Frequency Response Process
Setup a frequency response analysis with a series of step-by-step process templates.
These process templates prompt you to enter generic engineering data, and once the data is available, automatically create frequency response analysis loadcases and associated solver cards. The templates share a set of common process steps that are only described the first time they are used.
- This tool is also available in HyperMesh NVH on the NVH Tools ribbon.
- Click the arrow next to the tool to select one of the step-by-step process templates.
Setup a Normal Model Process
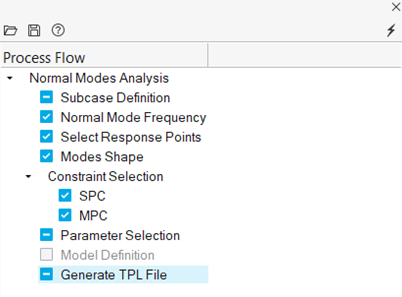
-
From the Analyze or NVH Tools ribbon, click the Normal
modes tool.
Figure 3. 
A normal modes analysis process template is loaded and opens in the Process Flow browser.
-
In the Subcase Definition task, create a new subcase or edit an existing
subcase.
Figure 4. 
-
In the Normal Mode Frequency task, define Normal Mode Frequency.
Figure 5. 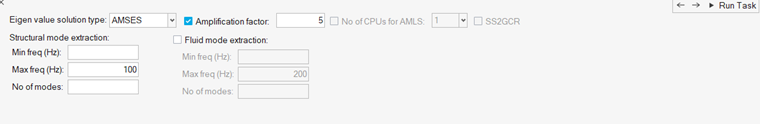
-
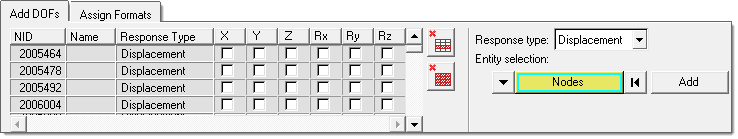
In the Select Response Points task, select response points for output.
Figure 7. 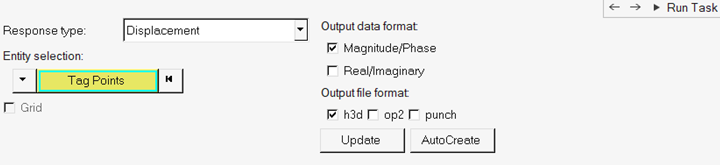
-
In the Constraint selection, SPC task, select the boundary condition of the
frequency response analysis.
- You can select existing SPCs by checking the corresponding box under the Active column, or click Create SPC to go to the Constraints panel and define a new SPC.
- Once the boundary condition has been fully defined, click Run Task to proceed.
-
In the Constraint selection, MPC task, select MPC equations to turn on for the
frequency response analysis.
-
In the Parameter Selection task, select typical solution parameters, such as
title, singular point constraints, and so on.
- Check all boxes under the Active column to activate the desired solution option.
- Once the parameters have been selected, click Run Task and a Process Manager message box pops up informing you that the process has come to an end.
- Click Yes to close the template, or No to review or edit the process steps.
Figure 8. 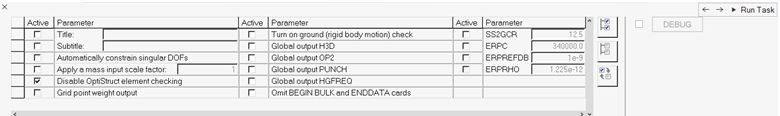
-
In the Generate TPL file task, generate and save the parameters defined in a
standard template file at your selected location.
In the Analysis Manager, the generated template file can be selected as loadcase and solver decks can be exported for normal modes analysis.
Figure 9. 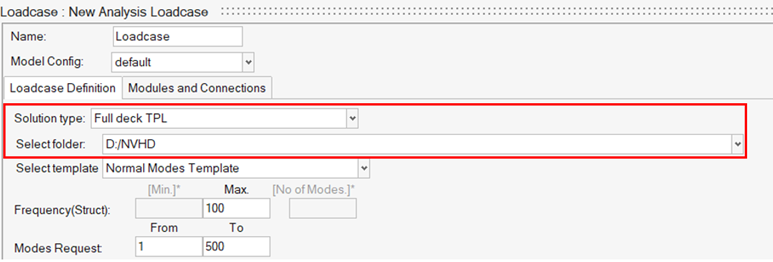
Setup CMS SE Generation Process
The CMS SE Generation process template helps you generate a CMS SuperElement (SE) modal model from a finite element based model.
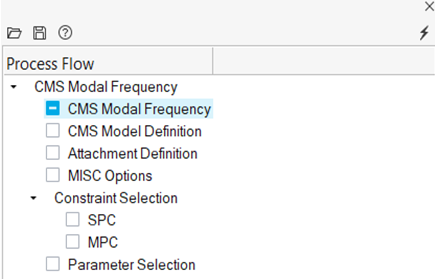
- From the Analyze or NVH Tools ribbon, click the arrow next to the Normal modes tool and select CMS SE.
