Example 2: Common Parametric Simulation with Frequency Sweep
This case explains how to calculate far-field, radiation pattern, current density, charge density, near field and coupling of a parametric open box with a dipole antenna insides the box and with a frequency sweep from 0.5 GHz to 1.5GHz with 3 samples.
Step 1: Create a new MOM Project.
Open newFASANT' and select 'File --> New' option.
Select 'MOM' option on the previous figure and start to configure the project.
Step 2: Create parameters for the parametric geometry model.
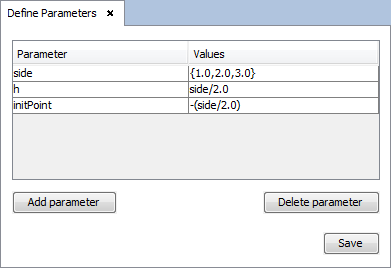
Select 'Geometry --> Parameters --> Define Parameters' option from the menu bar. Then, on the panel, set the follow parameters. 'side' parameter will be the values for the size of the box in width and depth, 'h' parameter will be the height value on the box and 'initPoint' will be the value for the initial point coordinates on the base of the box. To obtain more information about parameters definition see Parameters.
Step 3: Create the geometry model. To obtain more information about geometries generation see Parameters.
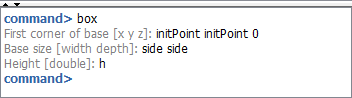
Execute 'box' command writing it on the command line and sets the parameters as the next figure shows when command line ask for it.
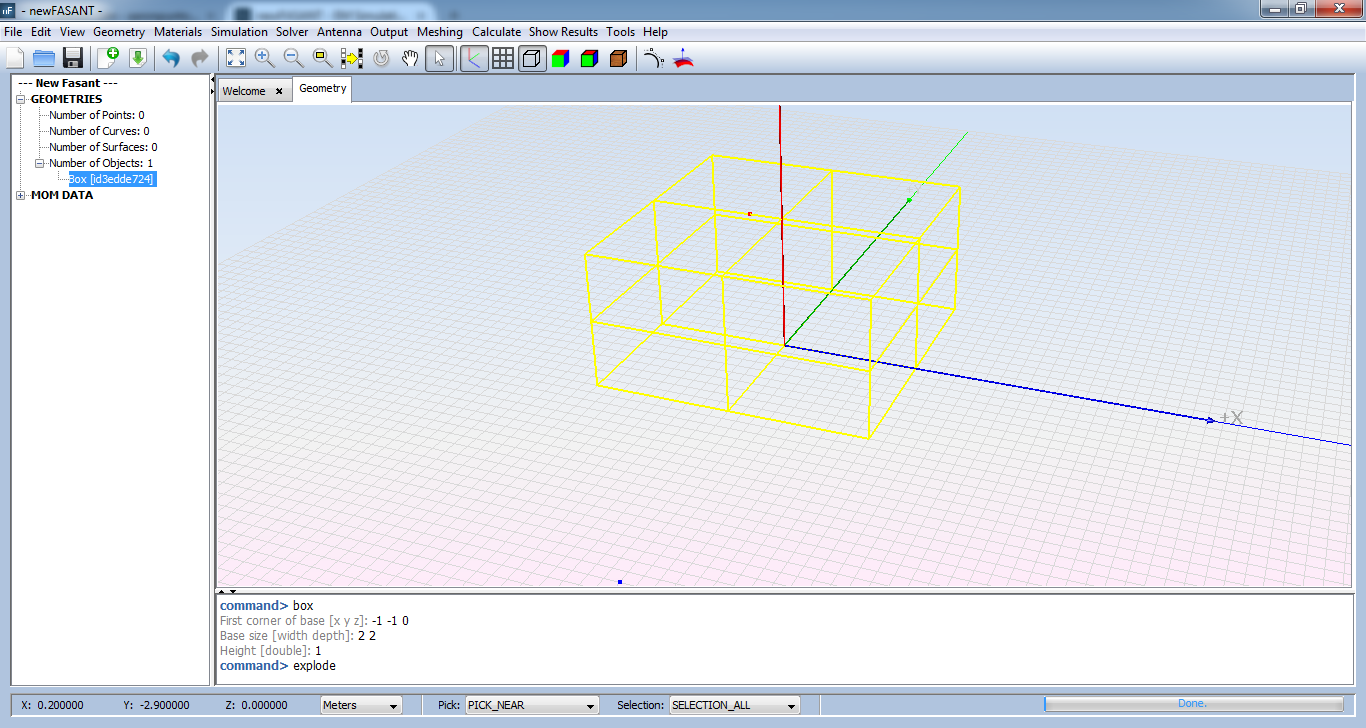
Select box geometry on main panel and execute 'explode' command writing it on the command line. Then the box will be transformed into 6 surfaces.
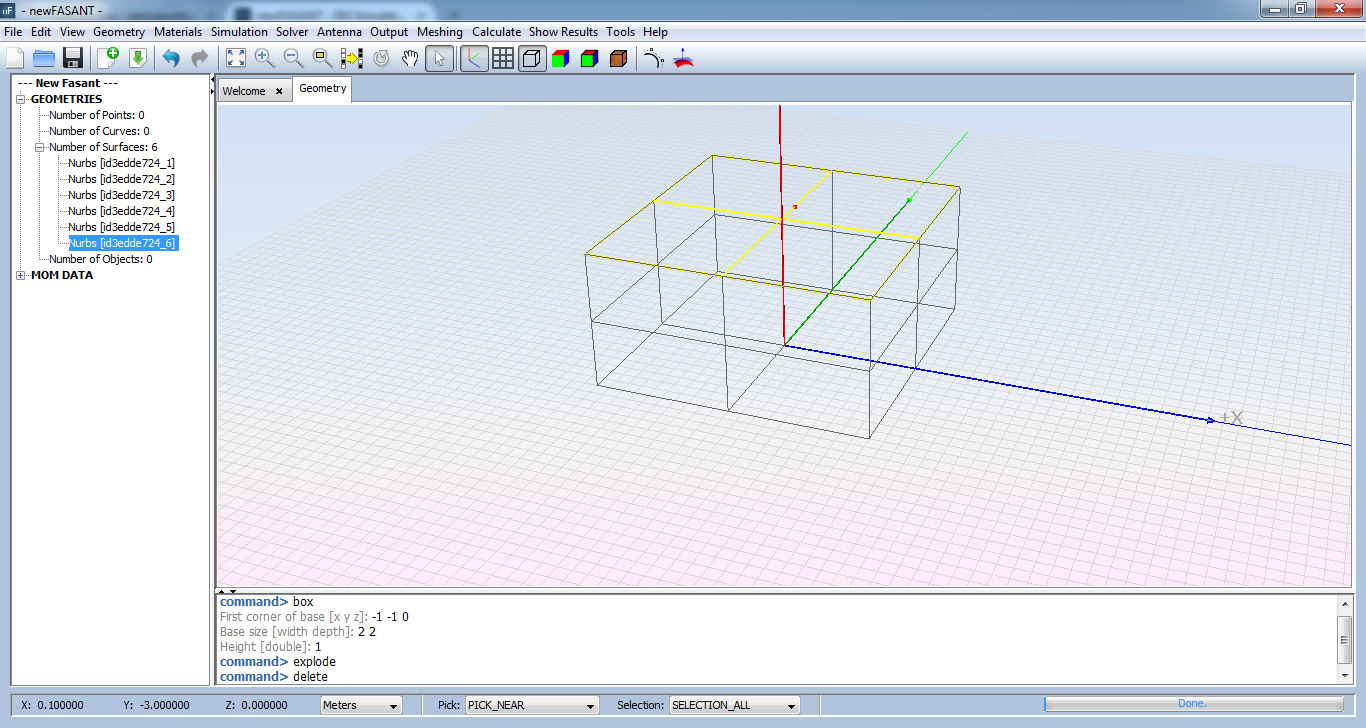
Select the top surface and execute 'delete' command. Then the surface will be removed from the geometry.
