Case Setup
New Features
- Thermal Simulations
- Temperature is now supported as a transport variable. This enables a
range of simulations, such as powertrain cooling, thermal convection,
and passive scalar transport. Features include:
- Model selection: Boussinesq and Passive scalar.
- Thermal boundary conditions for solid parts and the wind tunnel.
- Absorbing boundary conditions for the wind tunnel inlet and outlet.
- Advanced heat exchanger models with coolant properties.
- Updated outputs and output controls to account for temperature as a variable.
- Updated temperature dependent material properties.
- Gravity setup.
- Guide Panel for Wheels with Overset Mesh
- Wheels are now set up using a guide panel, which replaces the guide bar.
This workflow follows the fan setup process and includes features such
as overset mesh setup and optional mesh control settings.
Figure 1. 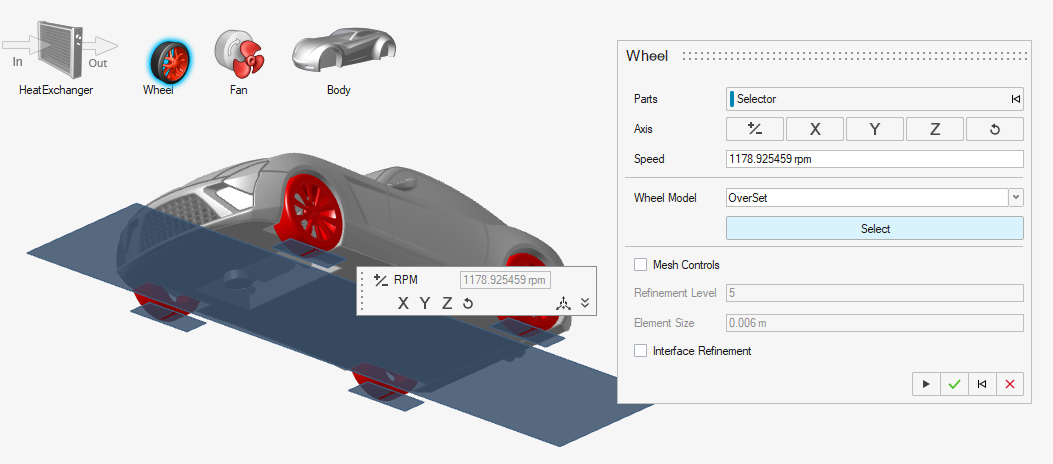
- Yawed Simulations
- Yawed vehicle simulations are supported via a standalone dialog that
lets you set up rotational transformations. This automatically applies
the yaw angle to belts and creates an STL-based belt part. The boundary
condition for the belts can be independently set and supports vectors
that are different from the inflow condition.
Figure 2. 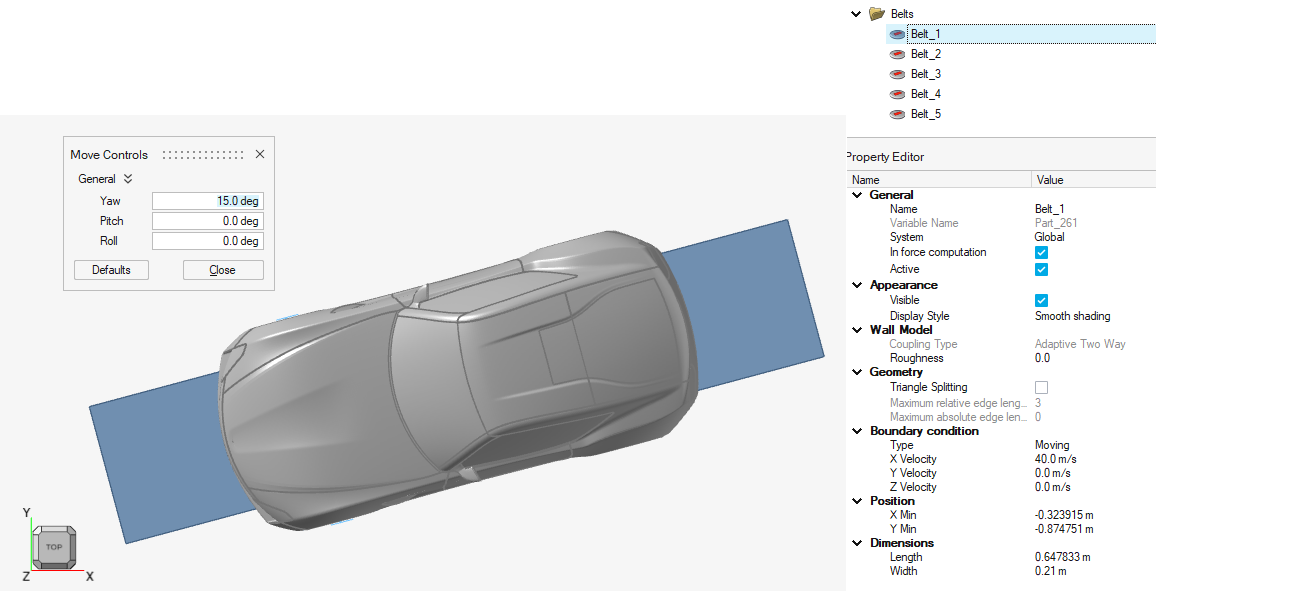
- Multiple STL Export
- The model assembly can now be split up into multiple STL files on export. This is performed automatically by the sub-assembly structure, one STL for each. You can control the output by organizing parts in sub-assemblies. The feature can be combined with compression and is set up in the Preferences menu.
- Virtual Fan with Momentum Source
- Momentum sources are now specified as a sub-model of the Virtual fan setup. Velocity and mass flow rate are both available.
- Double-click from the Property Editor
- Edit mode can be activated for derived entities directly from the Property Editor. All outputs and mesh control instances can be accessed right from the Property Editor with a simple double click.
Enhancements
- Inline Unit Switching
- Solver units such as time steps and output intervals now support inline
switching to time(s) and frequency (Hz). This is available in the Output
and Run dialogs.
Figure 3. 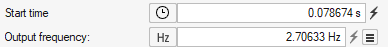
- Outputs
-
- Triangulation is supported for section cuts.
- Triangle splitting is supported for monitoring surfaces.
- Vorticity, Q-criterion, and Lambda are Supported as Output Variables
-
- Sectional drag is activated by default.
- Wind tunnel position is adjusted based on the vehicle’s bounding box.
- Updated icon graphics.
- Python API
- Added support for:
- Mesh transition layers.
- Output variables.
Resolved Issues
- Crash upon editing sketches.
- Crash upon editing output frequency in the Output Controls dialog.
- Batch mode in Linux.
- Mesh controls dialog gets reset when opened for the first time.
- Permeability directions for porous media are not visible unless edited.
- XML parameters resolved for the following scenarios:
- Virtual fan settings for “ramp up iterations” and “initial pressure rise”.
- Coarsen output settings in the Output Controls dialog.
- Fluid BC and thermal BC are grouped into the same wall instance.
- Offset mesh distance was incorrectly computed.
- Inconsistent computations for repeated modifications to run time (steps) and scaling factor.
- Triangulation for section cuts is shown in the Property Editor.
- Triangle splitting option for belts is now functional when reimporting a template file.
- Objects created in Python differed from those created in the user interface when saved as HyperMesh CFD files.
- Ground patch was visible as a part when importing a HyperMesh CFD file.
- Editing ground patch in Python created a second instance.
- Editing target frequency in the Outputs menu shows the correct value after a focus loss.
- Visibility issues with selecting Nastran parts.
- Icons in dialog windows are correctly shown.