With embedding, you can include information created in one diagram, referred to as the source diagram, in one or more other diagrams, referred to as the destination diagrams. Each time the source diagram changes, the changes are propagated in the destination diagrams. There can only be a single compound block at the top level of the source diagram; however, there can be any number of noncomputational blocks — such as label and comment blocks — at the top level.
When you embed a diagram, a read-only version of the diagram is inserted in the destination diagram along with a link to the source diagram. You can drill into the embedded diagram just as you would a compound block. You can even override the read-only status of the embedded diagram and make changes directly to it. These changes, however, are not saved until you execute File > Save Embedded.
If you want to restrict access to the embed block, you can apply protection to it.
To embed a block diagram
Embedding a diagram involves dragging an embed block into the work area and setting up the link to the source file. Before you can embed a diagram, check that its top level is a single compound block. If it’s not, use Edit > Create Compound Block to create one.
1. Open the destination diagram and move to the diagram level where you want to insert an embedded diagram.
2. Insert an embed block.
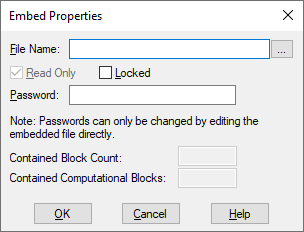
3. Right-click the embed block, or choose Edit > Block Properties and click the block.

4. In the File Name box, do one of the following:
•Enter the name of the diagram file to be embedded. If you do not see the file you want, click … to search for it.
•Enter a path alias as $(path-alias). You define path aliases with Edit > Preferences.
The dialog also lists the total number of blocks contained in the embedded diagram, along with the number of computational blocks.
5. Click OK, or press ENTER.