-
In the CMS Modal Frequency step, define the CMS modal frequency.
Figure 11. 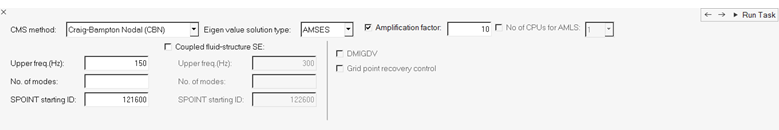
-
In the CMS Modal Definition task, specify what recovery information is to be
stored in the CMS SE.
- Select a set of elements, for which the keyword Plotel is a valid specification, or a set of grids.
- To exclude/include rigid elements from the recovery set, select the Rigid checkbox.
- Once the model recovery set has been defined, click Run Task to proceed.
Figure 12. 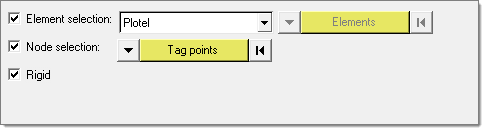
-
In the Attachment Definition task, specify attachment point sets.
- Both fixed and free-free attachments can be specified for a mixed (GM) CMS SE, while only fixed attachments can be specified for a fixed (CBN) CMS SE.
- Once the attachment set has been defined, click Run Task to proceed.
Figure 13. 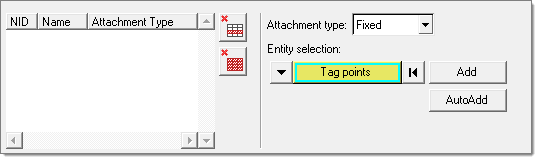
-
In the MISC Options task, specify structural damping and fluid-structure
coupling options.
Figure 14. 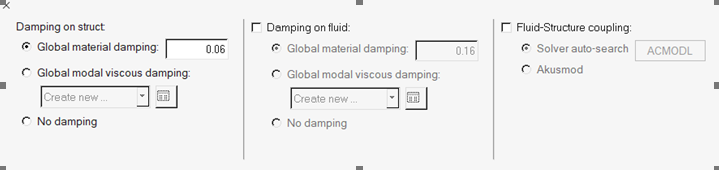
-
In the Parameter Selection task, select typical solution parameters, such as
title, singular point constraints, and so on.
- Check all boxes under the Active column to activate the desired solution option.
- Once the parameters have been selected, click Run Task and an Process Manager message box pops up informing you that the process has come to an end.
- Click Yes to close the template, or No to review or edit the process steps.
Figure 15. 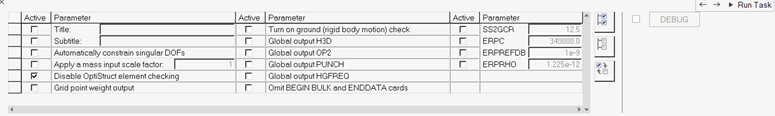
Setup CDS SE Generation Process
Generate a CDS SuperElement (SE) from a finite element based model.
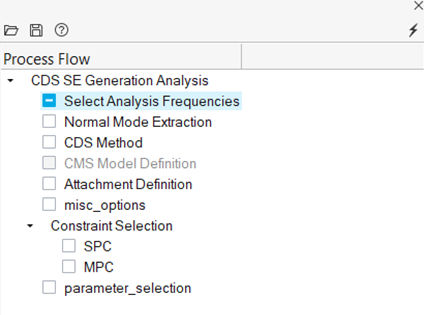
- From the Analyze or NVH Tools ribbon, click the arrow next to the Normal modes tool and select CDS SE.
-
In the Select Analysis Frequencies task, enter the frequencies for which
response solution is needed.
Figure 17. 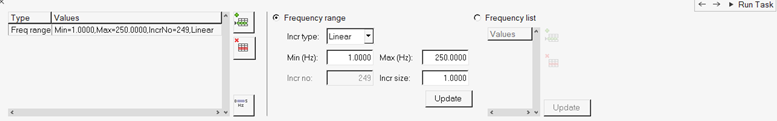
-
In the Normal Mode Extraction task, the default frequencies filled in are based
on the max. frequency you filled in for the previous step.
Figure 18. 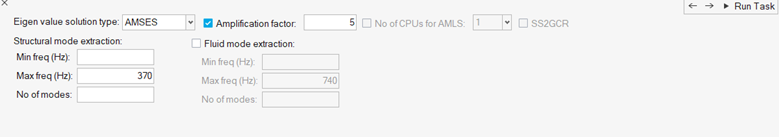
-
In the CDS Method task, define the CDS method.
Figure 19. 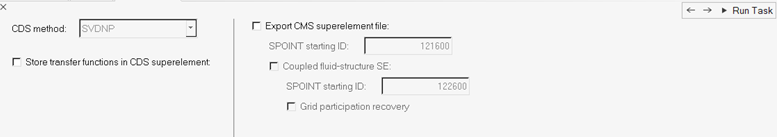
-
In the CMS Model Definition task, specify which
recovery information is to be stored in the CMS SE.
