Free Surface Formulation
Standard SPH interpolation heavily depends on the basic premise that each particle has the so called full support. Full support implies that the owner particles can see particles all around itself within the smoothing length of the particle, which mathematically implies that the sum of the kernel, also known as Shepard coefficient, is equal to one.
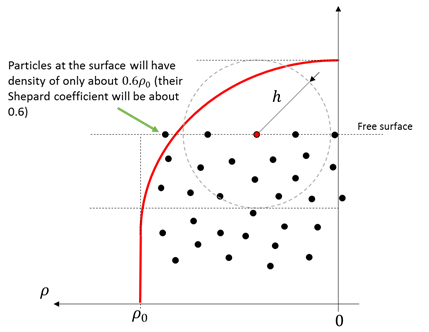
Free surface switch (freesurface) enables a numerical treatment that prevents the artificial drop of density near a free surface which is facing the particle vacuum, therefore maintaining the physicality of the solution. Despite being designed for single-phase flows, it is strongly recommended to keep the freesurface switch set to true at all times.