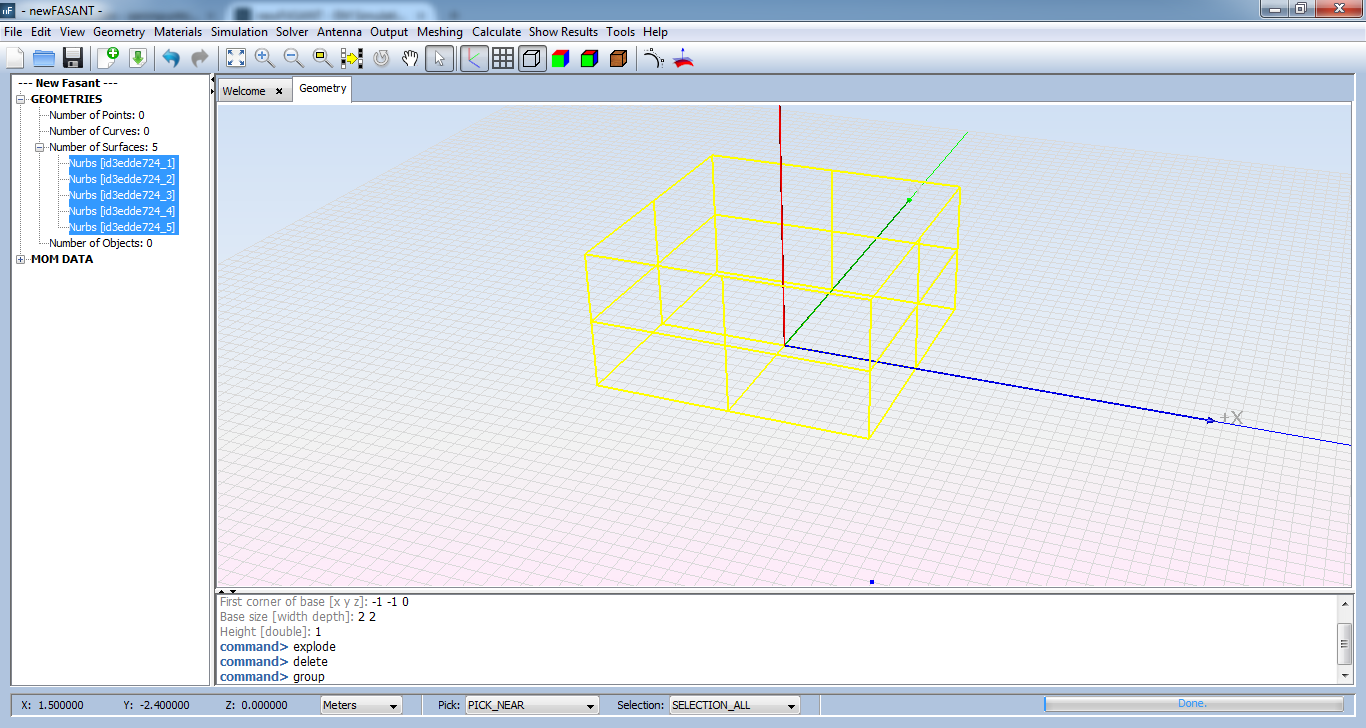
Select all remaining surfaces and execute 'group' command.
Step 4: Set Simulation Parameters
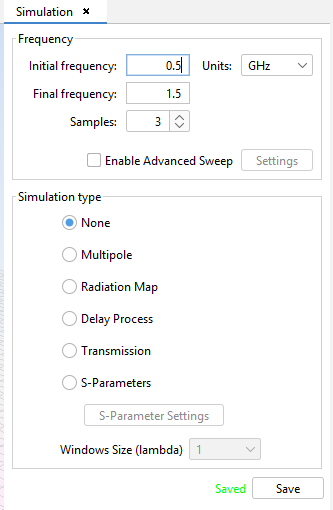
Select 'Simulation --> Parameters' option on the menu bar and the following panel appears. Set the parameters as the next figure shows and save it.
Step 5: Set the source parameters. To obtain more information about sources and antennas see Antennas.
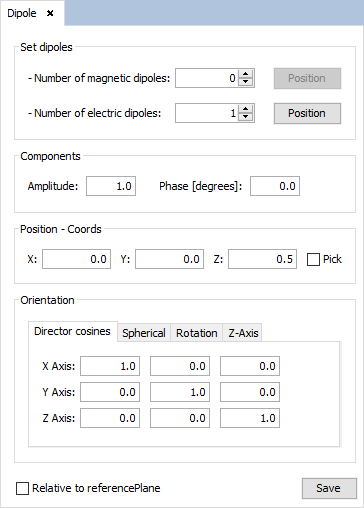
Select 'Source --> Dipole --> Dipole Antenna' option and set the parameters as show the next figure. Then save the parameters and the dipole appears.
Step 6: Set Near Field parameters.
Select 'Output --> Observation Points' option. The following panel will appear.
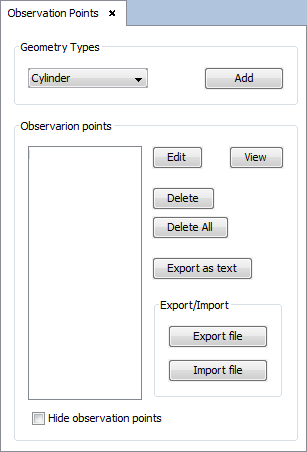
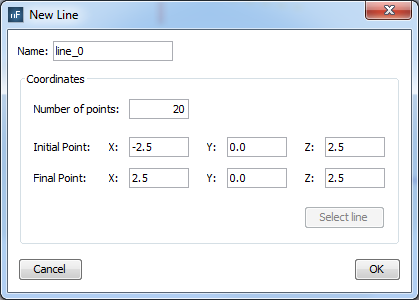
To add a line visualization, select 'line' on the selector of 'Geometry Types' section and click on 'Add' button. The line parameters panel will appear, then configure the values as the next figure show and accept it clicking on 'OK' button.
