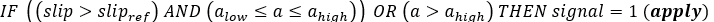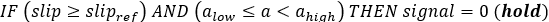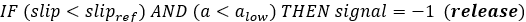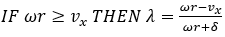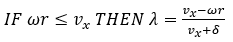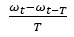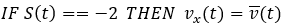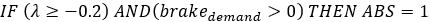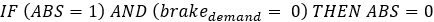Anti-lock Braking System
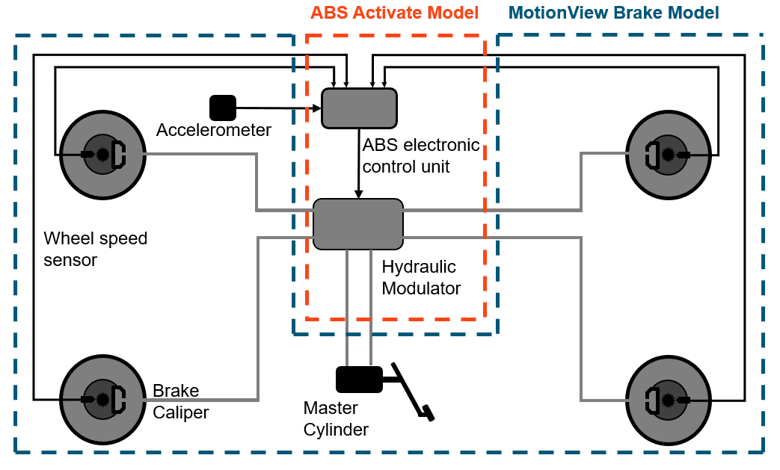
Figure 1.
The following sections describe the ABS Twin Activate Model and how to use the Assembly Wizard to build a vehicle model that includes ABS.
ABS Twin Activate Model
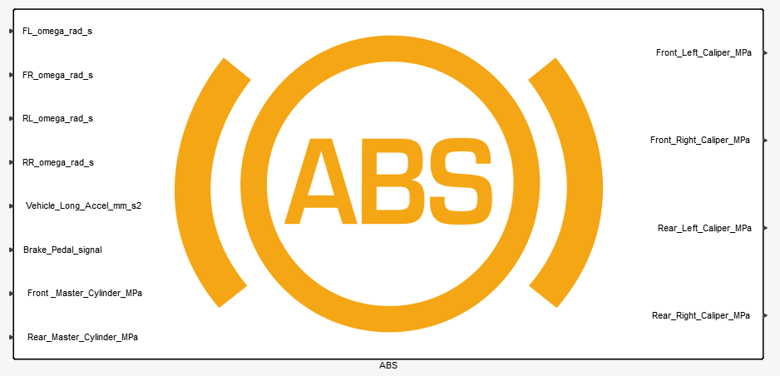
Figure 2.
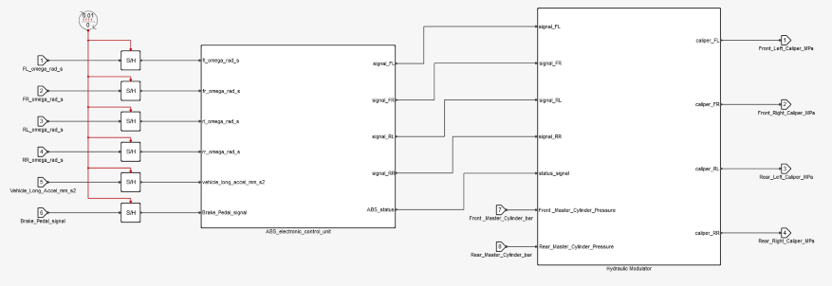
Figure 3.
- ABS Electronic Control Unit
- The ABS Electronic Control Unit estimates the wheel slips and determines whether to
modulate the hydraulic pressure and then sends control signals to the Hydraulic
Modulator.
