Release Notes: Altair Feko 2025.1
Altair Feko 2025.1 is available with new features, corrections and improvements. Altair Feko 2025.1 is a major release. It can be installed alongside other instances of Altair Feko.
Feko is a powerful and comprehensive 3D simulation package intended for the analysis of a wide range of electromagnetic radiation and scattering problems. Applications include antenna design, antenna placement, microstrip antennas and circuits, dielectric media, scattering analysis, electromagnetic compatibility studies including cable harness modelling and many more.
WinProp is the most complete suite of tools in the domain of wireless propagation and radio network planning. With applications ranging from satellite to terrestrial, from rural via urban to indoor radio links, WinProp’s innovative wave propagation models combine accuracy with short computation times.
WRAP is a comprehensive tool for electromagnetic propagation, antenna collocation and spectrum management. WRAP combines propagation analysis, often over large areas with many transmitters and receivers, with system analysis to include complex non-linear equipment properties.
Highlights of the 2025.1 Release
The most notable extensions and improvements to Feko, WinProp and WRAP in the 2025.1 release.
Salient Features in Feko
- A sinuous spiral antenna was added to the Component library in CADFEKO. The antenna model is parametrised with six design variables.
Figure 1. The Sinuous Antenna that is now available in the Component Library. 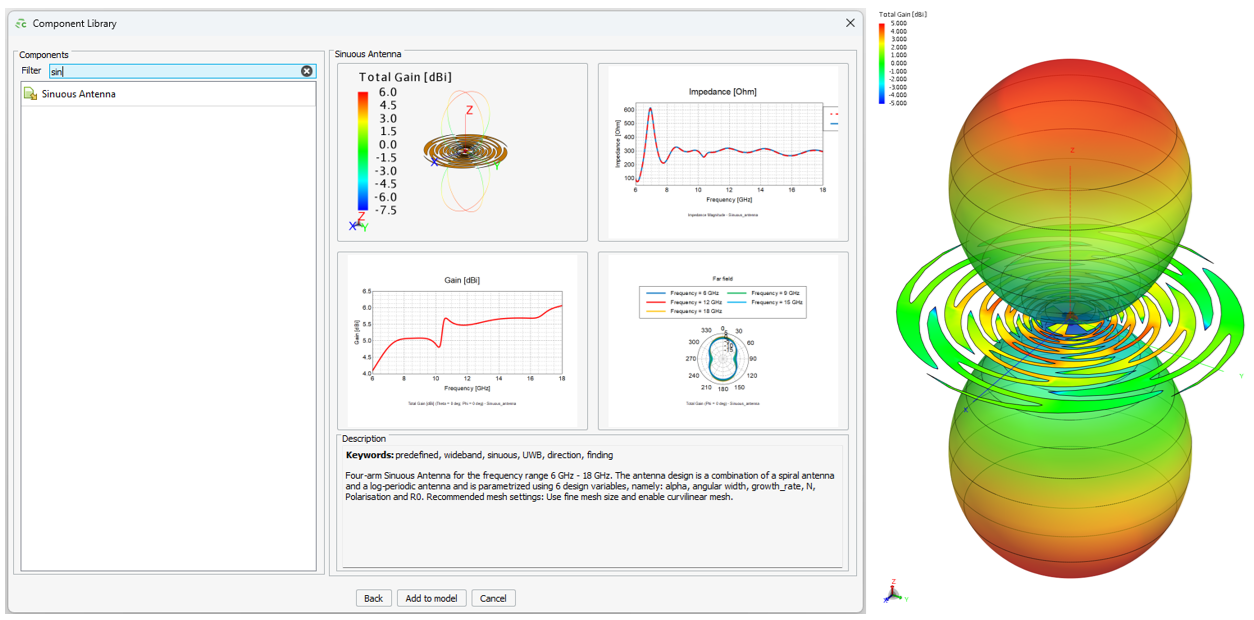
- A new iterative solver (FGMRES1) was
added for the MLFMM, hybrid FEM/MoM, hybrid FEM/MLFMM and FEM simulations. This iterative
solver provides an improved rate of convergence and monotonically decreasing residuum.
Figure 2. A comparison of FGMRES) and RBi-CGstab for a Cassegrain reflector (35 GHz) at 12U CubeSat. 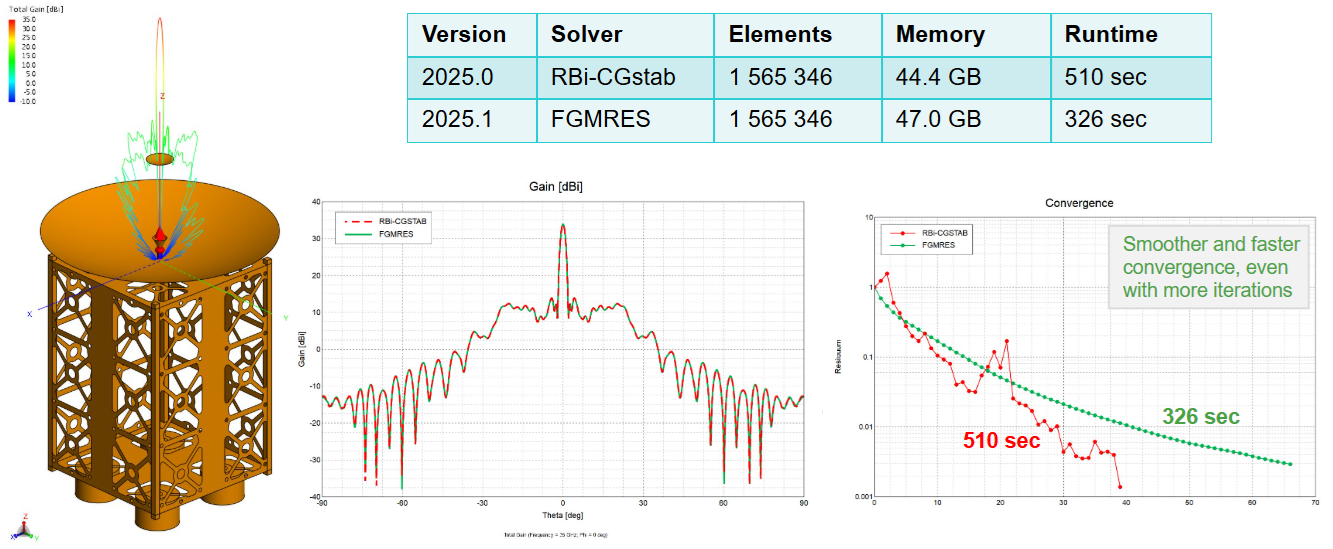
- A new Domain-Level Preconditioner (DLP) was added for the MLFMM that has repeatable memory requirements and is more efficient for massive parallel scaling.
- The speed and accuracy for RL-GO was improved. Significant run-time reductions
(dependent on the example, several orders of magnitude) and accuracy improvements when
incident plane waves are used as excitation.