The observation line will appear as a dashed line on the position configured.
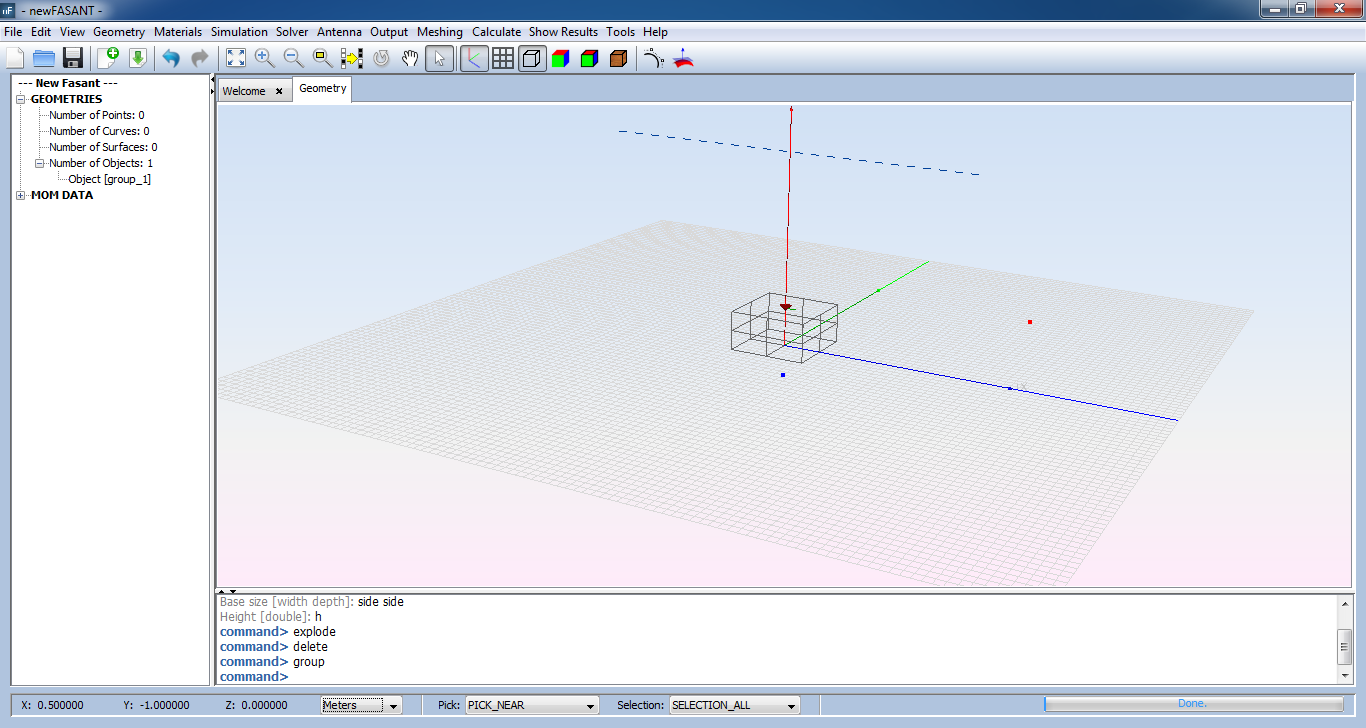
Step 7: Set Passive Antenna parameters for coupling results.
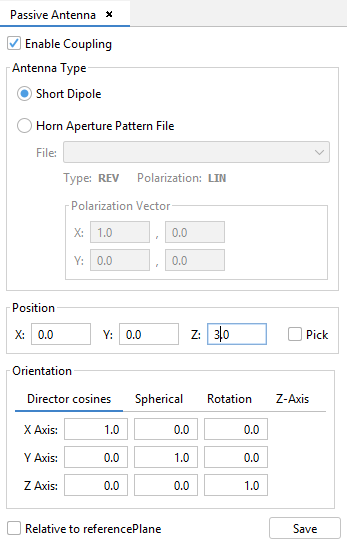
Select 'Output --> Passive Antenna' option. On the panel show, select the 'Enable / Disable Coupling' check box and set the parameters as the next figure. Then save the parameters and the passive antenna appears as a magenta dipole.
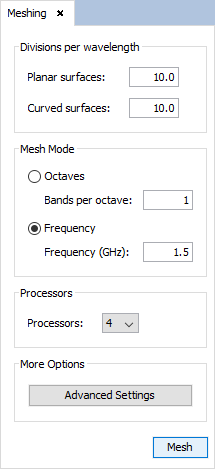
Step 8: Meshing the geometry model.
Select 'Meshing --> Parameters' to open the meshing configuration panel and then set the parameters as show the next figure. In order to obtain the shortest possible time for meshing,it is recommended to run the process of meshing with the number of physical processors available to the machine.
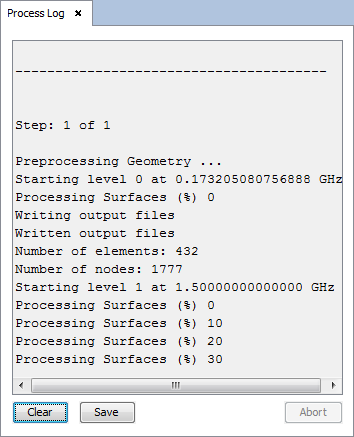
Then click on 'Mesh' button to starting the meshing. A panel appears to display meshing process information.
Step 9: Execute the simulation. In order to obtain the shortest possible time for calculating the results,it is recommended to run the process with the number of physical processors available to the machine.
Select 'Calculate --> Execute' option to open simulation parameters. Then select the number of processors as the next figure show.
Then click on 'Execute' button to starting the simulation. A panel appears to display execute process information.
Step 10: Show Results. To get more information about the graphics panel advanced options (clicking on right button of the mouse over the panel) see Annex 1: Graphics Advanced Options.
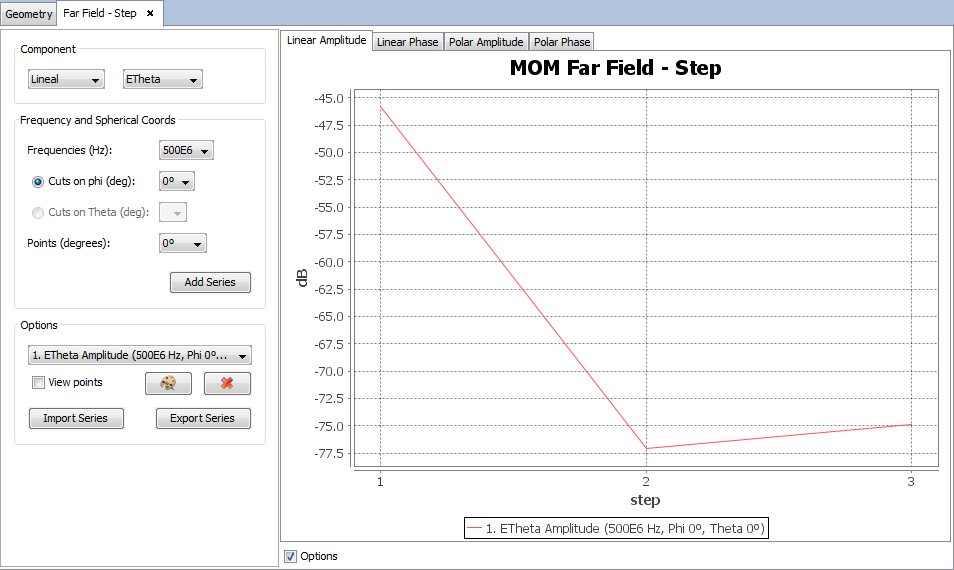
Select 'Show Results --> Far Field --> View Cuts' option to show the cuts of the observation directions options.