Restriction: This task is only activated when the Export CMS superelement file checkbox is selected.
- Select a set of elements, for which Plotel is a valid specification, or a set of grids.
- To include or exclude rigid elements from the recovery set, select the Rigid checkbox.
- Once the model recovery set has been defined, click Run Task to proceed.
Figure 20. 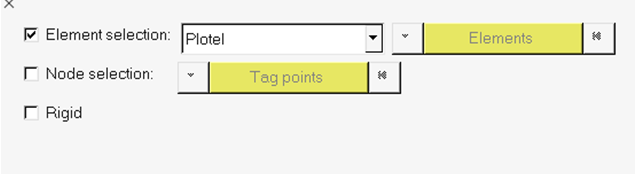
-
In the Attachment Definition task, specify attachment point sets.
- Both fixed and free-free attachments can be specified for a mixed (GM) CMS SE, while only fixed attachments can be specified for a fixed (CBN) CMS SE.
- Once the attachment set has been defined, click Run Task to proceed.
Figure 21. 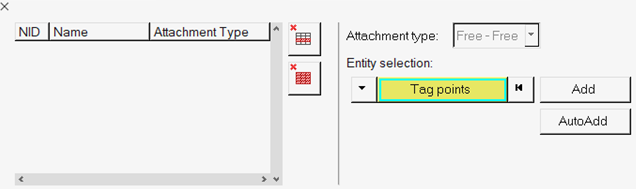
-
In the MISC Options task, specify structural damping and fluid-structure
coupling options.
Figure 22. 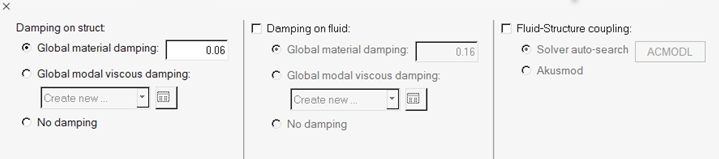
-
In the Parameter Selection task, select typical solution parameters, such as
title, singular point constraints, and so on.
- Check all boxes under the Active column to activate the desired solution option.
- Once the parameters have been selected, click Run Task and an Process Manager message box pops up informing you that the process has come to an end.
- Click Yes to close the template, or No to review or edit the process steps.
Figure 23. 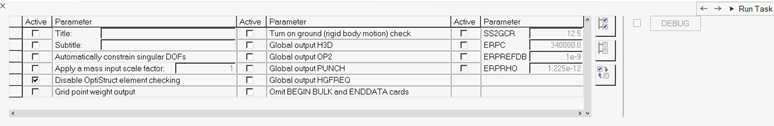
Setup Unit Input Frequency Response Process
Set up subcases with unit inputs. In practice, this is common to generate vibration and noise sensitivity results.
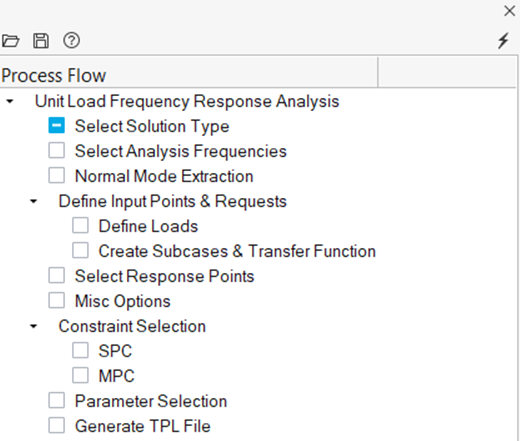
- From the Analyze or NVH Tools ribbon, click the arrow next to the Normal modes tool and select Unit input frequency response.
-
In the Select Solution Type task, select a solution method.
- Select either the Direct Frequency Response solution method, or the Modal Frequency Response solution method. For large problems involving more than a few frequencies, the modal solution is typically the most efficient solution.
- Click Run Task to proceed.
-
In the Select Analysis Frequencies task, enter the frequencies for which
response solution is needed.
Figure 25. 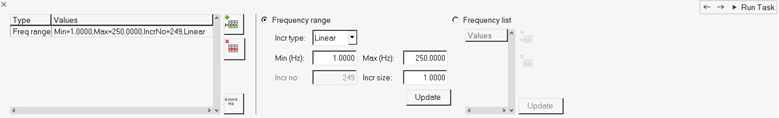
-
In the Normal Mode Extraction task, the default frequencies filled in are based
on the max. frequency you filled in for the previous step.
Figure 26. 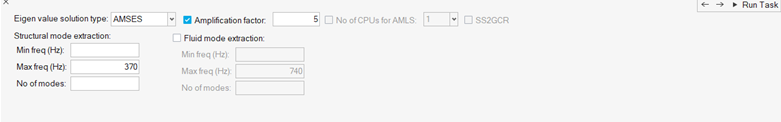
-
In the Define Input Points & Requests, Define Loads task, define what type
of load is applied.
The first four types are only applicable for structural nodes, and the last one for fluid nodes.