Figure 3. Examples showing the run-time reductions and accuracy improvements when incident plane waves are used as excitation. 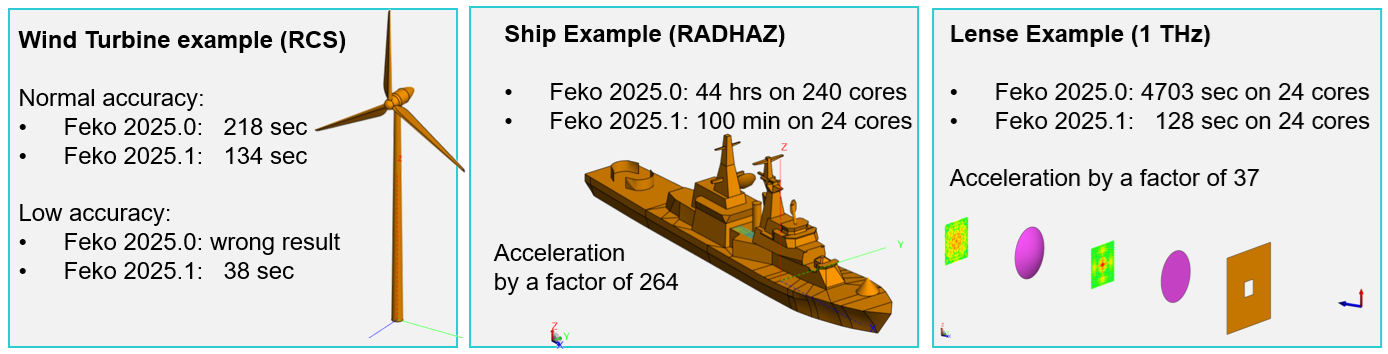
- Support was added for a FEM distributed line port that defines a Norton equivalent
circuit port in a FEM region. The two terminals of the port are formed by two N-point
polylines, defining the start and end points, respectively, of N discrete lines.
- The distributed FEM line port can be used as a replacement for the FEM line port, where a distributed excitation current or lumped-element loading along two selected edges (a positive edge and a negative edge) in the FEM model is preferable to a single point excitation/load.
- The distributed FEM line port may also be used as a replacement for waveguide/modal or microstrip-port excitations/loads on structures such as coaxial lines and microstrips where a uniformly distributed current or load is preferred.
Figure 4. A dielectric resonator antenna excited using a FEM modal port, a distributed FEM line port and a FEM line port respectively. S-parameters computed using the distributed FEM line port impedance agree far better with the FEM modal excitation, but the port may be used to apply a lumped excitation or load rather than a mode-based excitation/termination. 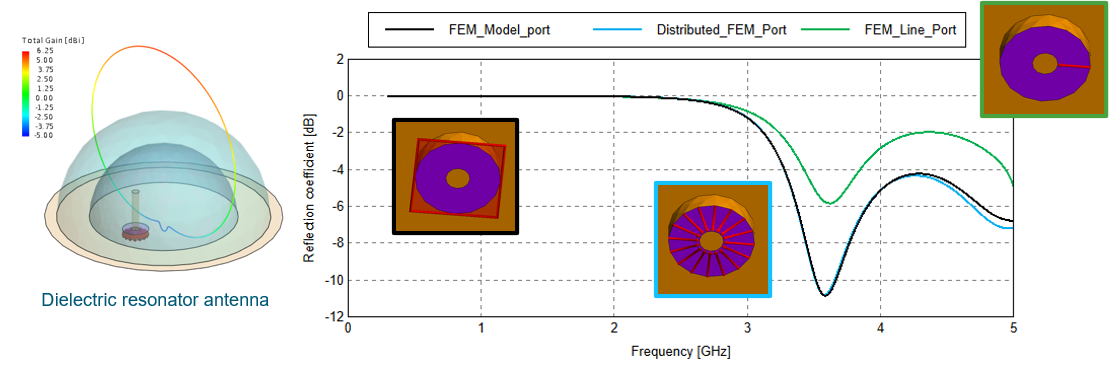
- A MoM surface or region can now be set to perfect magnetic conductor (PMC), in a similar
way to PEC. Support was also added to treat dielectric boundary faces on the outside of
FEM regions as perfect magnetic conductors (PMC’s) rather than absorbing boundaries when
decoupled from the MoM.
Figure 5. An example of where the boundaries of PCB cutout are modeled as perfect magnetic conductor. The S-parameter comparison in frequency range 50 MHz – 20 GHz. FEM using distributed line ports (decoupled from MoM, PMC BC), FEM using waveguide ports (decoupled from MoM, PMC BC) and SEP using waveguide ports (bounded by MoM PMC triangles) are compared. 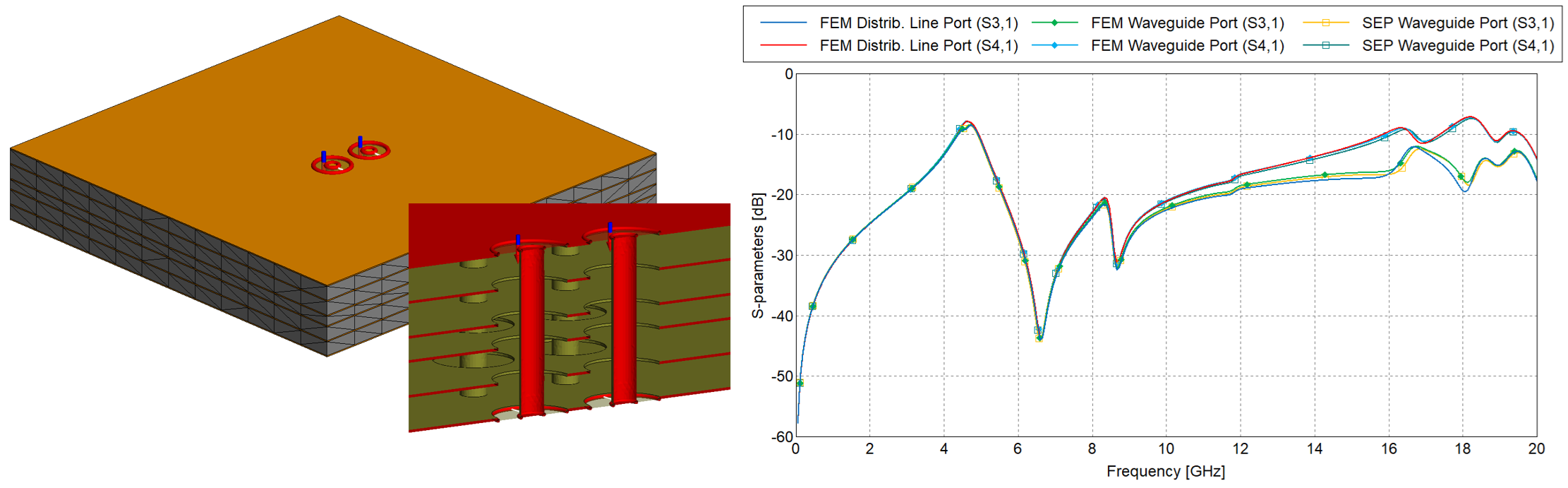
- The robustness of the hybrid Characteristic Mode Analysis (CMA) tracker was enhanced
using the linear sum assignment optimization algorithm and the resonant frequency
estimates are now written to the .out file.