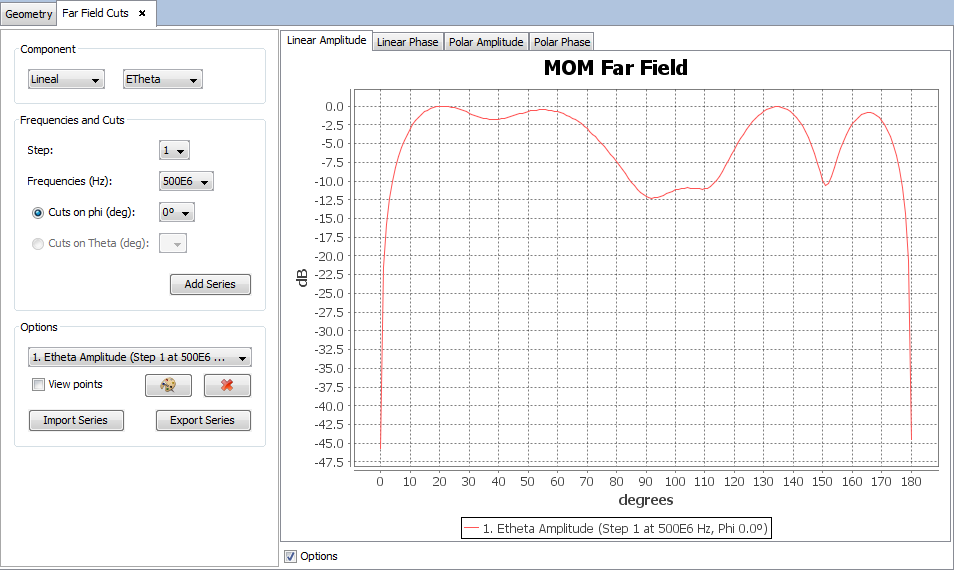
Selecting other values for the component, step, frequency or cut parameters and clicking on 'Add Series' button a new cut will be added to the selected parameters.
On 'Show Results --> Far Field' menu, other results are present such as 'View Cuts by Step' and 'View Cuts by Frequency' and this option display the values for one selected point for each step or frequency.
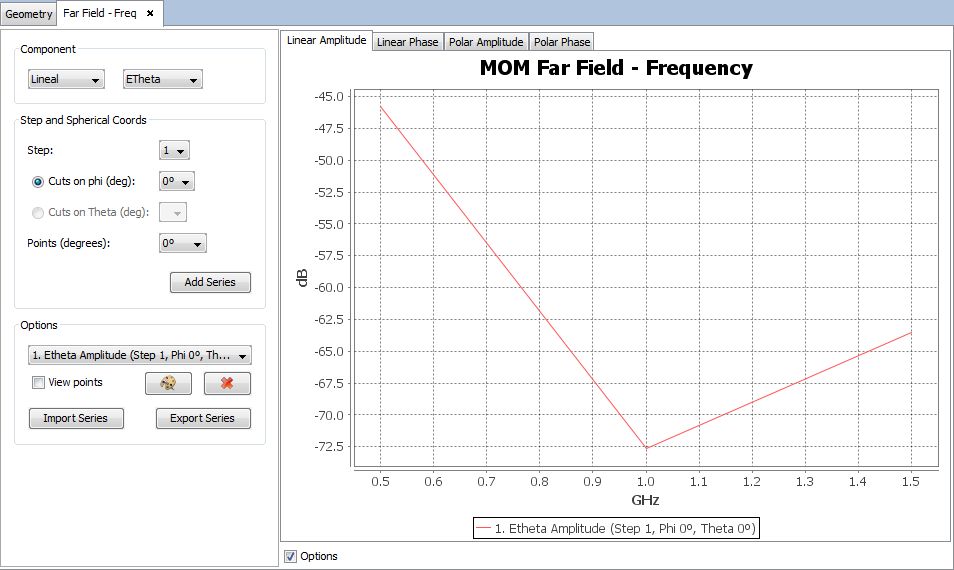
Select 'Show Results --> Radiation Pattern --> View Cuts' option to show the cuts of the radiation pattern options.
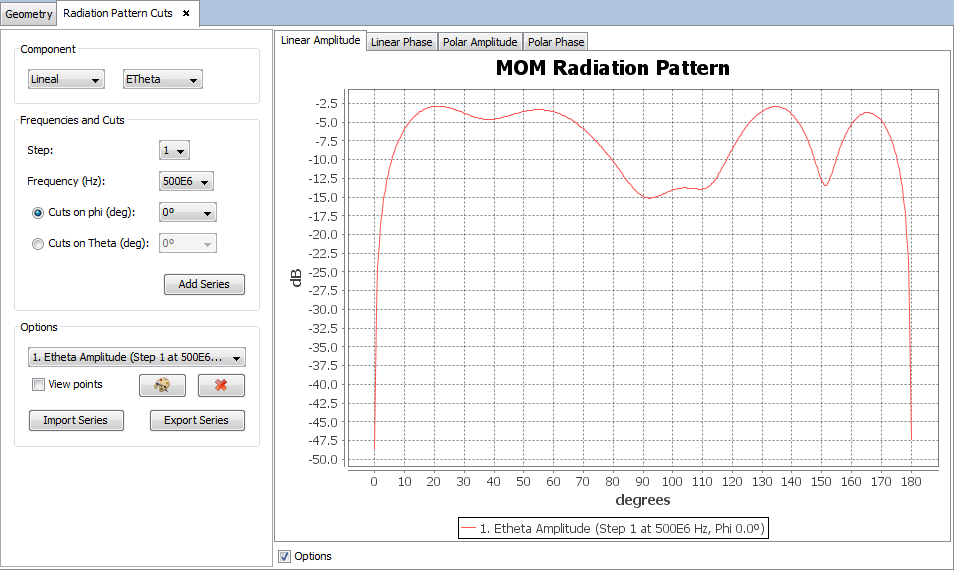
Selecting other values for the component, step, frequency or cut parameters and clicking on 'Add Series' button a new cut will be added to the selected parameters.