Figure 27. 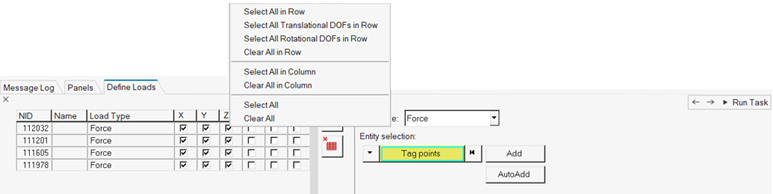
-
In the Define Input Points & Requests, Create Subcases & Transfer
Function task, select to output transfer function between input points.
Of particular interest are driving point (response taken at the same point as input) transfer functions, which are commonly used as a measure for local dynamic stiffness, or full matrix (all possible pairs of input point combinations) output, which is sometimes used as input for FRF based substructuring analysis.
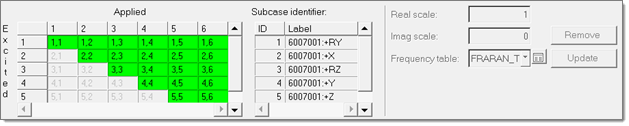
It is also possible to create new subcase groups of input to be used in individual subcases. New subcase groups can be added by clicking the Add Group icon. You can make a single or multiple row selections within the table, and then select the newly created Subcase group and click Update. All input dofs belonging to one subcase group will be used as simultaneous excitations in one subcase.Figure 28. 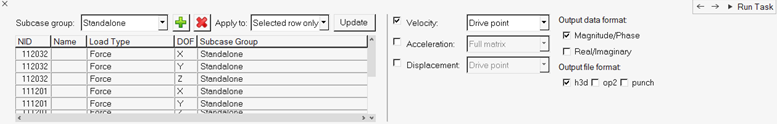
-
In the Select Response Points task, select response points for output.
Figure 30. 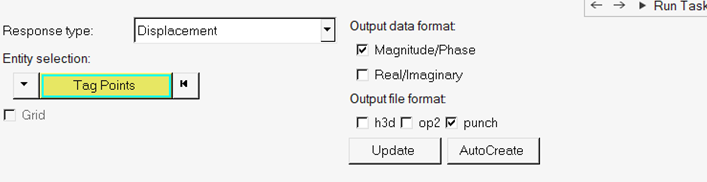
-
In the Misc Options task, select from the damping options that are available,
including the global modal viscous damping on the structure side, and global
material and viscous damping on the fluid side.
Figure 31. 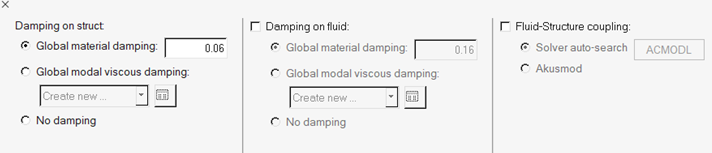
-
In the Constraint selection, SPC task, select the boundary condition of the
frequency response analysis.
- You can select existing SPCs by checking the corresponding box under the Active column, or click Create SPC to go to the Constraints panel and define a new SPC.
- Once the boundary condition has been fully defined, click Run Task to proceed.
Figure 32. 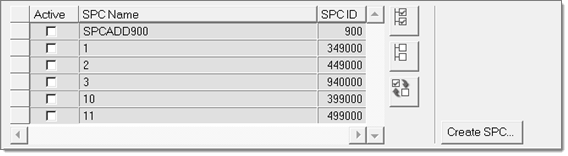
-
In the Constraint selection, MPC task, select MPC equations to turn on for the
frequency response analysis.
- Select existing MPCs by checking the corresponding box under the Active column.
- Once the MPC equations have been selected, click Run Task to proceed.
-
In the Parameter Selection task, select typical solution parameters, such as
title, singular point constraints, and so on.
- Check all boxes under the Active column to activate the desired solution option.
- Once the parameters have been selected, click Run Task and an Process Manager message box pops up informing you that the process has come to an end.
- Click Yes to close the template, or No to review or edit the process steps.
Figure 33. 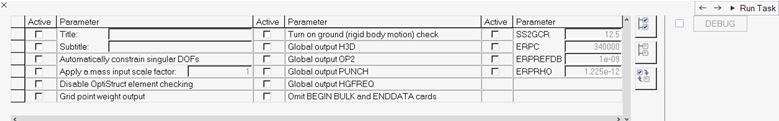
-
In the Generate TPL file task, generate and save the parameters defined in a
standard template file at your selected location.
- Choose Full deck TPL to access the file that has
all of the parameters for the complete unit load FRF process manager. In the
Analysis Manager, the generated template file can be selected as loadcase
for the Solution type Full deck TPL and solver decks can be exported for the
unit FRF.