Figure 6. An example of a CMA analysis for a conservation Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV). 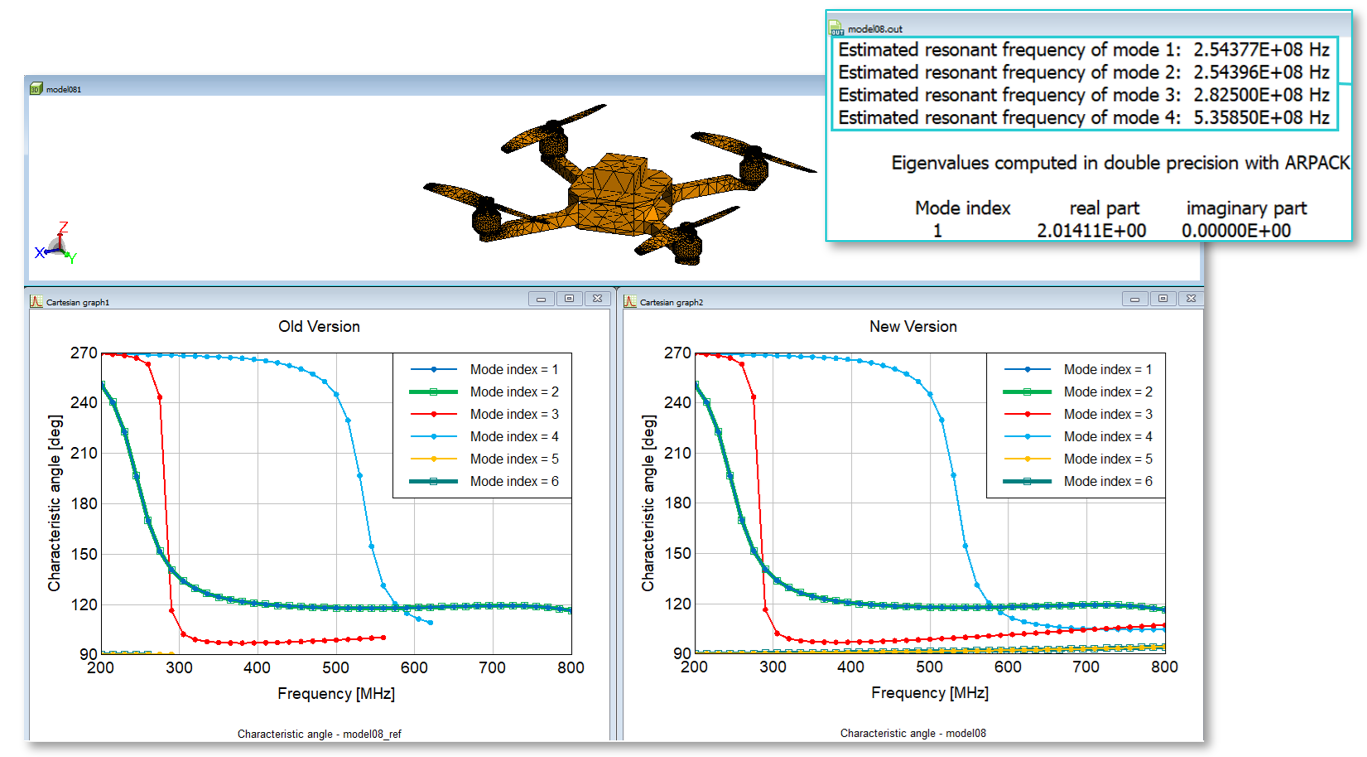
- The Feko GUI components now support remote execution using PowerShell-Invoke. The setting is available on the Launch Options dialog.
- The following extensions were made to the meshing workflow in CADFEKO:
- Simulation mesh from unlocked and locked parts are now loaded from legacy
.cfxfiles. No re-meshing is done after loading the model until changes are made. This behaviour is the same as in legacy CADFEKO. - Added the Create Mesh button where the meshing scope can be
specified on the Create Mesh dialog. Specifying the scope allows
you only to mesh a selected entity or multiple selected entities. All parts in a mesh
group are meshed.
Figure 7. An example showing that only the selected part is meshed. 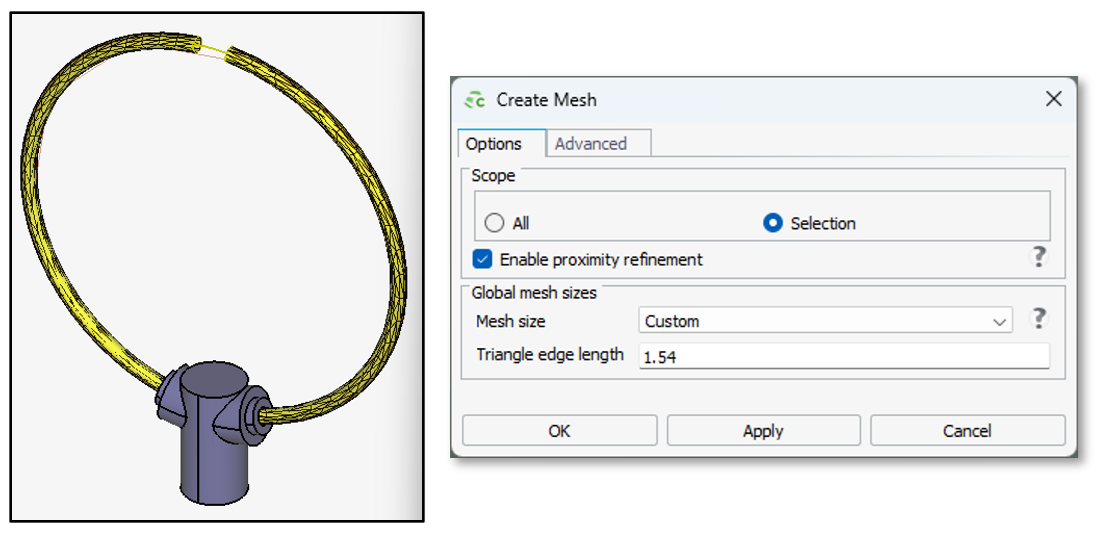
- Added the option to activate and deactivate smart refinement to account for the
proximity of objects when meshing a model or a specific primitive part. In previous
CADFEKO versions, the impact of proximity of parts was
always considered.Objects for which proximity meshing is disabled are meshed in isolation, and the mesh and characteristics of nearby parts will have no effect on the meshing. You can control the application of proximity meshing during meshing (global) for a specific part and can also define the default behaviour to be used for new models.
Figure 8. An example showing the effect of proximity refinement. 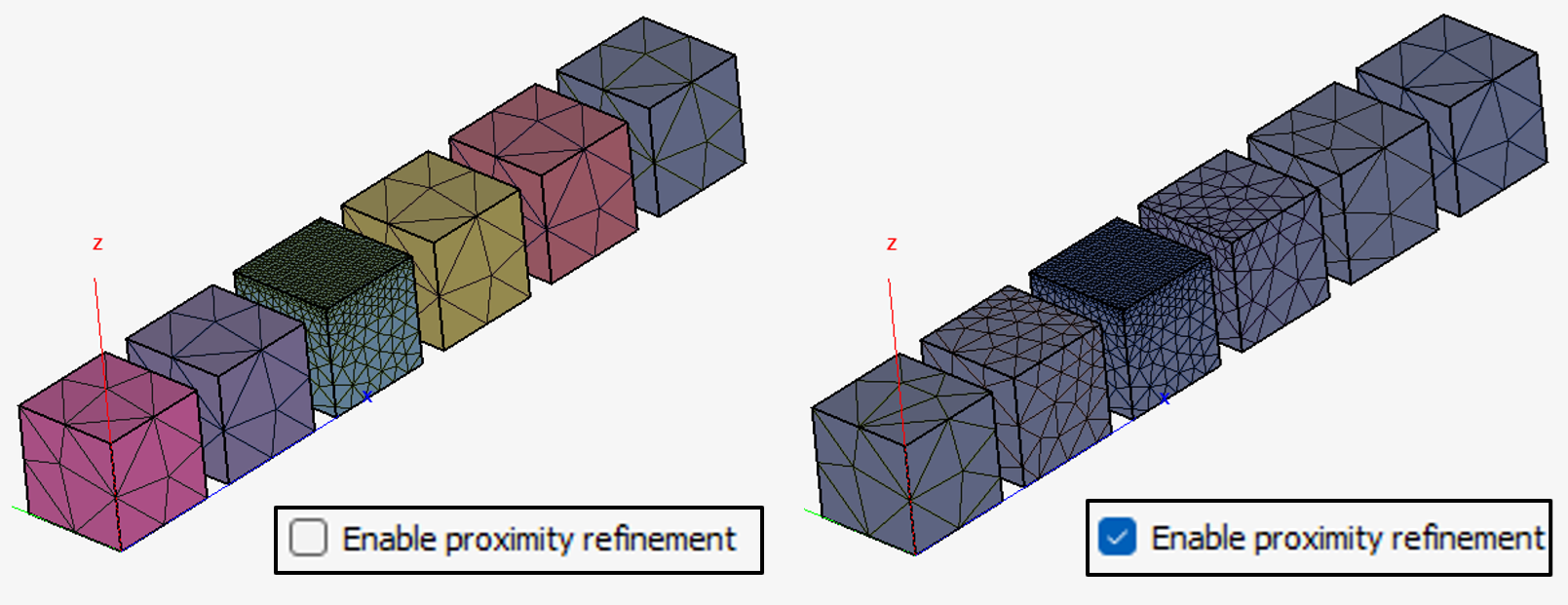
- You can now choose to terminate an ongoing meshing process. For larger meshes it may take time for mesher to be stop. A progress bar is shown to indicate that the termination process is ongoing.