On 'Show Results --> Radiation Pattern' menu, other results are present such as 'View Cuts by Step' and 'View Cuts by Frequency' and this option display the values for one selected point for each step or frequency.
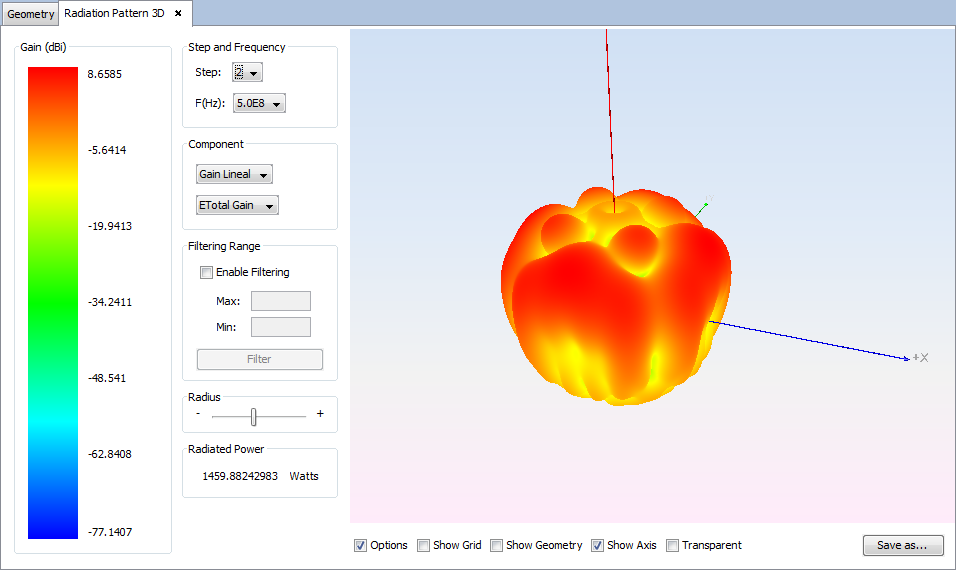
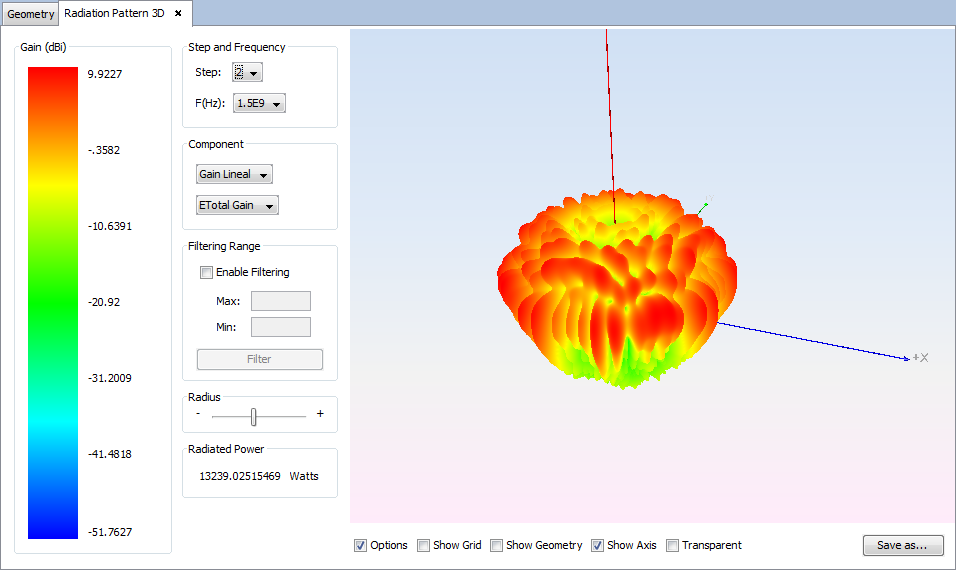
Select 'Show Results --> Radiation Pattern --> View 3D Pattern' option to show the cuts of the radiation pattern options.
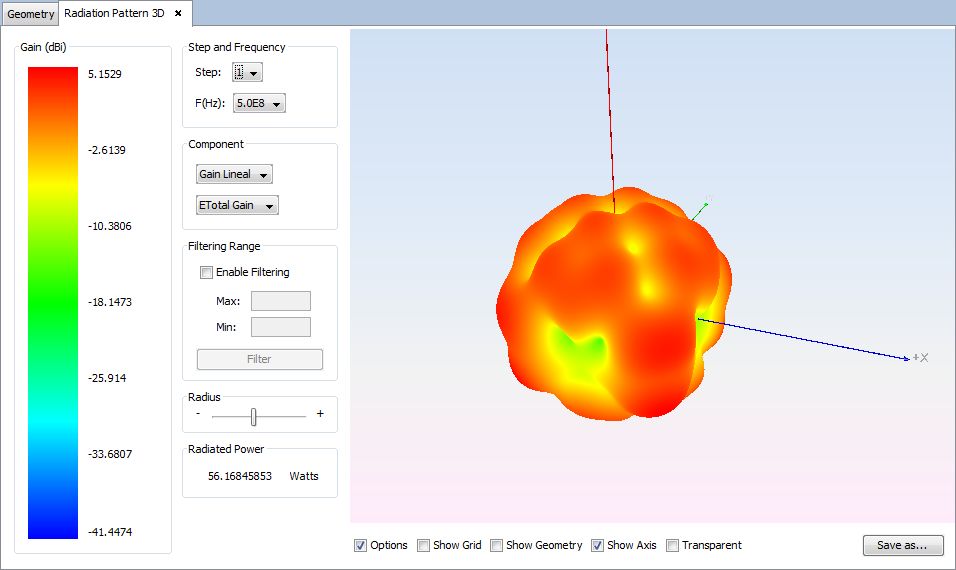
Changing values for step, frequency, component or filtering parameters the visualization for the new parameters will be shown.
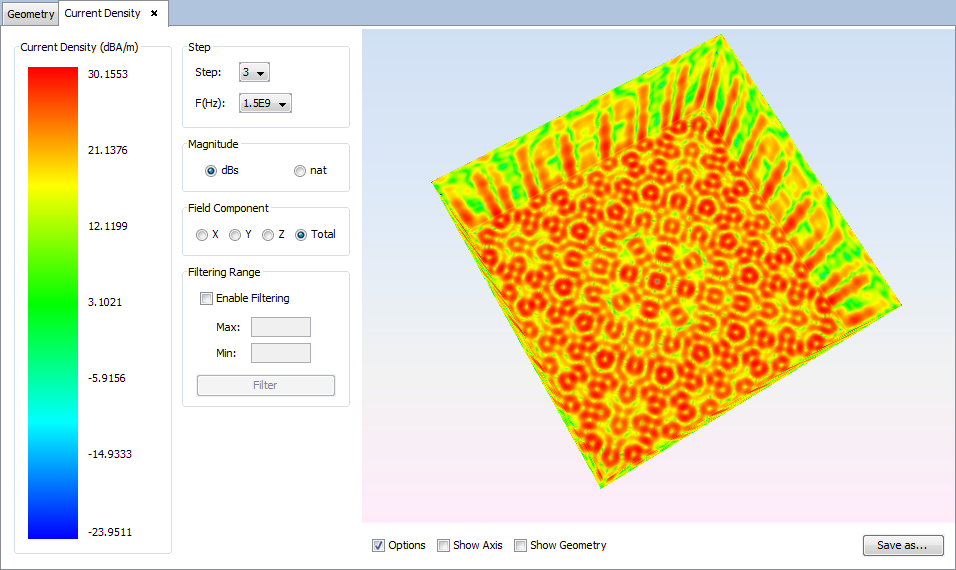
Select 'Show Results --> View Currents' option to show the current density.