Figure 34. 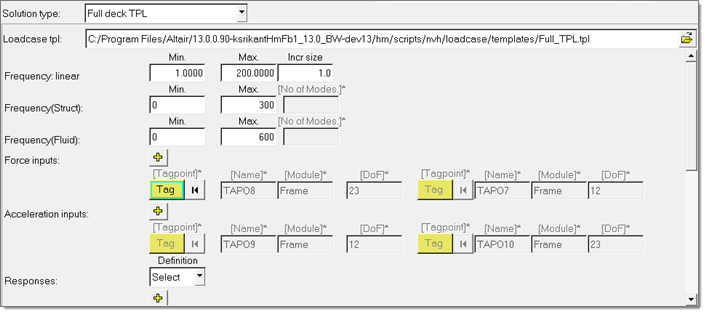
- Choose Loads Only TPL to access the file that
contains only the parameters for the loadcase portion of the unit load FRF
process manager. In the Analysis Manager, the generated template file can be
selected as the loadcase for the Solution type Frequency Response and solver
decks can be exported for general FRF.
Figure 35. 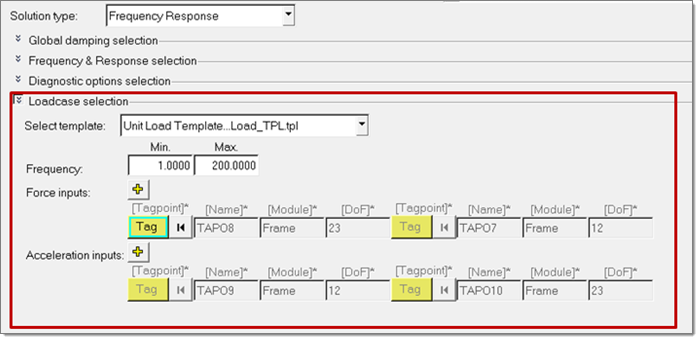
- Choose Full deck TPL to access the file that has
all of the parameters for the complete unit load FRF process manager. In the
Analysis Manager, the generated template file can be selected as loadcase
for the Solution type Full deck TPL and solver decks can be exported for the
unit FRF.
Setup Random PSD Frequency Response Process
Perform random frequency response analysis.
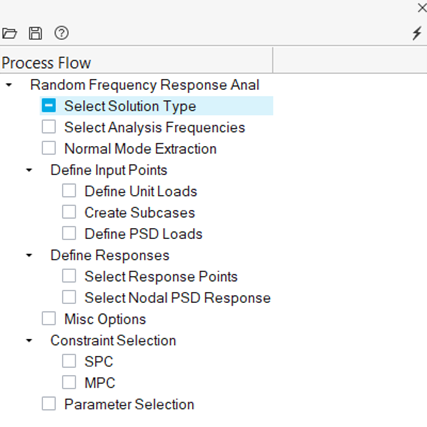
- From the Analyze or NVH Tools ribbon, click the arrow next to the Normal modes tool and select Random PSD frequency response.
-
In the Select Solution Type task, select a solution method.
- Select either the Direct Frequency Response solution method, or the Modal Frequency Response solution method. For large problems involving more than a few frequencies, the modal solution is typically the most efficient solution.
- Click Run Task to proceed.
-
In the Select Analysis Frequencies task, enter the frequencies for which
response solution is needed.
Figure 37. 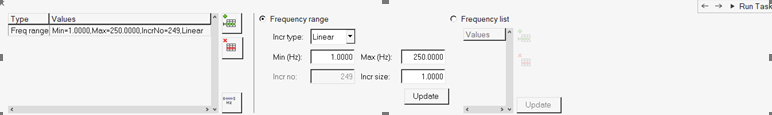
-
In the Normal Mode Extraction task, the default frequencies filled in are based
on the max. frequency you filled in for the previous step.
Figure 38. 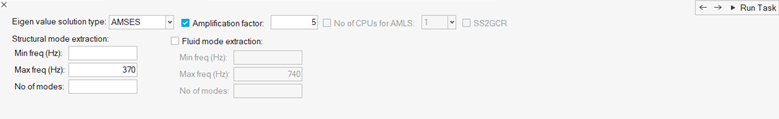
-
In the Define Input Points, Define Unit Loads task, define what type of load is
applied.
The first four types are only applicable for structural nodes, and the last one for fluid nodes.
Figure 39. 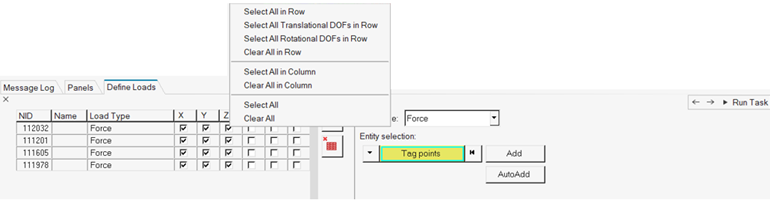
-
In the Define Input Points, Create Subcases task, select to output transfer
function between input points.
Of particular interest are driving point (response taken at the same point as input) transfer functions, which are commonly used as a measure for local dynamic stiffness, or full matrix (all possible pairs of input point combinations) output, which is sometimes used as input for FRF based substructuring analysis.