- Simulation mesh from unlocked and locked parts are now loaded from legacy
Salient Features in WinProp
- Beam steering was improved for Non-Line-of-Sight (NLOS) scenarios to determine the
optimum direction that maximises the received power. The API now also supports beam
steering in 5G networks based on phased array antennas, where the antenna array forms a
focused beam in the desired direction and can track the movement of users.
Figure 9. An example showing the beam steering for a user along a trajectory. The bottom images show the beam steering in NLOS scenarios. 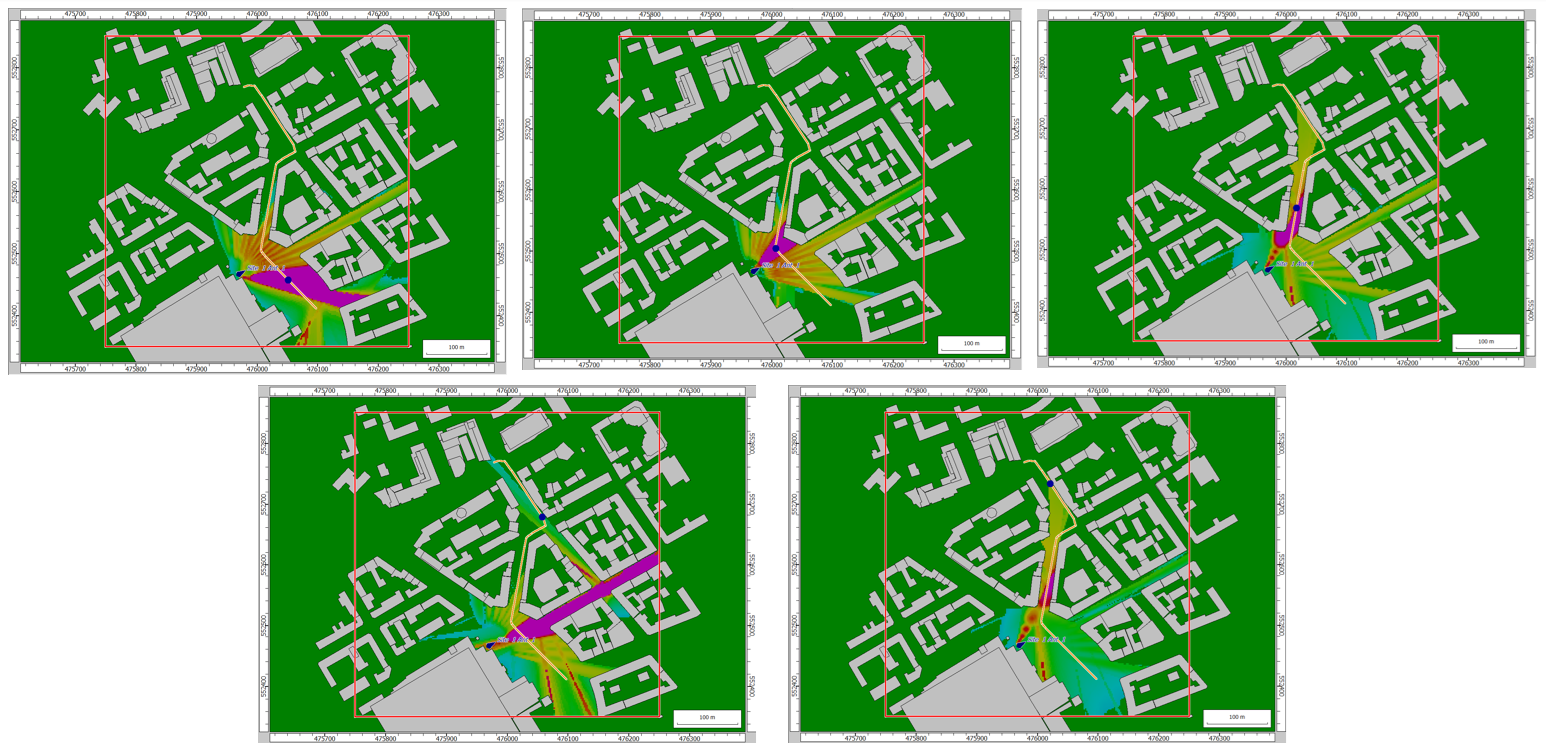
- The Standard Ray Tracing (SRT) in ProMan was extended for
computing reflections at pixel topography. You can now define tiles on which a reflection
is being searched for. For each tile at maximum one reflection can be searched for. There
can be multiple reflections between transmitter and receiver at multiple tiles.
Figure 10. An example where reflections are computed on pixel topography for SRT. 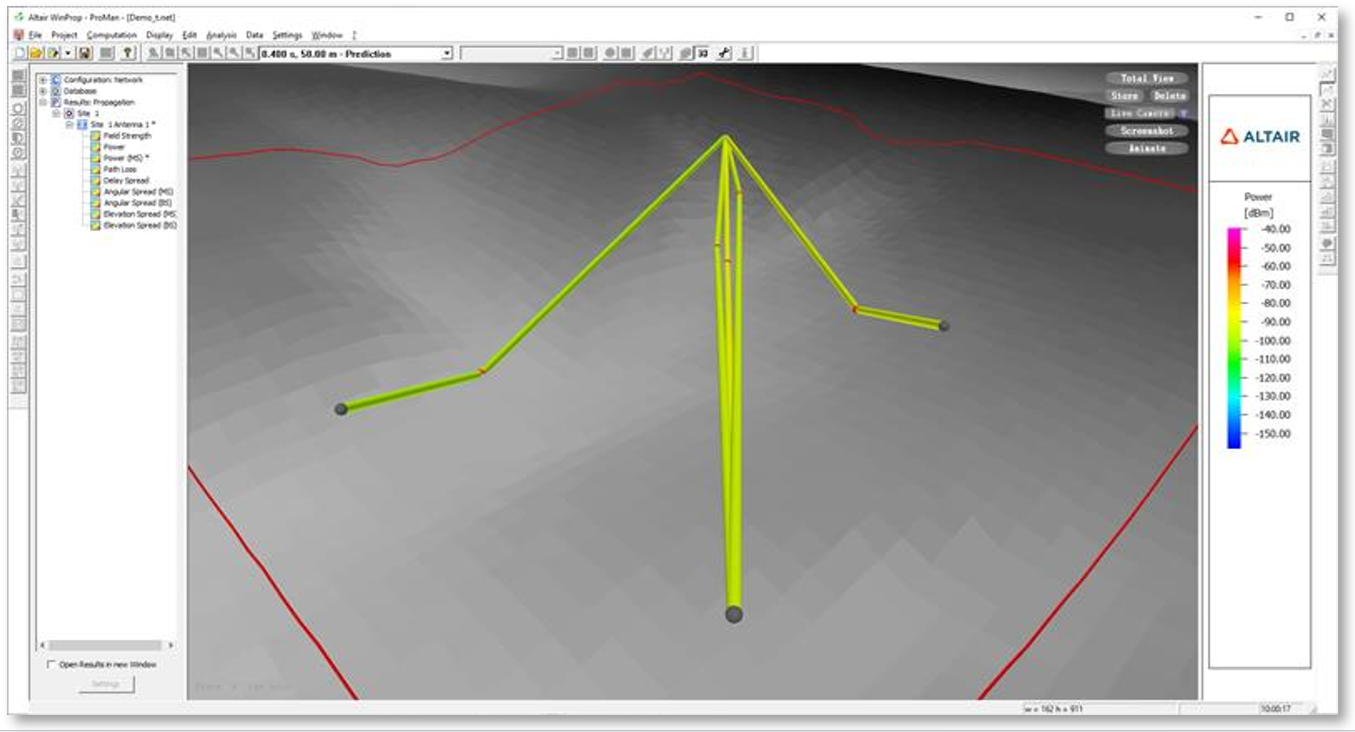
- The FMCW radar post-processing algorithms were extended to include:
- Constant False Alarm Rate (CFAR)
- CFAR is a widely used algorithm in radar systems for target identification while minimizing false positives. It adaptively sets the detection thresholds based on the surrounding noise to maintain a constant false alarm rate.