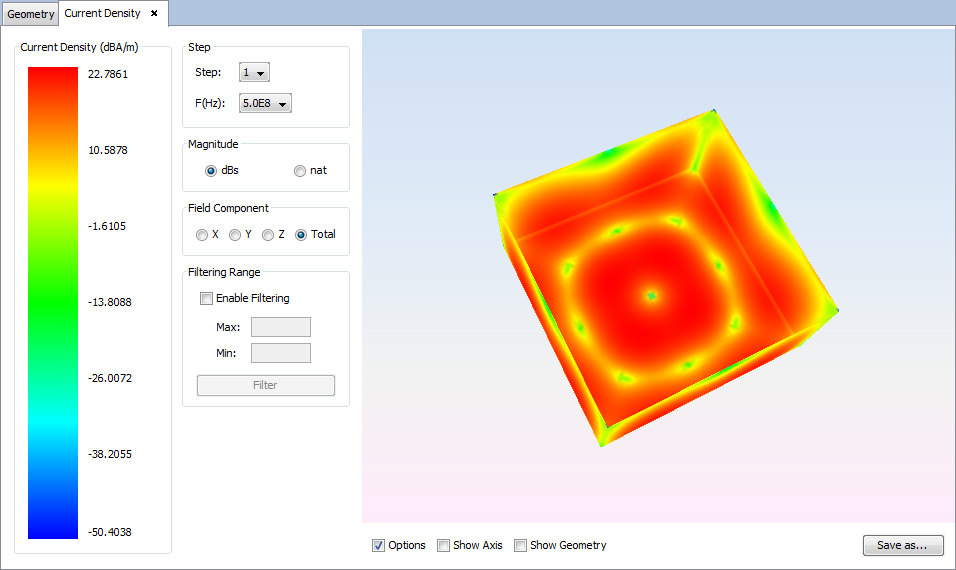
Changing values for step, frequency, magnitude, component or filtering parameters the visualization for the new parameters will be shown.
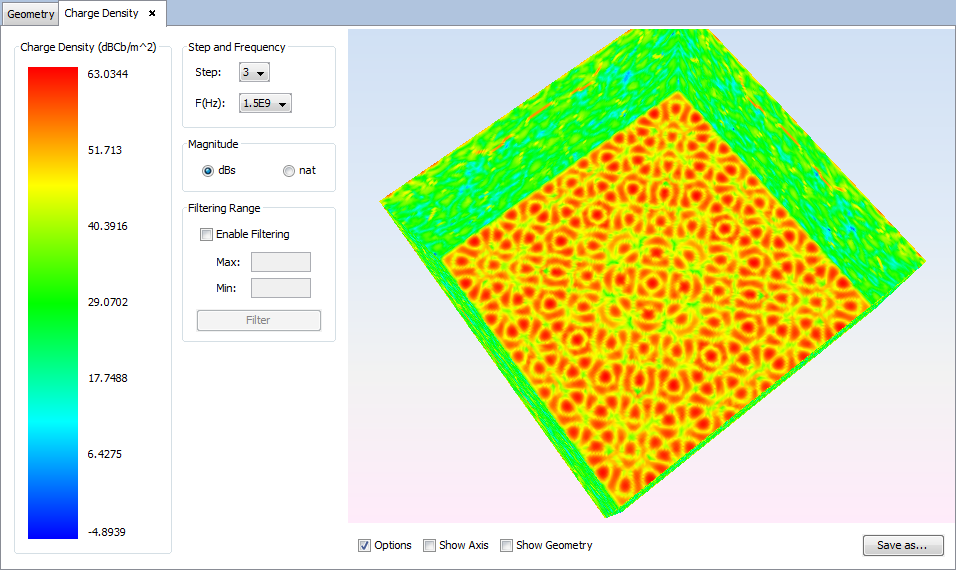
Select 'Show Results --> View Charges' option to show the charge density.
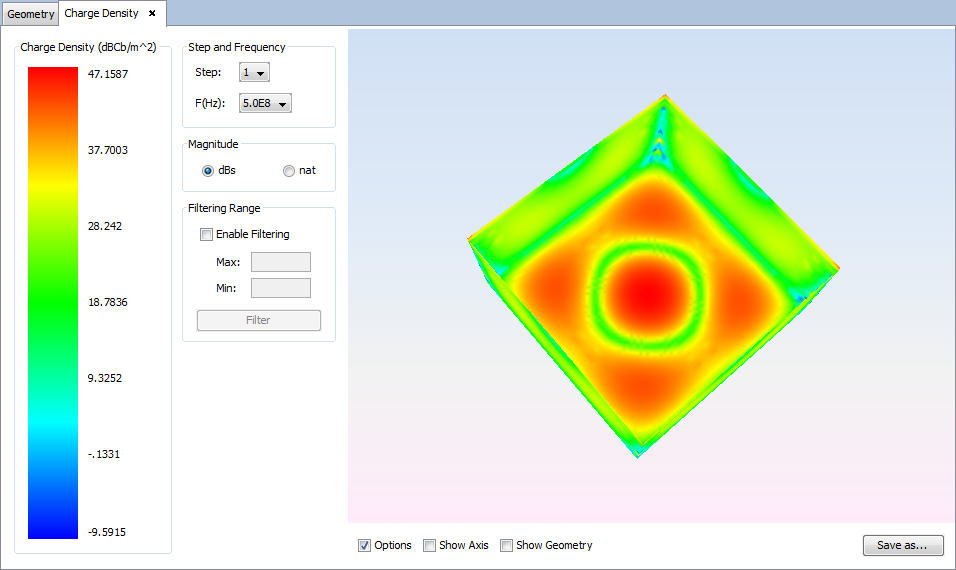
Changing values for step, frequency, magnitude or filtering parameters the visualization for the new parameters will be shown.
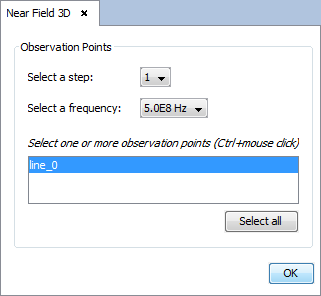
Select 'Show Results --> Near Field --> View Near Field Diagram' option to show the observation points diagram. Previously, select the observation to visualize and the step and frequency on the next figure.