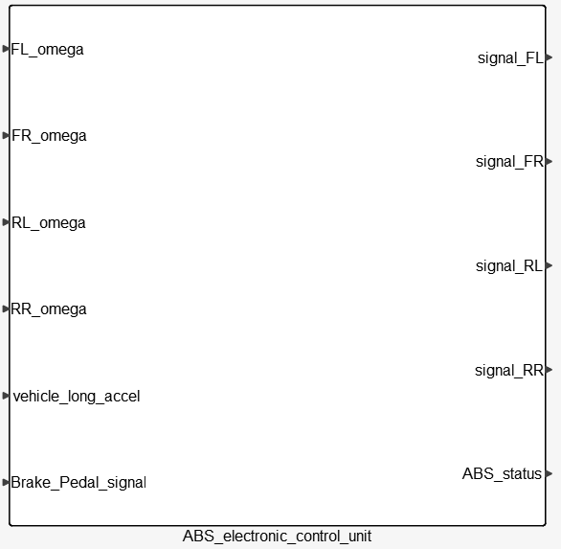
Figure 4.Most ABS control algorithms use bang-bang control abruptly switching between states. The ABS controller here switches between three states: “apply”, “hold” or “release” pressure. The controller estimates the wheel slip ratio and wheel angular acceleration and then outputs the desired valve state signal in accordance with the following algorithm:Wheel slip is estimated from the wheel rotational velocity and the vehicles longitudinal velocity as:Where: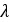 : wheel slip
: wheel slip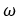 : wheels rotational velocity
: wheels rotational velocity 
 : vehicle’s longitudinal velocity
: vehicle’s longitudinal velocity 
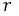 : tires radius
: tires radius 
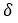 : a small number
: a small number 

Figure 5.The wheel's angular acceleration is calculated using wheels rotational velocity as: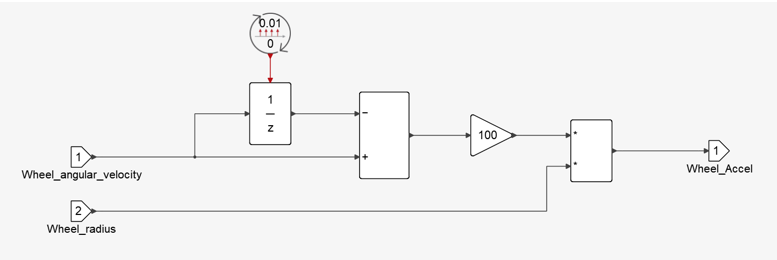
Figure 6.Where
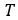 is the sampling time of sensors.The vehicle’s longitudinal velocity used in slip calculation refers is estimated from the wheel speeds and vehicle’s longitudinal acceleration.
is the sampling time of sensors.The vehicle’s longitudinal velocity used in slip calculation refers is estimated from the wheel speeds and vehicle’s longitudinal acceleration.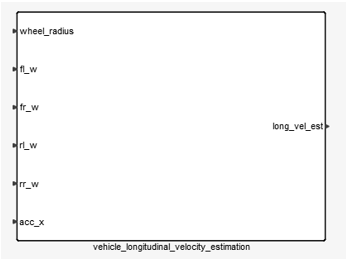
Figure 7.Each sampling instant three auxiliary signals are computed:- Average wheel speed of the four tires
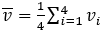
- Average wheel speed of the two non-driven tires
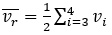
- Longitudinal Acceleration

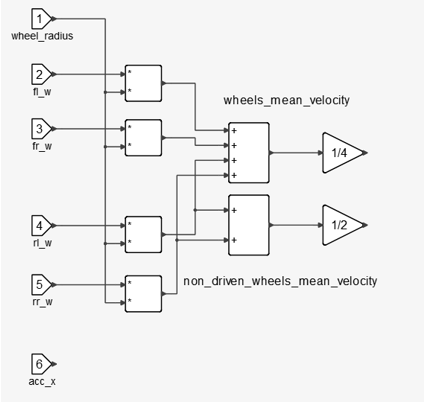
Figure 8.Estimation algorithm behavior changes according to the status of vehicle which can be represented by four values: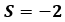 Vehicle's velocity is very low
Vehicle's velocity is very low Vehicle is accelerating
Vehicle is accelerating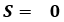 Vehicle has constant velocity or decelerating
softly
Vehicle has constant velocity or decelerating
softly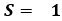 Vehicle is decelerating
Vehicle is decelerating
Status is computed based on previous step status and some threshold values alongside with some hysteresis in order to keep the algorithm stable.