- MUSIC (Multiple Signal Classification)
- MUSIC is a high-resolution subspace-based algorithm used for angle-of-arrival (AOA) estimation. It can estimate the angular directions (azimuth or elevation) of targets with high accuracy. However, it is not always necessary for 4D radar due to its computational complexity, which makes it less practical for real-time systems compared to FFT-based AOA estimation.
Figure 11. An example of an 8x8 MIMO radar with the following configuration for range angle. 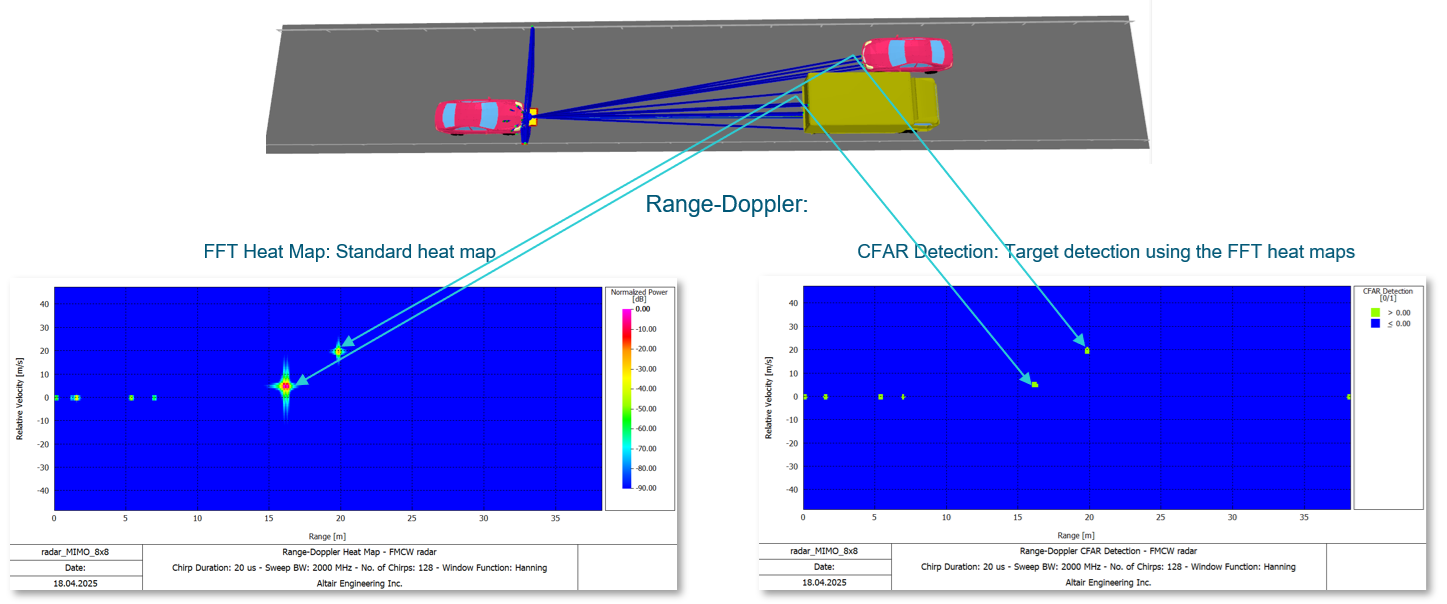
- The handling of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) using bistatic RCS computed in
Feko was improved for a single incidence direction. You can
compute the RCS for the desired incidence angle in Feko and
then set the azimuth adjustment correctly in ProMan.
Figure 12. An example where the RCS was computed in Feko and then the azimuth was adjusted in ProMan. 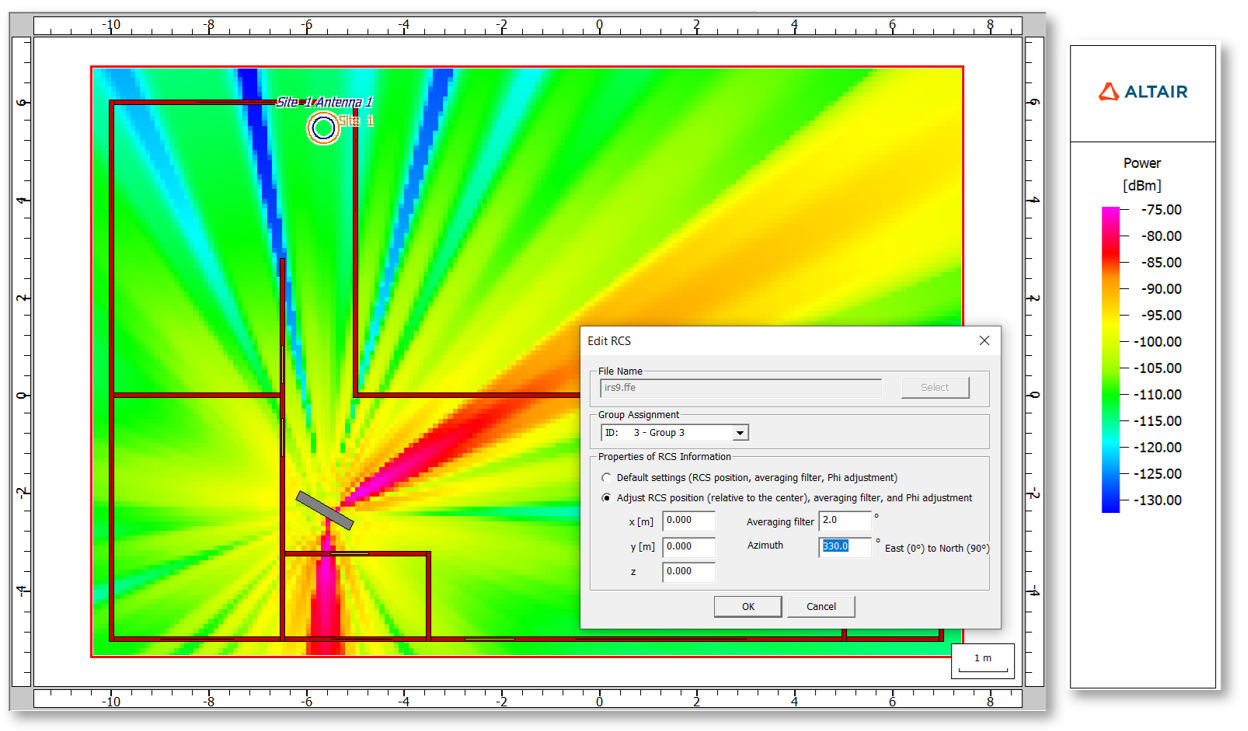
Salient Features in WRAP
- Support was added for Microsoft SQL Server 2022 as a database engine.
- A license pool for API licenses has been added. A single license is checked out at the start of WRAP. At exit, WRAP will check in all of the checked-out licenses. Using the license pool will let the API calls execute immediately, without any lengthy license checkout, if a license is available.
- Units can now be converted between m and feet and between km and NM on the Radio Calculator dialog.
- When saving .wpr/.wpe project files, information is written to a log file (which includes error information).