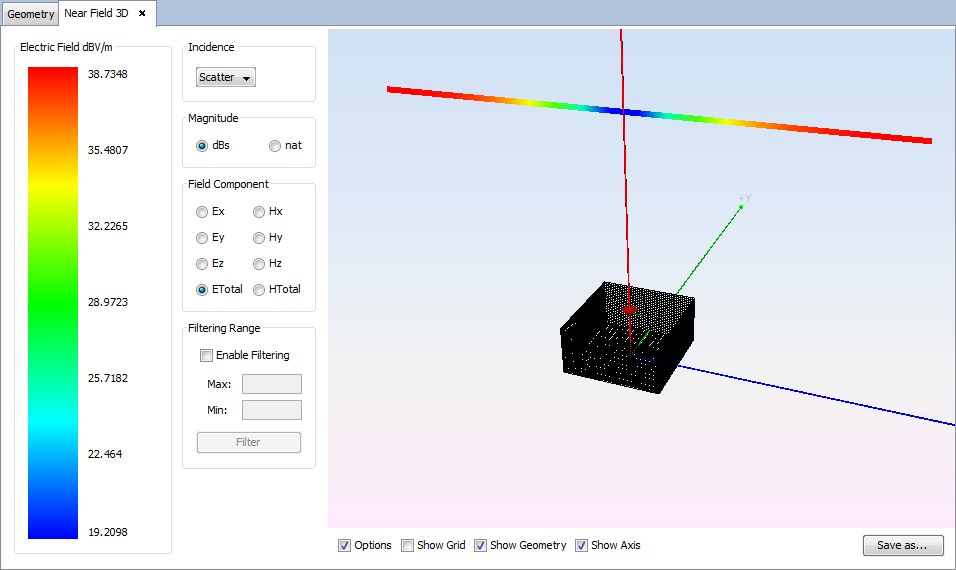
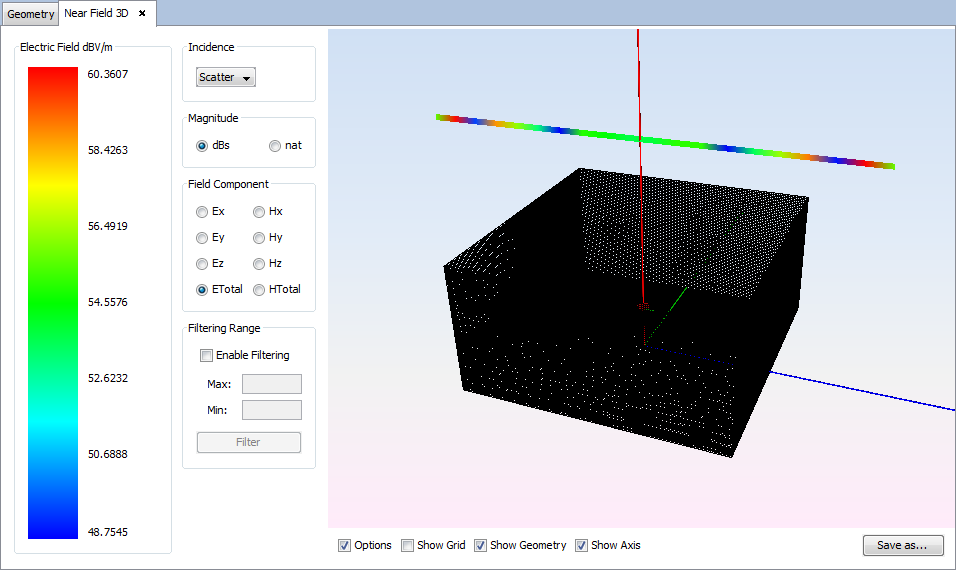
Changing values for incidence, magnitude, field or component parameters the visualization for the new parameters will be shown.
Select 'Show Results --> Near Field --> View Observation Points' option to show the observation points chart.
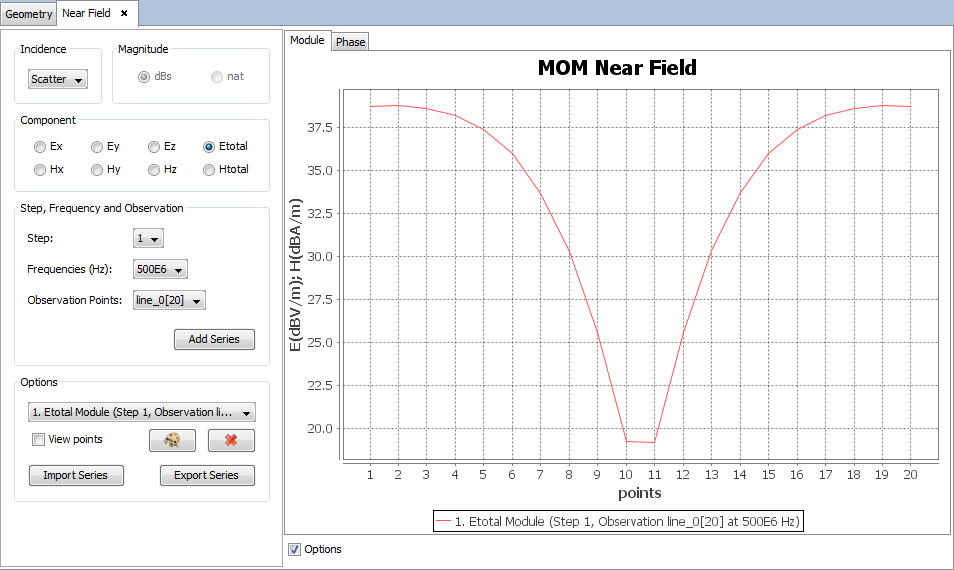
Selecting other values for incidence, component, step, frequency or observation parameters and clicking on 'Add Series' button a new cut will be added for the selected parameters.
On 'Show Results --> Near Field' menu, other results are present such as 'View Cuts by Step' and 'View Cuts by Frequency' and this option display the values for one selected point for each step or frequency.