It is also possible to create new subcase groups of input to be used in individual subcases. New subcase groups can be added by clicking the Add Group icon. You can make a single or multiple row selections within the table, and then select the newly created Subcase group and click Update. All input dofs belonging to one subcase group will be used as simultaneous excitations in one subcase.Figure 40. 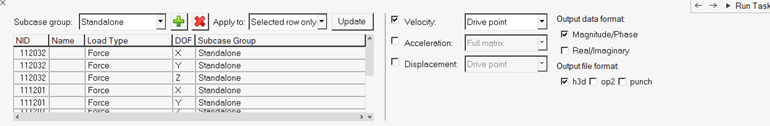
-
In the Define Input Points, Define PSD Loads task, input the NxN 2 dimensional
PSD matrix (here N is the number of subcases whose response are used in the
random PSD calculations.
-
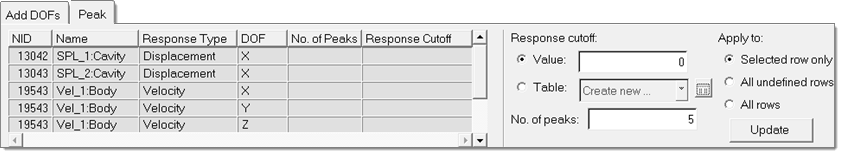
In the Define Responses, Select Response Points task, select response points
for output.
Figure 43. 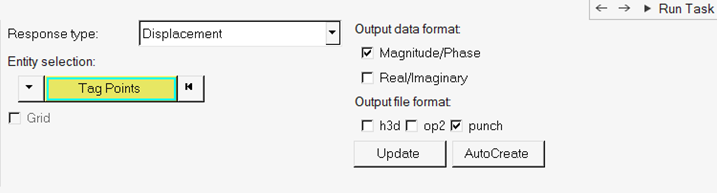
-
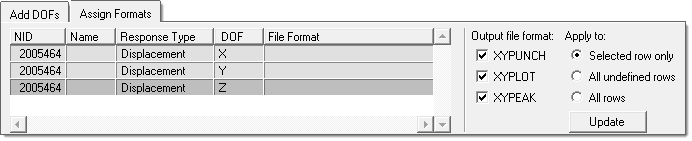
In the Define Responses, Select Nodal PSD Response task, define the response
points and DOFs to be output.
Response points and DOFs can be output into the following formatted files: XYPUNCH, XYPLOT, and XYPEAK.
-
In the Misc Options task, select from the damping options that are available,
including the global modal viscous damping on the structure side, and global
material and viscous damping on the fluid side.
Figure 46. 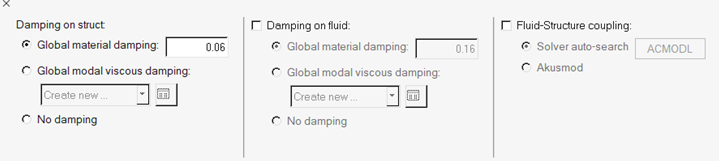
-
In the Constraint selection, SPC task, select the boundary condition of the
frequency response analysis.
- You can select existing SPCs by checking the corresponding box under the Active column, or click Create SPC to go to the Constraints panel and define a new SPC.
- Once the boundary condition has been fully defined, click Run Task to proceed.
Figure 47. 
-
In the Constraint selection, MPC task, select MPC equations to turn on for the
frequency response analysis.
- Select existing MPCs by checking the corresponding box under the Active column.
- Once the MPC equations have been selected, click Run Task to proceed.
-
In the Parameter Selection task, select typical solution parameters, such as
title, singular point constraints, and so on.
- Check all boxes under the Active column to activate the desired solution option.
- Once the parameters have been selected, click Run Task and an Process Manager message box pops up informing you that the process has come to an end.
- Click Yes to close the template, or No to review or edit the process steps.
Figure 48. 
Setup General Frequency Response Process
Run Task loads at multiple DOFs simultaneously with arbitrary magnitude and delay (relative phase).
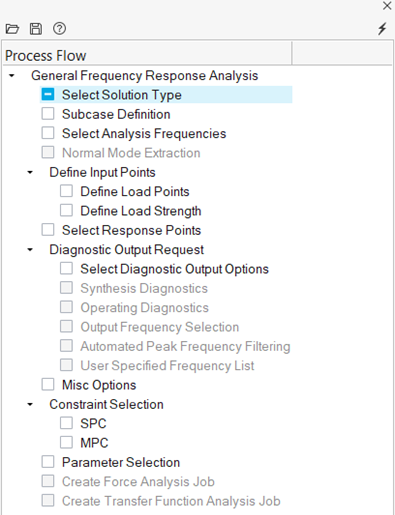
- From the Analyze or NVH Tools ribbon, click the arrow next to the Normal modes tool and select General frequency response.
-
In the Select Solution Type task, select a solution method.
- Select either the Direct Frequency Response solution method, or the Modal Frequency Response solution method. For large problems involving more than a few frequencies, the modal solution is typically the most efficient solution.
