AbsoluteSensor
Measure absolute kinematic quantities of frame connector
![]()
Library
Modelica/Mechanics/MultiBody/Sensors
Description
Absolute kinematic quantities of frame_a aredetermined and provided at the conditional output signal connectors.For example, if parameter "get_r = true", the connector"r" is enabled and contains the absolute vector from the world frameto the origin of frame_a. The following quantities can be providedas output signals:
- Absolute position vector (= r)
- Absolute velocity vector (= v)
- Absolute acceleration vector (= a)
- Three angles to rotate world frame into frame_a (= angles)
- Absolute angular velocity vector (= w)
- Absolute angular acceleration vector (= z)
Via parameter resolveInFrame it is defined, in which framea vector is resolved:
| resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA. | Meaning |
|---|---|
| world | Resolve vectors in world frame |
| frame_a | Resolve vectors in frame_a |
| frame_resolve | Resolve vectors in frame_resolve |
If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA.frame_resolve, the conditional connector"frame_resolve" is enabled and the vectors are resolved in the frame, towhich frame_resolve is connected. Note, if this connector is enabled, it mustbe connected.
In the following figure the animation of an AbsoluteSensorcomponent is shown. The light blue coordinate system isframe_a and the yellow arrow is the animated sensor.
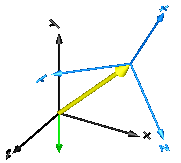
Velocity, acceleration, angular velocity and angular acceleration aredetermined by differentiating them in the world frame and then transformingthem in to the frame defined by resolveInFrame.
For example, if resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA.frame_a, then
v0 = der(frame_a.r0); v = resolve2(frame_a.R, v0);
is returned, i.e., the derivative of the absolute distance from theworld frame to the origin of frame_a, resolved in frame_a.
The cut-force and the cut-torque in frame_resolve arealways zero, whether frame_resolve is connected or not.
If get_angles = true, the 3 angles to rotate the worldframe into frame_a along the axes defined by parameter sequenceare returned. For example, if sequence = {3,1,2} then the world frame isrotated around angles[1] along the z-axis, afterwards it is rotatedaround angles[2] along the x-axis, and finally it is rotated aroundangles[3] along the y-axis and is then identical to frame_a.The 3 angles are returned in the range
-p <= angles[i] <= p
There are two solutions for "angles[1]" in this range.Via parameter guessAngle1 (default = 0) thereturned solution is selected such that |angles[1] - guessAngle1| isminimal. The absolute transformation matrix of frame_amay be in a singular configuration with respect to "sequence", i.e.,there is an infinite number of angle values leading to the same absolutetransformation matrix. In this case, the returned solution isselected by setting angles[1] = guessAngle1. Then angles[2]and angles[3] can be uniquely determined in the above range.
The parameter sequence has the restriction thatonly values 1,2,3 can be used and that sequence[1] ≠ sequence[2]and sequence[2] ≠ sequence[3]. Often used values are:
sequence = {1,2,3} // Cardan or Tait-Bryan angle sequence = {3,1,3} // Euler angle sequence = {3,2,1}Parameters

| Name | Label | Description | Data Type | Valid Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
mo_animation | animation | = true, if animation shall be enabled (show arrow) | Scalar | true |
mo_resolveInFrame | resolveInFrame | Frame in which vectors are resolved (world, frame_a, or frame_resolve) | Structure | |
mo_resolveInFrame/choice1 | Resolve in world frame | Number | 0 | |
mo_resolveInFrame/choice2 | Resolve in frame_a | Number | 0 | |
mo_resolveInFrame/choice3 | Resolve in frame_resolve (frame_resolve must be connected) | Number | 0 | |
mo_get_r | get_r | = true, to measure the absolute position vector of the origin of frame_a | Number | 0 |
mo_get_v | get_v | = true, to measure the absolute velocity of the origin of frame_a | Number | 0 |
mo_get_a | get_a | = true, to measure the absolute acceleration of the origin of frame_a | Number | 0 |
mo_get_w | get_w | = true, to measure the absolute angular velocity of frame_a | Number | 0 |
mo_get_z | get_z | = true, to measure the absolute angular acceleration of frame_a | Number | 0 |
mo_get_angles | get_angles | = true, to measure the 3 rotation angles | Number | 0 |
mo_sequence | sequence | If get_angles=true: Angles are returned to rotate world frame around axes sequence[1], sequence[2] and finally sequence[3] into frame_a | Vector of size 3 | |
mo_guessAngle1 | guessAngle1 | If get_angles=true: Select angles[1] such that abs(angles[1] - guessAngle1) is a minimum | Scalar |

| Name | Label | Description | Data Type | Valid Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
mo_arrowDiameter | arrowDiameter | Diameter of absolute arrow from world frame to frame_a | Scalar | |
mo_arrowColor | arrowColor | Color of absolute arrow from world frame to frame_b | Vector of size 3 | |
mo_specularCoefficient | specularCoefficient | Reflection of ambient light (= 0: light is completely absorbed) | Scalar |

| Name | Label | Description | Data Type | Valid Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
mo__nmodifiers | Number of Modifiers | Specifies the number of modifiers | Number | |
mo__modifiers | Modifiers | Add new modifier | Structure | |
mo__modifiers/varname | Variable name | Cell of strings | ||
mo__modifiers/attribute | Attribute | Cell of strings | 'start' | |
mo__modifiers/value | Value |
Ports
| Name | Type | Description | IO Type | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
frame_a | implicit | Coordinate system a of which the absolute kinematic quantities are measured | input | 1 |
Port 2 | implicit | Absolute position vector frame_a.r_0 resolved in frame defined by resolveInFrame | output | mo_get_r |
Port 3 | implicit | Absolute velocity vector | output | mo_get_v |
Port 4 | implicit | Absolute acceleration vector | output | mo_get_a |
Port 5 | implicit | Angles to rotate world frame into frame_a via 'sequence' | output | mo_get_angles |
Port 6 | implicit | Absolute angular velocity vector | output | mo_get_w |
Port 7 | implicit | Absolute angular acceleration vector | output | mo_get_z |
Port 8 | implicit | If resolveInFrame = Types.ResolveInFrameA.frame_resolve, the output signals are resolved in this frame | output | mo_resolveInFrame.choice3 |