Constraints Between Optimisation Parameters
A dynamic boundary is defined for an optimisation parameter by specifying a constraint.
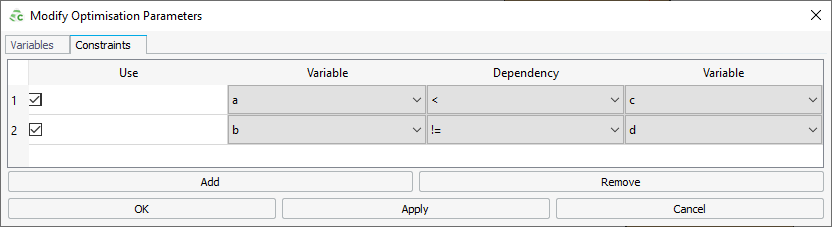
A constraint is defined by specifying two parameters and their dependency on one another, see Figure 1. The following dependencies are available: !=, <, <=, > and >=.
Parameter and Constraint Deactivation
For each parameter in the parameter list or constraint in the parameter constraints
list, a Use check-box is used to include or exclude each
specific parameter or constraint in the optimisation search process. If the
Use check box for a specific parameter or constraint is
not selected then that parameter or constraint is excluded in the .opt or .pfg files and does not influence the
optimisation search. If a parameter is deactivated, the value of the variable as
specified in the CADFEKO variables list is used as if
it is not defined as an optimisation parameter.
Note: All parameter and constraint
settings are local to each search. Deactivating a specific parameter or
constraint in the parameter settings of one search does not deactivate that
parameter or constraint in any other search.