENCE_TEMPERATURE
- Density of the material at reference temperature. Solver will also support a temperature dependent table in the place of a single value at the reference temperature. Units: kg/m3
- Solver keyword: DENSITY
- Specific heat of the material at reference temperature. Solver will also support a temperature dependent table in the place of a single value at the reference temperature. Units: J/(kg-K)
- Solver keyword: SPECIFIC_HEAT
- Thermal conductivity of the material at reference temperature. Solver will also support a temperature dependent table in the place of a single value at the reference temperature. Units: W/(m-K)
- Solver keyword: CONDUCTIVITY
- Young's modulus of the material. Units: Pa
- Solver keyword: YOUNG_MODULUS
- Poisson's ratio of the material.
- Solver keyword: POISSON_RATIO
- The thermal expansion coefficient of the material. Units: 1/K
- Solver keyword: COEFFICIENT_THERMAL_EXPANSION
Unit Summary
| Data | Unit |
|---|---|
| Density | kg/m3 |
| Specific Heat | J/(kg-K) |
| Conductivity | W/(m-K) |
| Yield Stress | Pa |
| Young Modulus | Pa |
| Poisson Ratio | - |
| Coefficient Thermal Expansion | 1/K |
| Reference Temperature | K |
| Minimum Mold Temperature | K |
| Maximum Mold Temperature | K |
| Minimum Melt Temperature | K |
| Maximum Melt Temperature | K |
| Glass Transition Temperature | K |
| No Flow Temperature | K |
| Ejection Temperature | K |
| Viscosity model: | |
| Modified Cross: | - |
| Consistency | Pa.s |
| Exponent | - |
| Reference Shear stress (tau) | Pa |
| Zero Shear Viscosity | Pa.s |
| Infinite Shear Viscosity | Pa.s |
| Min Strainrate Limit | 1/s |
| Max Strainrate Limit | 1/s |
| Temperature Dependence: | |
| WLF: | |
| Constant C1 | - |
| Constant C2 | K |
| Pressure Dependency D3 | K/Pa |
|
Tait Parameters:
|
|
| Filler Data: | |
| Fiber Percentage | Percentage of fiber in the melt by weight |
| Fiber Minimum Length | m |
| Fiber Maximum Length | m |
| Fiber Average Diameter | m |