Material Parameters
Define the color, reflectivity, roughness, transparency, and more.
- Color
- To define the color, choose from the following
options:
- Select a color.
- Select a texture. The texture overrides the color.
- To blend the color with the texture, click the plus symbol (+). You can tell if the blend option is turned on by looking at the image preview.
To define the shade, enter a value of 0-100, where 100 is the true color and 0 is black.
- Reflectivity
- Define the strength of the reflections.
Enter a value of 0-100, where 100 produces perfect mirror reflections and 0 produces the weakest reflections.
- Roughness
- Roughness adds texture to the material at a microscopic level. When you
modify the roughness, the surface texture still looks the same; however,
tiny changes invisible to the naked eye have occurred, affecting
reflectivity.
0 can produce a perfect mirror reflection.
Lower values produce crisper and brighter reflections.
Higher values produce blurrier, dimmer reflections. Increasing the roughness spreads and distributes reflections over the surface and creates a more matte surface.
At values approaching 100, light becomes so scattered that reflections are barely visible, if at all.
- Transparency
- Define the level of the material transparency. 100 = completely transparent, 0 = fully opaque.
- Bump
- Bump adds texture to the material at a macroscopic level. Because it visibly
affects the surface texture, Bump is useful for simulating irregular
surfaces.A bump map gives the illusion of texture without physically distorting the geometry, minimizing rendering time. The grayscale map tells Inspire Studio how to change the surface normals as if the surface had been displaced; the modified normals are used in lighting calculations. A bump map looks like the inverse of what you might expect: black represents the highest extreme and white represents the flattest extreme, while shades of gray represent grades in between.

- Coating
- Create varnishes and paints on a layered material.
The coating will reflect some light, while the rest of the light will be absorbed by the layer of material underneath; the extent to which this happens affects how the final material looks.
Several coatings may be applied one after the other, simulating multiple varnishes and paints.
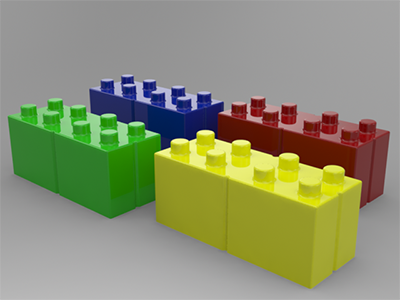
Figure 1. Plastic without a Coating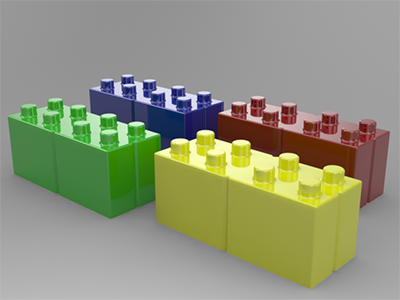 Figure 2. Plastic with a Coating
Figure 2. Plastic with a Coating - Scratches
- Add scratches to a material.
- Wear
- Add wear to a material.
- Trimming
- Add cut-out patterns to a material.
- Texture
- Select or upload a texture to apply to the object.
- Anisotropy
- Stretch and blur highlights. Anisotropic reflections are like regular reflections, except they are stretched and blurred against the grain of the material. They are often used to simulate finely brushed metals.
- Brushed
- Add a brushed finish to a material.
- Glow Color
- Define the color of the glow.
- Glow Intensity
- Define the intensity of the glow. Increase this value for a brighter glow; decrease it for a softer glow.