- The British National Grid was added to the recognized coordinate systems. Area patches
in Shapefile format may now use coordinate systems other than Lat-Long WGS84, if a
standard project file (.prj) is supplied.
Figure 13. Samples from building height vector data based on GBNG, converted to the WRAP format. 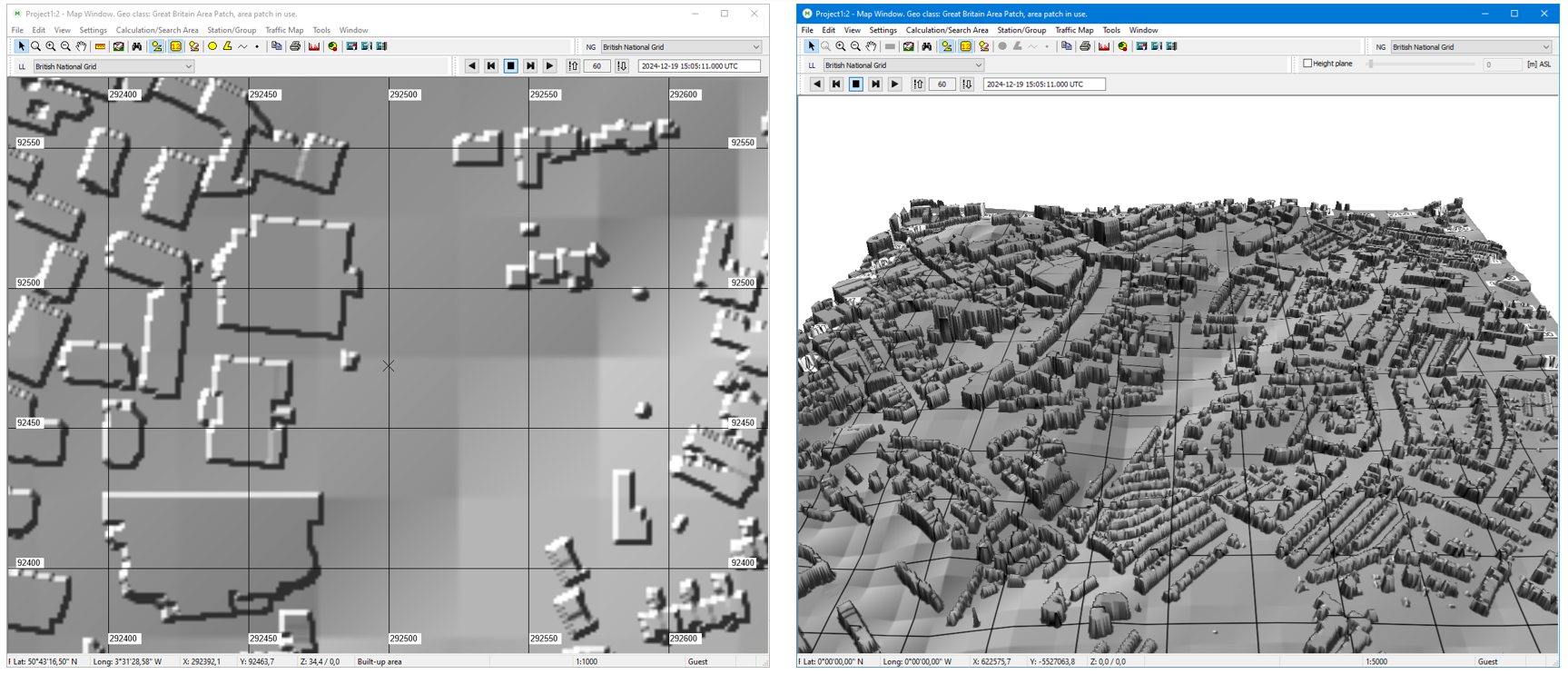
- Added support for the import of Ofcom WTR Database.
- Review date has been added to the following:
- Allotments: The review date is included in allotment searches both from GUI and API
- Equipment: The review date is added for all types of Equipment and included in their associated search functions.
- Added the feature to allow the user to save allotments, stations and equipment to read-only databases using the API. Also, the .wpc file has been extended to handle preferred allotments and multiple modes on equipment.
- The format of SMADEF has evolved and with that the structure in the SMIR database. The SMADEF43 version in WRAP was updated to support version 4.3.3.
Feko 2025.1 Release Notes
The most notable extensions and improvements to Feko are listed by component.
CADFEKO
Features
- Added the ability to only mesh selected parts.
- Introduced a new option for controlling proximity refinement when meshing multiple geometry parts. Proximity refinement can be globally enabled or disabled from the mesh settings dialog or can be enabled or disabled per part. By default, proximity refinement meshing is disabled for locked parts.
- Added a setting under Preferences to configure whether proximity refinement for meshing should be enabled by default.
- Re-meshing multiple touching model meshes will produce a valid mesh. Note that proximity refinement is not supported for model mesh parts.
- Locking a part with a simulation mesh will keep its simulation mesh while allowing the part to be transformed. Once locked, if the part's proximity refinement setting is set to Auto, the part will not be considered during meshing. The user can change this setting before locking the part if they want the part to affect the mesh of nearby parts, which, depending on the model, could increase the meshing time.
- Improved the performance of including and excluding parts while automatic mesh generation is enabled.
- Automatic meshing can be disabled for new models by deselecting it under the default preferences. If a model is opened that has automatic meshing enabled, when this preference is set, a dialog will allow the user to decide if it automatic meshing should be disabled (preventing meshing) when loading the model.
- The simulation mesh of a part can be deleted. When deleted, it forces a complete re-mesh of the part next time it is meshed.
- Added a check that all meshes are available. A notice will be printed in the model status window if a model includes a part that does not have an associated simulation mesh.
- Added a verification info message when cancelling background processes. This is most notable for automatic meshing.
- CADFEKO_BATCH will now remesh the model even if parts were already meshed. This gives the user more control to get an updated mesh using the latest version of CADFEKO.
- Loading a legacy CADFEKO model (.cfx file) will transfer the simulation mesh of a part when available.
- Loading a legacy CADFEKO model (.cfx) file will disable the global proximity refinement mesher setting.
- Implemented a new two-step process for converting legacy CADFEKO models that improves the handling of geometry parts that are difficult to convert.
- CADFEKO model (.cfx file) import will now first resave models older than 2025.1 in the latest version before importing it. The original model is not modified, since the model gets saved in a temporary location. This improves the robustness of CADFEKO model imports.
- Updated the surface mesher library to the latest version. Bug fixes include improved meshing growth rate of triangles around short edges on curved surfaces and addressing incorrect meshing of helixes at certain number of turns.
- Added the option to show tick marks on the global axes in the 3D view.
- Added support for the rendering of mesh connectivity for simulation mesh display.
- Implemented windscreen layer rendering for model mesh parts.
- Windscreen layers are no longer shown for hidden parts.
- Added opacity to windscreen layer rendering.
- Added the ability to specify the compression level for CADFEKO model (.cfx) and CADFEKO mesh (.cfm) files. The default setting provides a good speed versus size tradeoff. Selecting Best compression results in smaller file sizes at the expense of longer file save times, whereas selecting Best speed results in larger files but decreased file save time. The default setting (applicable to new models) can be found at . To adjust the level for the current model, open the setting at .
- Added support for the FEM distributed line port.
- Added support for applying perfect magnetic conductor (PMC) to regions and faces for MoM and MLFMM with surface equivalence principle (SEP). PMC regions are allowed to intersect PMC ground planes.
- Added support for decoupling the FEM problem from the MoM solution using a PMC boundary condition.
- Added the Domain Level Preconditioner solver option.
- Schematic inductors and capacitors now support negative and zero values.
- Added verification warnings to protected models that have locked parts as this could lead to issues with mesh quality or connectivity.