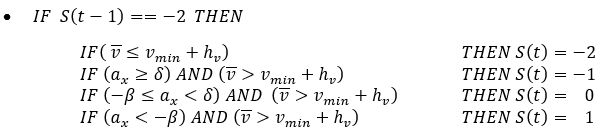
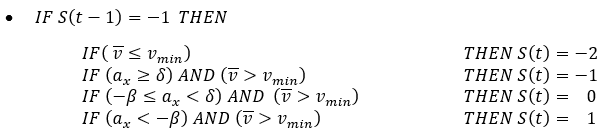

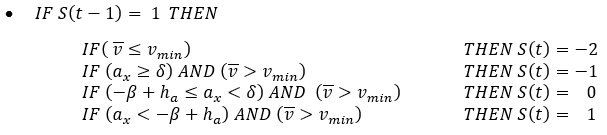
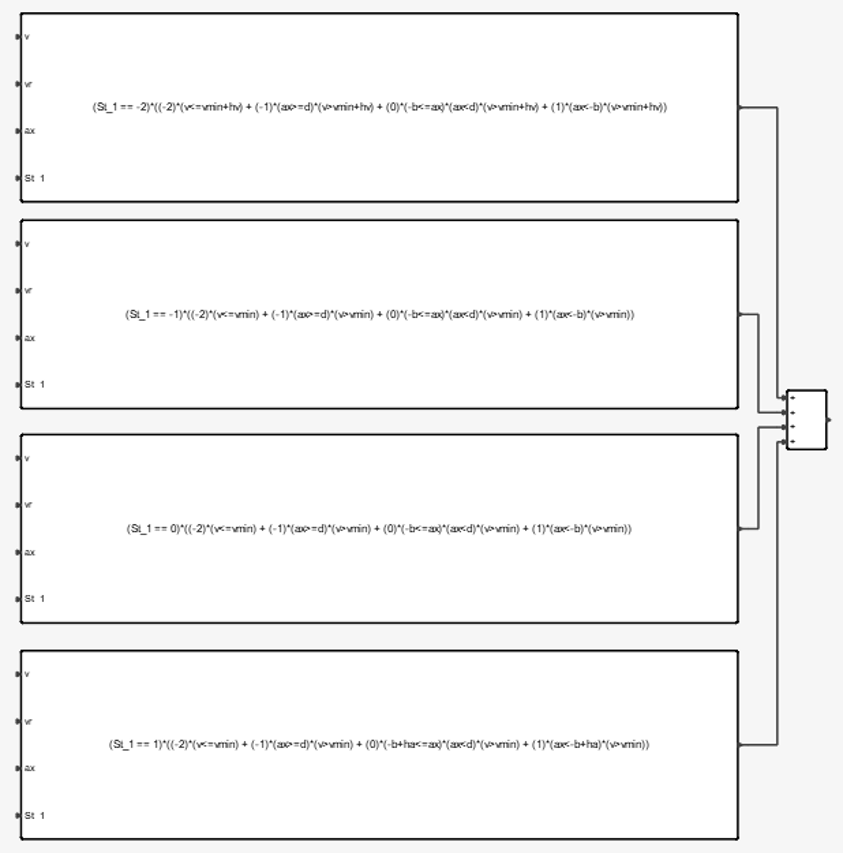
Figure 9.Velocity estimation based on the current status of the vehicle is:Finally, the ABS Electronic Control Unit is also responsible to trigger ABS. This happens after a significant amount of wheel slip occurs. Here the electronic control unit works as a switch specifying if brake pressure is controlled by ABS module.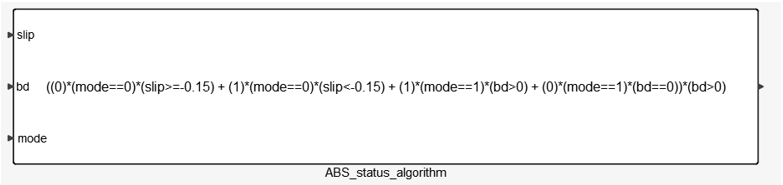
Figure 10. - Hydraulic Modulator
- The Hydraulic Modulator is the actuator of the brake system. When a signal is
generated, it’s responsible for changing pressure according to the signal. In normal
conditions
 master cylinders pressure is acting on calipers. When ABS
is activated
master cylinders pressure is acting on calipers. When ABS
is activated 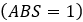 caliper pressure is reduced, hold, or increased at a
certain rate.
caliper pressure is reduced, hold, or increased at a
certain rate. 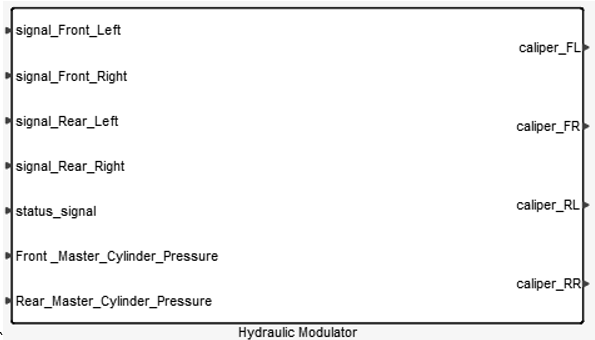
Figure 11.Pressure rate is modeled in Twin Activate as a first order transfer function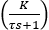 where
where 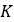 denotes the magnitude of pressure change rate and
denotes the magnitude of pressure change rate and 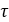 is the time delay of the valve to reach its steady
condition.
