/MAT/LAW14 (COMPSO)
Block Format Keyword This law describes an orthotropic solid material using the Tsai-Wu formulation that is mainly designed to model uni-directional composites. This material is assumed to be 3D orthotropic-elastic before the Tsai-Wu criterion is reached. The material becomes nonlinear afterwards.
The nonlinearity in direction 3 is the same as that in direction 2 to represent the behavior of a composite matrix material. The Tsai-Wu criterion can be set dependent on the plastic work and strain rate in each of the orthotropic directions and in shear to model material hardening. Stress based orthotropic criterion for brittle damage and failure is available. /MAT/LAW12 (3D_COMP) is an improved version of this material and should be used instead of LAW14.
Format
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /MAT/LAW14/mat_ID/unit_ID or /MAT/COMPSO/mat_ID/unit_ID | |||||||||
| mat_title | |||||||||
| E11 | E22 | E33 | |||||||
| G12 | G23 | G31 | |||||||
| B | n | fmax | |||||||
| Ef | c | ICC | |||||||
Definition
| Field | Contents | SI Unit Example |
|---|---|---|
| mat_ID | Material identifier. (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| unit_ID | Unit Identifier. (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| mat_title | Material title. (Character, maximum 100 characters) |
|
| Initial density. (Real) |
||
| E11 | Young's modulus in direction
1. (Real) |
|
| E22 | Young's modulus in direction
2. (Real) |
|
| E33 | Young's modulus in direction
3. (Real) |
|
| Poisson's ratio between directions 1 and
2. (Real) |
||
| Poisson's ratio between directions 2 and
3. (Real) |
||
| Poisson's ratio between directions 3 and
1. (Real) |
||
| G12 | Shear modulus in direction
12. (Real) |
|
| G23 | Shear modulus in direction
23. (Real) |
|
| G31 | Shear modulus in direction
31. (Real) |
|
| Stress at the beginning of composite
tensile/compressive failure in direction 1. 4 Default = 1030 (Real) |
||
| Stress at the beginning of composite
tensile/compressive failure in direction 2. 4 Default = (Real) |
||
| Stress at the beginning of composite
tensile/compressive failure in direction 3. 4 Default = (Real) |
||
| Maximum damage factor. 4 Default = 0.05 (Real) |
||
| B | Global plastic hardening
parameter. (Real) |
|
| n | Global plastic hardening
exponent. Default = 1.0 (Real) |
|
| fmax | Maximum value of the Tsai-Wu criterion
limit. 3 Default = 1010 (Real) |
|
| Reference plastic work per unit solid
volume. Default = 1.0 (in local unit system) (Real) |
||
| Yield stress in tension in direction
1. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
||
| Yield stress in tension in direction
2. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
||
| Yield stress in compression in direction
1. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
||
| Yield stress in compression in direction
2. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
||
| Yield stress in tensile shear in
direction 12. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
||
| Yield stress in compressive shear in
direction 12. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
||
| Yield stress in tensile shear in
direction 23. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
||
| Yield stress in compressive shear in
direction 23. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
||
| Fiber volume fraction. 5 Default = 0.0 (Real) |
||
| Ef | Fiber Young's modulus. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
|
| c | Global strain rate coefficient.
(Real) |
|
| Reference strain
rate. (Real) |
||
| ICC | Strain rate effect flag. 3
(Integer) |
Example (Metal)
#RADIOSS STARTER
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
/UNIT/1
unit for mat
kg cm ms
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
#- 2. MATERIALS:
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
/MAT/COMPSO/1/1
Metal
# RHO_I
.0078
# E11 E22 E33
10 100 1
# NU12 NU23 NU31
0 0 0
# G12 G23 G31
0 0 0
# SIGMA_T1 SIGMA_T2 SIGMA_T3 DELTA
1E31 1E31 1E31 0
# B n fmax Wpref
1E31 1E31 1E31 0
# sigma_1yt sigma_2yt sigma_1yc sigma_2yc
1E31 1E31 1E31 1E31
# sigma_12yt sigma_12yc sigma_23yt sigma_23yc
1E31 1E31 1E31 1E31
# ALPHA E_f c EPS_RATE_0 ICC
0 0 0 0 0
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
#ENDDATA
/END
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|Comments
- This material requires an orthotropic solid property (/PROP/TYPE6 (SOL_ORTH), /PROP/TYPE21 (TSH_ORTH) or /PROP/TYPE22 (TSH_COMP)). It can only be used with solid elements for a 3-dimensional analysis. This law is compatible with 10-node tetrahedron and 4-node tetrahedron elements. The orthotropic material directions are specified in the property entries.
- Stress-strain relation in elastic
phase.
The stresses and strains are connected as:
Where,- Strains
- Stresses
- , and
- Distortions in the corresponding material directions
Figure 1. 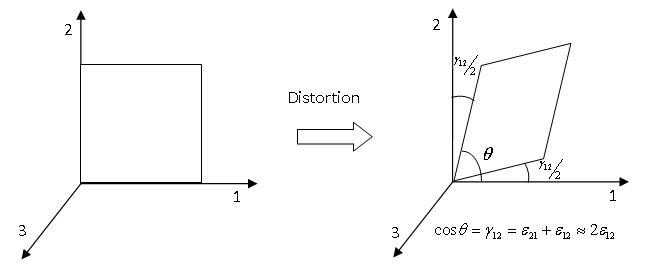
- Tsai-Wu criterionThe material is assumed to be elastic until the Tsai-Wu criterion is fulfilled. After exceed the Tsai-Wu criterion limit , the material becomes nonlinear.
- If : elastic
- If : nonlinear
Where,- Stress
in element for Tsai-Wu criterion computed as:
The coefficients of the Tsai-Wu criterion are determined from the limiting stresses when the material becomes nonlinear in directions 1, 2, 3 or 12, 23, 31 (shear) in compression or tension as:The nonlinear behavior in directions 2 and 3 is assumed to be the same to represent the composite matrix material. It is assumed that yield stresses of the composite matrix material (in directions 2 and 3) are related as:-
is the variable Tsai-Wu criterion limit
defined:Where,
- Reference plastic work
- Relative plastic work
- Plastic hardening parameter
- Plastic hardening exponent
- Reference true strain rate
- Strain rate coefficient
the maximum value of the Tsai-Wu criterion limit depends on ICC:- If ICC=1
- If ICC=2
Where,
- Stress damage
When the limiting stress value of is reached in tension, then the corresponding stress value is scaled as . The value of is updated on each time step . After reaches the value of 1 the stress in corresponding direction is set to 0. The damage is irreversible, if a value of is attained the material will not reach any lower damage value.
- Fiber reinforcement
These parameters allow the user to define additional fiber reinforcement in the 11 direction. Additional stress in direction 11 will be added equal to .