- Click Run Task to proceed.
-
In the Subcase Definition task, create a new subcase or edit an existing
subcase.
Figure 50. 
-
In the Select Analysis Frequencies task, enter the frequencies for which
response solution is needed.
Figure 51. 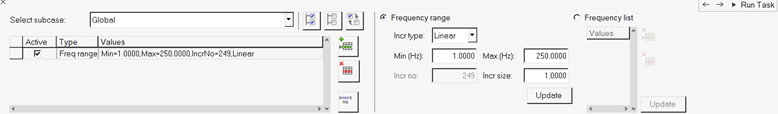
-
In the Normal Mode Extraction task, the default frequencies filled in are based
on the max. frequency you filled in for the previous step.
Figure 52. 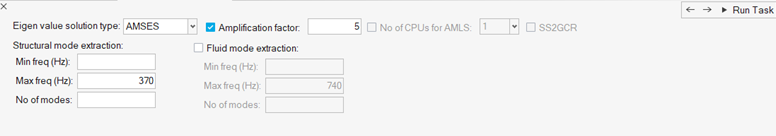
-
In the Define Input Points, Define Load Points task, define what type of load
is applied.
The first four types are only applicable for structural nodes, and the last one for fluid nodes.
Figure 53. 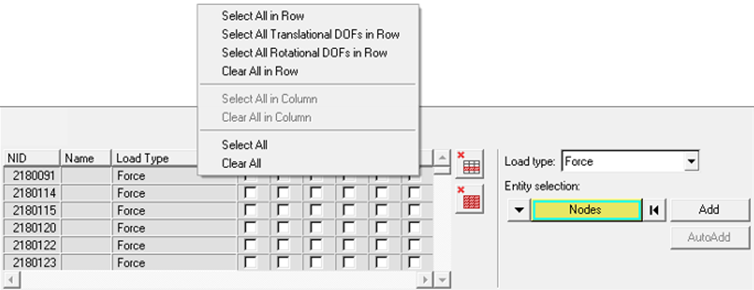
-
In the Define Input Points, Define Load Strength task, define frequency
dependent load strength and delay for individual subcases or DOFs in one
subcase.
- For subcase based definition, once the subcase is selected, select a DOF
row from the list box, and then add load strength frequency tables in either
real/imaginary or magnitude/phase form.Delay or phase relative to a reference input DOF can optionally be specified as well. Loading strength can be defined manually, with external files in csv/text format and also universal (.unv) files from external data acquisition tools such as LMS and B&K. Import the .csv/text or universal file, select the relevant loading strength and click Save to define it. You can select one of the radio buttons on the right to control how the definitions provided are filled into various rows. It is also possible to go back to the Subcase Definition panel by clicking the Create Subcase icon to add new subcases or edit existing subcases. If subcases are added or edited, then you will be redirected to the Select Analysis Frequencies task to repeat all the steps prior to defining load strengths. If subcases are not edited then you will come back to the Define Load Strength task.
Figure 54. 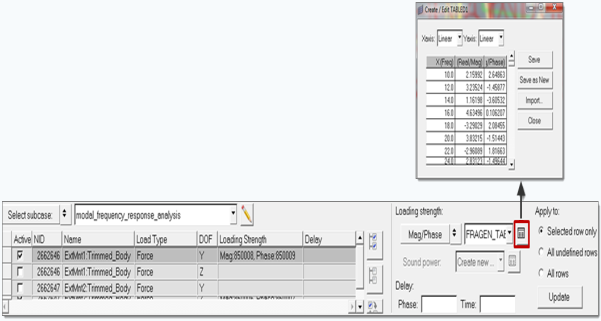
- For DOF based definition, once the DOF is selected, select a subcase row
from the list and follow the same process described in the above section.
With this option it is not possible to add or edit subcases.
Figure 55. 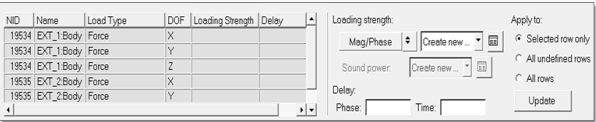
- For subcase based definition, once the subcase is selected, select a DOF
row from the list box, and then add load strength frequency tables in either
real/imaginary or magnitude/phase form.
-
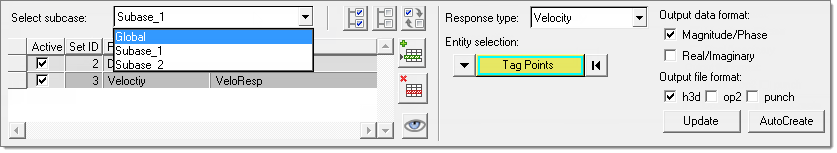
In the Select Response Points task, select response points for output.
Response selection can be global or subcase specific.