- Upgraded the ECAD import library to the latest version provided by Altair PollEx. Improvements in this upgrade include improvements in the stackup formulation that could have resulted in some layers being missed or merged together.
- Added support for setting S-parameter Touchstone parameter format and parameter precision.
- Added a parametric four arm sinuous antenna to the component library.
- Improved the random colour generation algorithm to try to avoid using colours that are similar to colours that are already being used.
- Write out UT cards more compactly in the .pre file.
- Added a command line option --platform to allow use of the
minimal
oroffscreen
platform plugins to allow running automation scripts on machines that do not support graphical environments.
Resolved Issues
- Resolved a performance regression that got introduced in CADFEKO 2023.1 that caused a slowdown when meshing models containing many wires.
- Extended CADFEKO mesh (.cfm) file writing to detect wires inside PEC regions and not write them out to avoid an error regarding a singular field on the axis of a segment. These wires should rather be removed with the simplify tool, but due to backwards compatibility, the feature was implemented.
- Improved general tree performance when selecting and scrolling.
- Improved the rendering performance of models with large numbers of model mesh items.
- Improved the scrolling behavour of the run dialog.
- Improved the CADFEKO model (.cfx) import process to resolve application crashes happening when importing a model.
- Improved the robustness of importing older CADFEKO model (.cfx) files by first saving them in the latest version and then importing the model.
- CADFEKO model (.cfx file) importing will import work surface definitions.
- CADFEKO model (.cfx file) importing will import the local mesh settings.
- Resolved a crash when copying faces.
- Resolved a crash that could occur when switching focus to the FEM line port dialog.
- Resolved a crash when adding a source or a load to a wire port that was added to a wire before symmetry was defined that intersects the wire.
- Resolved an issue where applying a wire port to a wire that crosses a symmetry plane could result in an internal error or an assertion failure.
- Resolved an issue where an empty .pre file could be generated in some cases when saving a model.
- Resolved an issue where, in some cases, the FDTD mesh size was not correctly restored from a saved model.
- Avoid a crash when using stop/step after running a script with breakpoints in the script editor.
- Fixed a crash when trying to create a windscreen surface from a surface that is not suited to windscreens.
- Resolved a surface meshing issue where fixed points were not always respected.
- Resolved an issue where selecting a vertex on a copied and translated model mesh part would highlight multiple vertices in the 3D view.
- Avoid overlapping segments when wires are in the symmetry plane.
- Mesh refinement is now correct around a wire port if the port is on the symmetry plane.
- Resolved an issue where the regions of a mesh part were ignored when determining if an entity is the last entity in the part. This would have caused the part to be deleted when the last other entity (such as a face or a wire) was removed from the part even when it still had regions (tetrahedra).
- Corrected a problem with CADFEKO mesh (.cfm) file writing where the medium on the two sides of a triangle was incorrectly identified for model mesh faces that consist of one or more small triangles.
- Fixed a problem with the surface line primitive and other primitives created on a work surface that is very large or very small. The legacy converter could have failed to convert some legacy windscreen models due to this problem.
- Resolved an issue with KBL (*.kbl) file importing where curves of degree 1 were represented as straight lines instead of with their consecutive sequence of points.
- Corrected the file extension when exporting a mesh in Nastran format and specifying the filename with the .bdf extension.
- FEM modal mesh ports that are defined using vertices will render the faces transparent.
- Updated validation to not require sources for S-parameter configurations and characteristic mode configurations.
- Improved behaviour relating to workplanes of geometry groups as follows:
- When creating a group, the Global XY plane is used and not the default workplane.
- It is now possible to modify the workplane of a model mesh group, a mesh refinement rule group or a model mesh part from its properties modification dialog.
- Fixed the problem that the model was not indicated as modified after adding or removing model protection. This allows the user to save the model if the only change was the protection status of the model.
- The mesh histogram is now cleared on the mesh info dialog along with the mesh statistics when the mesh is removed from the part under consideration.
- Ensure that the details tree updates to show the selected part when selecting between model mesh topology belonging to different parts in the 3D view.
- Resolved an issue where a model verification error would be issued when using the MTL cable solution method and having defined the frequency as a list of discrete points. The error, that incorrectly indicated that the frequency needed to be set, would not be issued if the frequency was first defined using a different option and then changed to a discrete list.
- Relaxed edge delete validation to allow a redundant edge to be deleted if it is the last edge of the object.
- Disabled memory protection for CADFEKO_BATCH meshing. A warning is printed if there is a chance that the meshing cannot complete with the available memory.
- Voxel grid generation now uses the maximum identical distance for tolerance. For certain cases of small models at high frequency the voxel grid should now be calculable.
- Fixed the issue that the offset Cassegrain reflector antenna from the component library failed with the error Invalid solver variant encountered when selecting MLFMM/PO as the solver type.
- Improved the stability of the Generate Antenna Array application macro to avoid application crashes when creating large arrays with hundreds of elements.
- Re-added the Farm Model to Cluster macro to the application macro library. It was accidentally removed in version 2024.
- Added API functionality to set thickness enabled when thickness is directly set on a face (not via SetProperties).
EDITFEKO
Features
- Extended the CG card with the Domain Level Preconditioner solver option.
- Extended the CG card with the FGMRES solver option.
- Added support to the DA card to allow specifying Touchstone parameter format and Touchstone parameter precision.
- Extended the FP card to define FEM to use a PMC boundary condition.
- Extended the ME card to support PMC triangles.
- Extended the PS card super user options to support magnetic current coefficients.
- Extended the PT card to support FEM distributed line ports.
- Extended the TG card to support PMC triangles.
POSTFEKO
Features
- Added support for the reading in and display of perfect magnetic conductor mesh triangles, as well as the display of magnetic surface currents and error estimation results on perfect magnetic conductor triangles.
- Added support for the FEM distributed line port.
- Updated the data source tool XML to the 2025 format for the Optimise model in HyperStudy application macro.
Resolved Issues
- Fixed the loading of results from the .bof file. The list of frequencies when setting the fixed axis on a graph could have been incomplete when the .fek file was not present and the solution frequency had been specified as a list of discrete points.
- When selecting distance in the slice widget, values very close to zero will be rounded to 0.0.
- Fixed an issue in the DRE import application macro with the auto result detection which did not pick up the far field result type correctly from .dres file.
Solver
Features
- Updated HDF5 to the latest available version bringing through security fixes.
- Improved CMA performance in case RHS vector(s) are used by dropping orthogonality checks and avoiding the solution of the standard MoM matrix equation
- Untracked characteristic mode indices have been removed, since the characteristic mode tracking has been improved to no longer require this.
- Improved CMA mode tracking algorithm based on a hybrid eigencurrent-eigenpattern correlation approach
- Algorithmic changes to the Ray-Launching Geometrical Optics (RL-GO) solver framework resulting in significant run-time reductions (dependent on the example several orders of magnitude) combined with accuracy improvements when incident plane waves are used as excitation. Similar improvements for point sources/antenna will follow in a later release.
- Improved speed and memory requirements for RL-GO when used in connection with ground planes.
- Issue an error if problems solved with asymptotic solvers are too small compared to the wavelength.
- Improvements in the management of mesh storage can dramatically improve runtime performance for models with extremely high numbers of mesh elements and models with non-uniform meshes or fine details. For extreme cases, a 4x speedup for geometry initialization is observed.
- Add the received mode phase information to the received mode expansion data at waveguide and modal ports in the .out file.
- We have updated OptiX to version v9.0. OptiX 9.0 requires the following: 1. Driver version: NVIDIA R570 or newer. 2. CUDA version: CUDA 11.8 or higher is recommended for optimal performance and compatibility. It's important to note that OptiX 9.0 supports NVIDIA GPUs from the Maxwell architecture and newer, including GeForce, RTX/Quadro, and Data Center/Tesla series.
- Computation of PBC interpolation tables is parallelised.