is the time delay of the valve to reach its steady
condition. 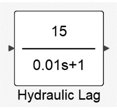
Figure 12.Finally, an integrator is used in order to change the applied pressure on the caliper. This integrator is simulating caliper’s pressure, so it needs to be correctly initialized and saturated. For its initialization an event trigger is used which tracks the activation of ABS. For its saturation an anti-windup integrator was designed so the ABS cannot exceed master cylinder pressure given from the driver.
Figure 13.
Create a Vehicle Model with ABS
- Load the MBD-Vehicle Dynamics Tools preference file ()
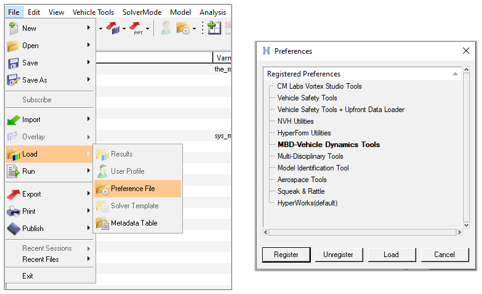
Figure 14. - From the Model tab, select the Assembly Wizard.
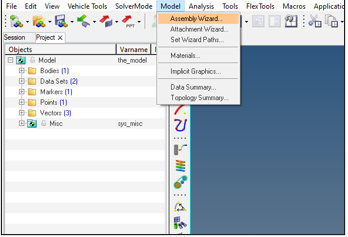
Figure 15. - On Page 8 of the dialog, select the Anti-Lock Brake System.
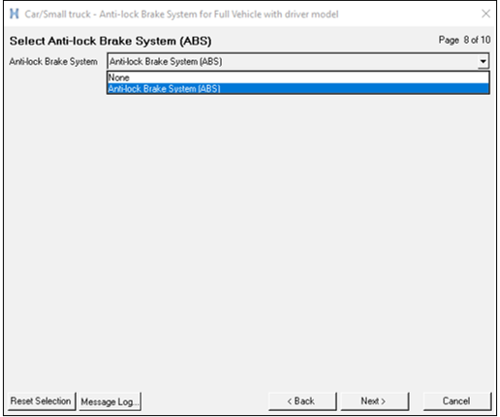
Figure 16.
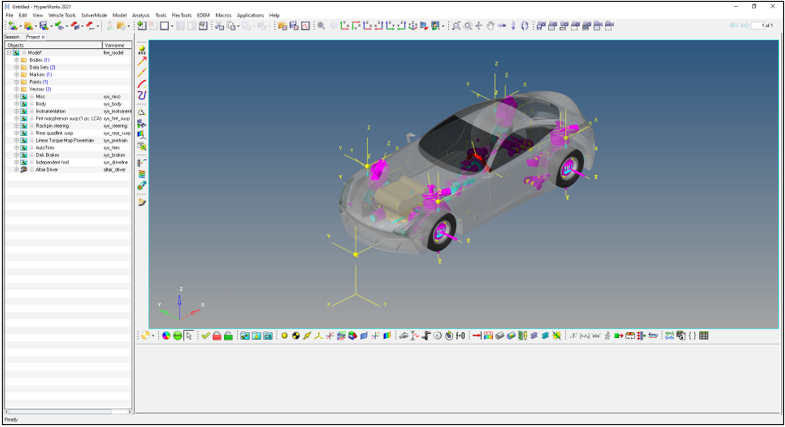
Figure 17.
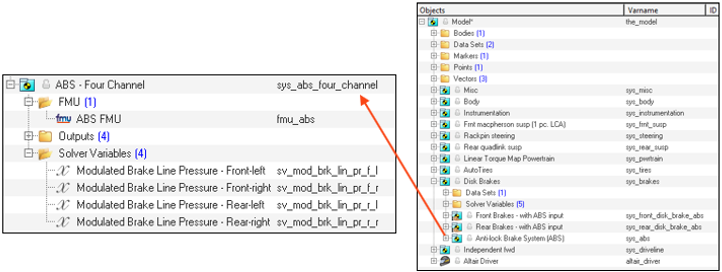
Figure 18.