Responses selected for the global subcase are by default available for other individual subcases. Additional responses can be added and used for an individual subcase. It is also possible to add duplicate response types to any individual subcase, in addition to those in the global subcase. In this case a separate response set will be created for that subcase which will be a union of entities in global and individual subcases.Figure 58. 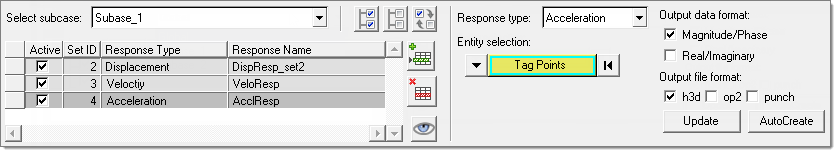
-
In the Diagnostic Output Request, Select Diagnostic Output Options task,
control if diagnostic outputs are to be generated.
- Select No to generate diagnostic output requests and the process will go directly to the Miscellaneous Options task. Select Yes to request diagnostic output only at selected response peaks.
- Click Run Task to proceed.
Figure 59. 
-
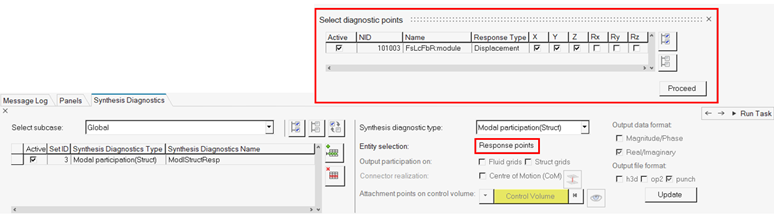
In the Select Diagnostic Output Request, Synthesis Diagnostics task, select the
Synthesis diagnostic type which presents a breakdown (participation factors) to
the response, such as modal participations.
This type will be output only at the peak frequencies of the corresponding response DOF. The selection of the Synthesis diagnostic type can be Global or Subcase Specific.
-
In the Select Diagnostic Output Request, Operating Diagnostics task, select the
Operating diagnostic type which is not response specific, such as ODS animation
or energy.
Output in this case will be generated at the super set of the peak frequencies of all selected response DOFs. In this case the selection of operating diagnostic type can be global or subcase specific.
Figure 63. 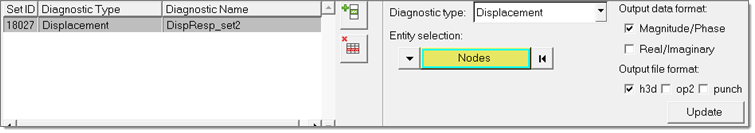
-
In the Select Diagnostic Output Request, Output Frequency Selection task,
control to select frequency at which diagnostic output is to be requested.
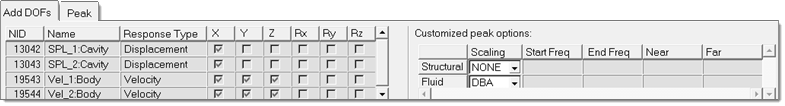
- Select Automated Peak Frequency Filtering to customize options used to define response peak frequencies through the PEAKOUT card.
- Select User Specified Frequency List to enter a list of frequencies for each subcase, which will be referenced by a OFREQ card in a separate diagnostic output subcase.
-
In the Select Diagnostic Output Request, Automated Peak Frequency Filtering
task, select the customized options specific for structural and acoustic
responses to be used for selected response peak frequencies.
-
In the Select Diagnostic Output Request, User Specified Frequency List task,
specify a list of frequencies at which diagnostic output is requested.
This definition is subcase specific. For subcases where a Frequency List is entered in the Select Analysis Frequencies task, the same frequency list values are automatically entered by default.
Figure 66. 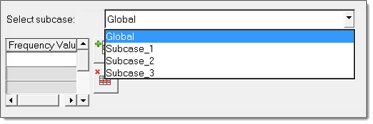
-
In the Misc Options task, select from the damping options that are available,
including the global modal viscous damping on the structure side, and global
material and viscous damping on the fluid side.
Figure 67. 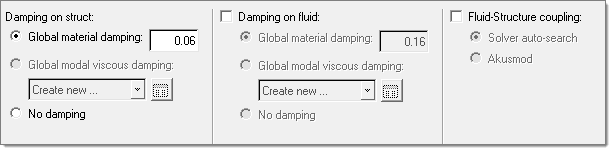
-
In the Constraint selection, SPC task, select the boundary condition of the
frequency response analysis.
- You can select existing SPCs by checking the corresponding box under the Active column, or click Create SPC to go to the Constraints panel and define a new SPC.
- Once the boundary condition has been fully defined, click Run Task to proceed.
Figure 68. 
-
In the Constraint selection, MPC task, select MPC equations to turn on for the
frequency response analysis.
- Select existing MPCs by checking the corresponding box under the Active column.
- Once the MPC equations have been selected, click Run Task to proceed.
-
In the Parameter Selection task, select typical solution parameters, such as
title, singular point constraints, and so on.
- Check all boxes under the Active column to activate the desired solution option.
- Once the parameters have been selected, click Run Task and an Process Manager message box pops up informing you that the process has come to an end.
- Click Yes to close the template, or No to review or edit the process steps.
Figure 69.