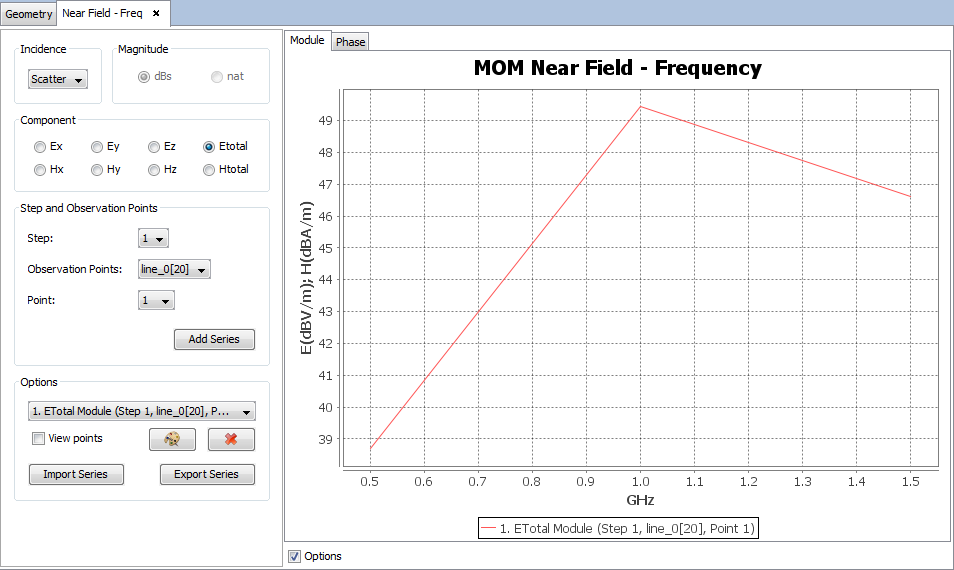
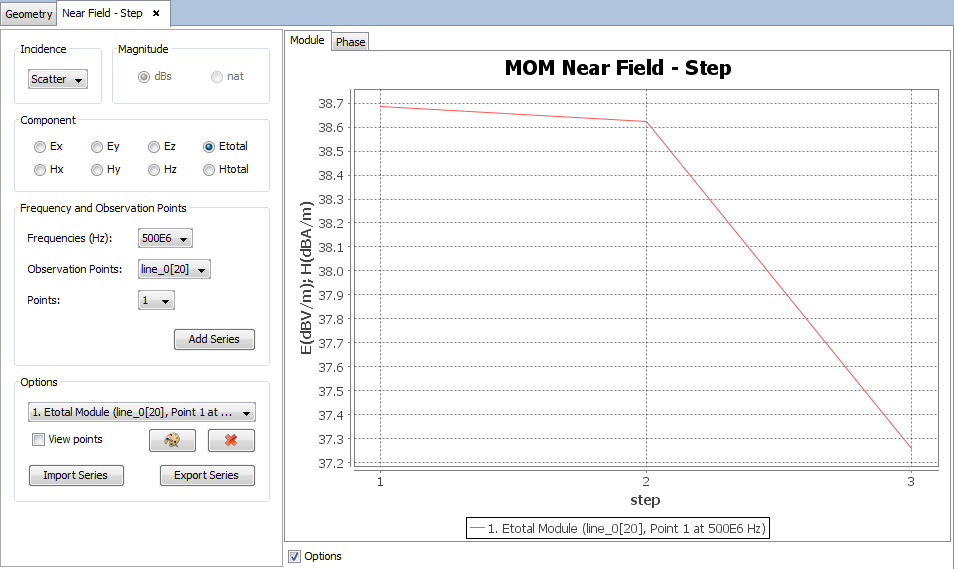
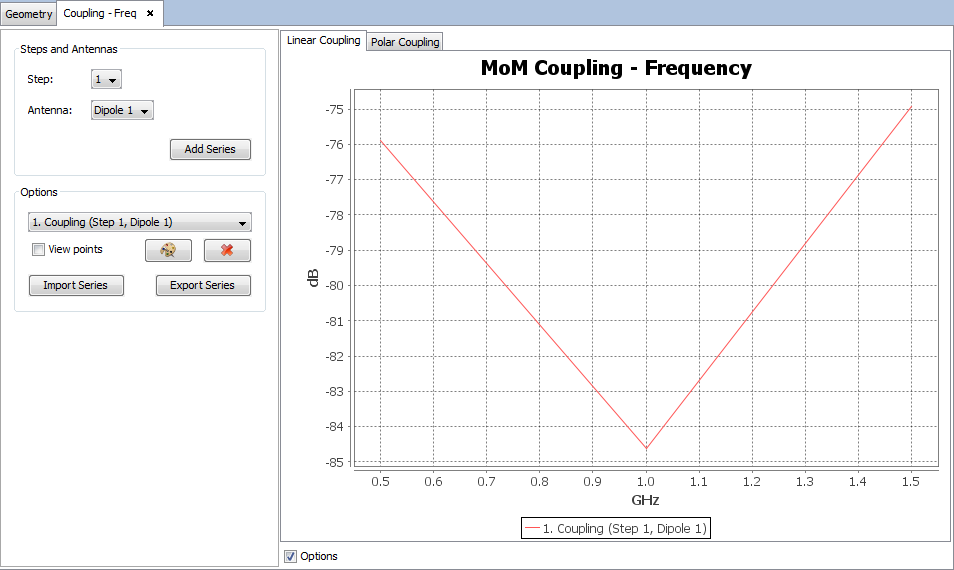
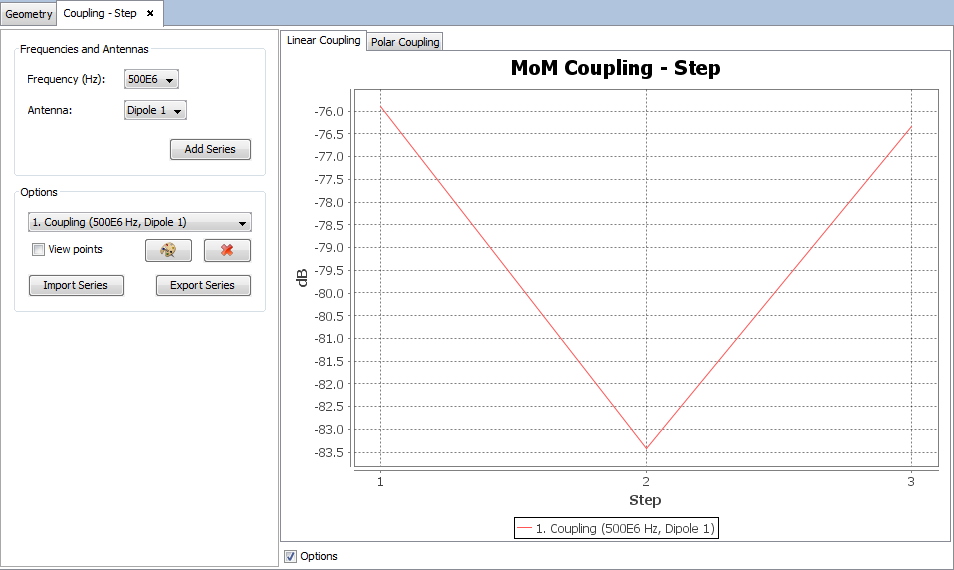
Select 'Show Results --> Coupling' option to show the value of the coupling between antennas.
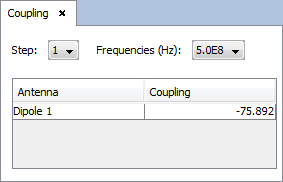
Selecting other values step or frequency parameters new table of values for the coupling between antennas and passive antenna will be shown.
On 'Show Results --> Coupling' menu, other results are present such as 'View Coupling by Step' and 'View Coupling by Frequency' and this option display the values for one selected point for each step or frequency.