Create Table
Table is used to define the varying or dependent data, which can further be used to create dynamic or distributed loads and to define different material behavior.
Table data may vary depending on,
- Time
- Space or location
- Physical parameters (Ex: Temperature, Pressure)
- Boundary conditions
Description
- Users can create dynamic or distributed boundary conditions by defining the tables.
- Also, Material with varying properties can be created by defining the tables.
- Table Type: Left side panel will list all the table type supported and it will depend on the source from where this dialog is launched. For Example: Pressure supports (XYZ Vs value) or (Frequency/Time Vs value) and Material's Youngs Modulus field will support (Stress,Strain,Temperature) input.
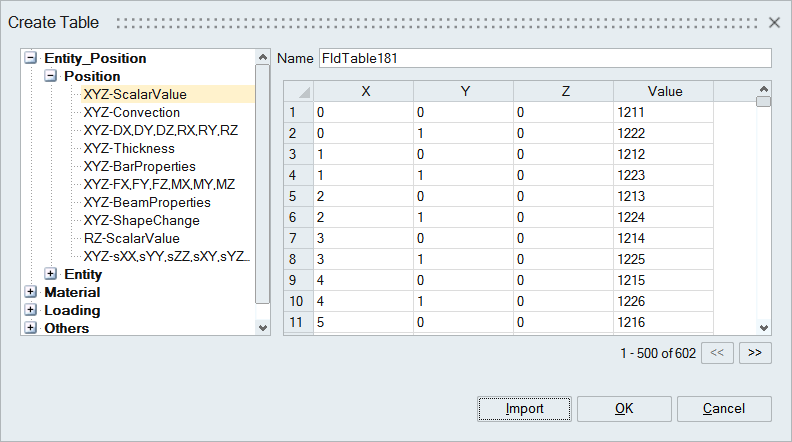
Working with Table Data:
- Pressing Enter in the previous row will automatically add a new row.
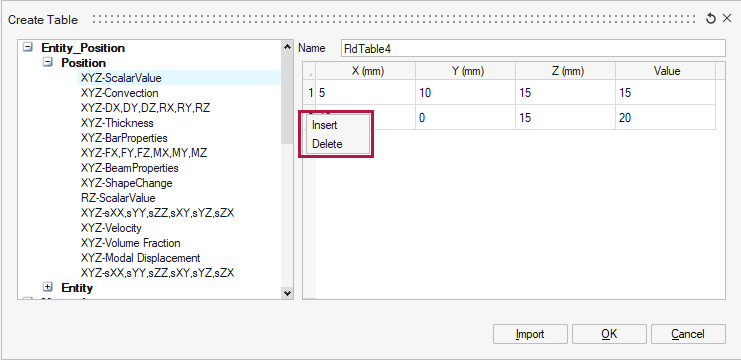
- User can also add or delete the row from the table by “Right click on Table row
header > Insert/Delete” options.
- Users can import their field data from the .csv, .dat or .txt files and the same can be exported as (*.csv / *.dat) file by using "Export" option in table right click menu.
- For spatially varying tables (Ex: X, Y, Z - Force Components), users can plot the Contour in table right click menu.
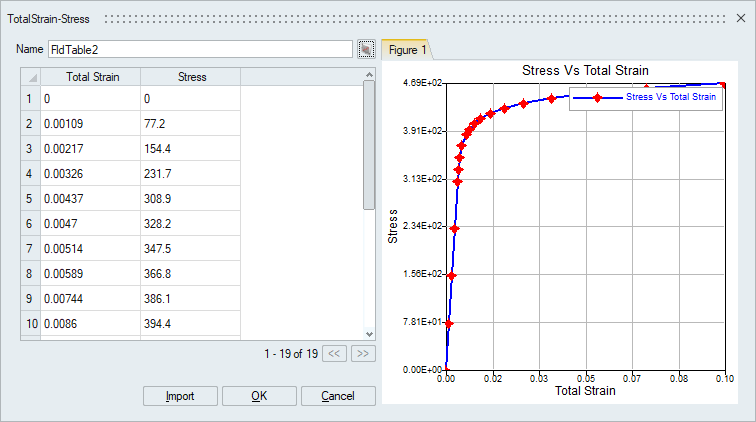
- Users can visualize their tabular data in 2D graph using the Plot Graph option in the table dialog. Note: The Preference | Result - "Enable new graphing tool" should be turned ON to enable this option.
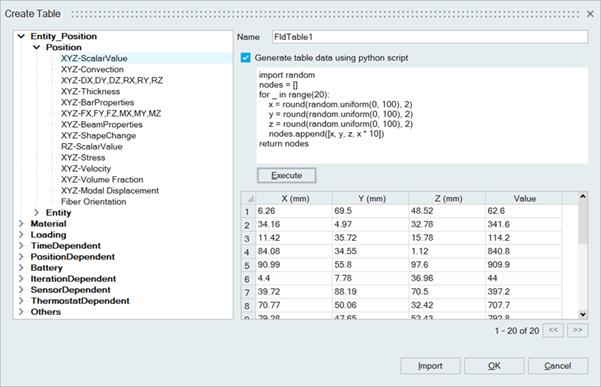
- Generate table data using python script: User can generate table data using python
script. The script output must be a list of lists where each inner list represents a
single row in the table.

Note:
- When the table is defined to vary the temperature in any boundary conditions, the temperature amplitude values are also scaled based on the unit system to accommodate the unit conversion across different unit systems.
- If the temperature value is changed in the boundary condition, users need to define the Amplitude table again for the corresponding temperature value.