Connector for MQTT
The MQTT connector allows:
- Connection to MQTT’s message bus on a real-time streaming basis.
- Panopticon to subscribe to FIX, JSON, Text, or XML based messages that are published on topics. The data format itself is arbitrary, and consequently, the connection includes the message definition.
- Encrypted/SSL/TLS connections using a CA certificate file, Client Certificate File, and Client Key File.
- Enter the following properties:
Property Description Broker URL
The location of the message broker. Default is tcp://localhost:1883.
Topic
The topic or the queue's physical name.
Example:
level1/level2/level3/level4 etc.
NOTES:
You can also opt to use a wild card in the topic name specification.
-
The plus sign symbol (+) can be used as a wild card for any value at one specific level.
Example: level1/level2/+/level4
-
The hash sign symbol (#) can be used as a wild card for any values across more than one level.
Example: level1/#/level4
User Id
The user Id that will be used to connect to MQTT.
Password
The password that will be used to connect to MQTT.
-
- To allow encrypted connections, you can either:
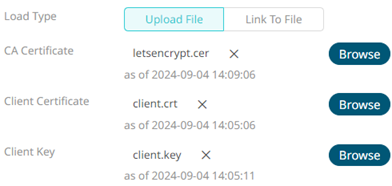
- Upload a CA Certificate file by clicking Upload File
 then Browse
then Browse  to browse to the file source.
to browse to the file source.
After selecting the file, it is displayed with the timestamp.
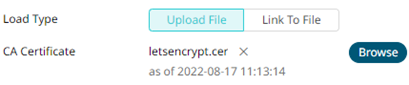
To change the certificate, click
 then Browse
then Browse  to browse to a new version of the file.
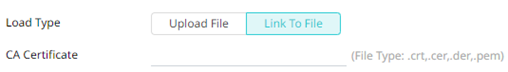
to browse to a new version of the file. - Link to a CA Certificate file by clicking Link to File
 and entering the File Path.
and entering the File Path.
- Upload a CA Certificate file by clicking Upload File
- Upload the Client Certificate and Client Key files by clicking
 to browse to the file sources.
to browse to the file sources.
NOTE: Panopticon only supports pem-encoded files for keys in MQTT.
- In MQTT, a topic consists of one or more topic levels. Enter the Topic Level Separator to use. Default is / (forward slash).
- Select the Message Type. This will specify the format of the data within the message:
- Select either the dot (.) or comma (,) as the Decimal Separator.
NOTE: Prepend 'default:' for the elements falling under default namespace.
- Click
 to the fetch the schema based on the connection details. Consequently, the list of columns with the data type found from inspecting the first ‘n’ rows of the input data source is populated and the Save button is enabled.
to the fetch the schema based on the connection details. Consequently, the list of columns with the data type found from inspecting the first ‘n’ rows of the input data source is populated and the Save button is enabled.
This also populates the Id Column with the set of columns, of arbitrary type, that can be concatenated to form a unique row identifier.
- You can also opt to load or save a copy of the column definition.
- Click
 to add columns to the MQTT connection that represent sections of the message. Then enter or select:
to add columns to the MQTT connection that represent sections of the message. Then enter or select:
Property Description Name
The column name of the source schema.
XPath/JsonPath/Fix Tag/Column Index
The XPath/JsonPath/Fix Tag/Column Index of the source schema.
Type
The data type of the column. Can be a Text, Numeric, or Time
Date Format
The format when the data type is Time.
NOTE:
To parse and format times with higher than millisecond precision, the format string needs to end with a period followed by sequence of upper case S. There can be no additional characters following them.
For example: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS
Filter
Defined parameters that can be used as filter. Only available for JSON, Text, and XML message types.
Enabled
Determines whether the message field should be processed.
To delete a column, select
 or for all the column entries select the topmost
or for all the column entries select the topmost  , then click
, then click .
- Text for topic levels can be consumed as additional columns into the data table.
The Topic Columns section shows and allows defining data table columns and mapping them to topic hierarchy levels (index based on left, 0 based).
Like columns from message data, manually add them by clicking
 . A new entry displays.
. A new entry displays.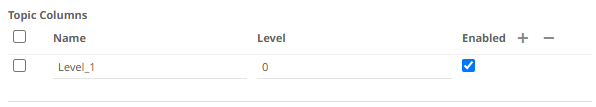
Name can be any unique topic level within the topic name. The Level is the hierarchy level of the topic column.
Select the Enabled checkbox to enable a topic column.
To delete a topic column, select
 or for all the topic column entries select the topmost
or for all the topic column entries select the topmost  , then click
, then click .
- Date/Time values of output data and Date/Time inputs, where supported, are by default unchanged.
You can opt to define the Show in Timezone and Source Timezone settings.
- For this section:
Refer to Define Real-Time Settings for more information.
(c) 2013-2025 Altair Engineering Inc. All Rights Reserved.