- The text in the out file was improved to indicate where surface integration is used as opposed to Huygens sources when solving using RL-GO.
- For FEM and FEM-MLFMM simulations, FGMRES is now the default iterative solver. If a different solver is required, users can manually select an alternative during simulation setup..
- The default iterative solver applied with MLFMM is now the FGMRES, which brings improved convergence and efficiency.
- Avoid incremental resizing when populating a secondary source list that consists of the port-based sources that should be checked for an overlap at a port definition.
- Compute the reflection and transmission for the main beam (ignoring grating lobes) for periodic boundary conditions
- Optimise spherical mode calculation times, also introducing the use of threaded parallelisation.
- Detect and give an informative error that the application of a metallic medium (exact expression of the skin effect) is not supported in an anisotropic FEM environment.
- Support PMC modelling with the MoM.
- Enable selection of FGMRES as iterative solver for the FEM, FEM/MoM and FEM/MLFMM.
- Optimise the calculation of complex spherical vector modes.
- Updated CUDA to version 12.8. The minimum driver version for CUDA 12.8 is 525.60.13 for Linux x86_64 and 527.41 for Windows. Regarding the minimum compute capability, CUDA 12.8 requires a GPU with compute capability 7.0 or higher.
- When exporting Touchstone S-parameter files, change the default format to RI (real/imaginary data pairs) and allow for the user to specify the precision with which data should be exported.
Resolved Issues
- Added UTD effects in addition to direct reflection where MoM elements are attached to UTD surfaces. This will improve accuracy for antenna coupling problems solved using MoM / UTD.
- Fixed a bug that caused incorrect results for some RL-GO examples where plane waves were used in conjunction with manual ray launching settings.
- Fixed a bug that caused a slight misalignment in some transmitted RL-GO rays with minor effects on accuracy.
- Fix bug for supporting Characterised Surfaces on top of dielectrics with RL-GO.
- Improved parallel scaling for periodic boundary conditions (PBC).
- Improve detection of the incorrect application of unsymmetrical loads/coatings/skin effect at symmetrical mesh elements.
- Fixed a problem with out-of-core file management on Windows when more than 1.1 TByte hard disk space is required for the sparse LU MLFMM preconditioner.
- Resolved an overflow error (internal error 3977) which could be caused during facetted UTD computations for some cases.
- Fixed a bug that caused segmentation violations when calculating creeping rays for the faceted UTD.
- Restore percentage progress output during LU decomposition of the MoM matrix when running the sequential version of Feko.
- Fix solution of a PEC shielded cable combined with the hybrid FEM/MoM in an S-parameter configuration program flow.
- Losses in infinite substrate layers are not included in the reported losses or efficiency calculations. Print a note to inform the user.
- Fixed a bug that caused incorrect values for theta/phi RL-GO using special external settings to be ignored.
- Fix a segmentation violation during the search for metallic triangles matching tetrahedral faces for some VEP models.
- Optimise the processing of source cards. This phase may have resulted in an execution slow down when the model consisted of a large numbers of dipoles.
Shared Interface Changes
Support Components
Features
- Removed newFASANT from the Feko Launcher utility. newFASANT is no longer actively being developed, with the solver technology having been incorporated into Feko. Users who would like to continue using newFASANT can install an older version of Feko that contains newFASANT as a concurrent installation alongside the latest version of Feko.
- New feature to use Windows Powershell for remote launching
Resolved Issue
- Fixed a bug in PREFEKO with the exporting of a multiline protected FR card to the .fek file.
WinProp 2025.1 Release Notes
The most notable extensions and improvements to WinProp are listed by component.
General
Resolved Issues
- The consideration of the antenna phase as given in the .ffe pattern during RunMS for the E field vectors and the transmission matrix has been corrected.
- The correct phase is saved in the .str file including the antenna phase for full polarimetric projects, both for RunPRO and RunMS results.
ProMan
Features
- Extended the FMCW radar post-processing algorithms to include Constant False Alarm Rate (CFAR) and MUSIC (Multiple Signal Classification).
- Improved the handling of bistatic RCS in ProMan (for example, for simulating the impact of RIS).
- Added the ground reflection on pixel topography to the SRT propagation model.
- Corrected the legend text for displaying channel impulse response.
- Five decimals for point and trajectory mode are now saved to the .str file for the x and y coordinates.
- Added support to select a carrier across different frequency bands on the Carrier Assignment dialog. If carriers are unique among different frequency bands, all carriers will be added to the project (each under its frequency band). If carriers are not unique, the Frequency Bands dialog will be displayed to select one of the frequency bands as in previous versions.
- Added the number of launched rays to the Parameter: Shooting and Bouncing Rays (SBR) dialog. The value updates when the Max ray tube width/height or Ray length to first split is modified.
- Improved beam steering for NLOS scenarios to determine the optimum direction that maximises the received power.
Resolved Issues
- Resolved a crash that could have occurred when using the urban IRT with Knife Edge (KE) preprocessing should the KE ray have line of sight (LOS).
- Resolved a crash that occurred when requesting Min. Number of Interactions as computed prediction results.
- The SRT propagation model can also be used for moving satellites in a time-variant project.
- Resolved an issue where not all transmitters were computed in parallel for the rural DPM.
- Resolved an issue where an MS antenna configuration without a name could have resulted in the wrong fields being read from the .mic file, resulting in a crash.
- Resolved a crash that could have occurred during an SBR computation.
- Resolved an issue for the urban IRT where an overflow could have occurred when computing the angles between objects.
- Corrected a bug where the absolute antenna height was not showing the correct antenna height in the PE vertical result plane. The Reset zoom window button is now enabled for arbitrary prediction planes to reset the zoom to the prediction plane extents. Corrected the scaling of the x-axis with the Line plot tool when tracing the result in a non-horizontal direction.
- Added the phase for the knife edge diffracted ray in the vertical plane as post-processing for the urban IRT result.
- Resolved a crash that could have occurred during a CNP IRT computation.
- Resolved a crash that occurred when displaying RCS and cancelling the Edit Project Parameter dialog.
- Duplicated wall numbers are now avoided when creating topo vector .tdv files with additional walls from an .idb file.
- When loading .ffe antenna patterns, undefined values are no longer interpolated; instead, a default value of -100 dBi is used.
- The extension of the prediction area in case of moving transmitter is only done for the DPM, but no longer for the other urban propagation models.
- Resolved issues with the 3D view of prediction results, in case the topo information was missing for some pixels.
- Resolved a crash that could have occurred when using the SBR propagation model for very long distances.
- Corrected the 2D display of very long rays (for example, from the Earth to the moon) and improved the performance when viewing the rays in the 3D view.
- Corrected the progress bar for SRT scattering on topo tiles where the number of tiles can be millions.
- Resolved a crash that could have occurred if with Show only if mouse location was activated.
- Resolved an issue where the displayed MS antenna orientation always showed the azimuth orientation of the default configuration.
- Resolved a crash that could have occurred in EMC analysis if there were many frequency bands and the project's path was long.
- Resolved an issue where incorrect breakpoints could have been considered when using the DPM for combined network planning (CNP).
- Resolved an issue with detecting duplicate rays for the IRT for rays containing reflection or scattering.
- Corrected a bug that could have occurred and accelerated the computation of diffraction angles for one-wall wedges using ray-tracing methods.
- Resolved an issue for the urban IRT where the diffraction angles computed during SRT post-processing were incorrect.
- Resolved an issue where the prediction area differs between the GUI and WinPropCLI when computing the prediction.
WallMan
Feature
- Added support to detect the model unit automatically when converting a .dxf/.dwg file should the INSUNITS variable be defined in the file.
Resolved Issues
- Resolved a crash that occurred when converting a CAD layer from .dwg/.dxf to .idb.
- Resolved problems when exporting a preprocessing project to a ZIP archive.
- Corrected an issue where exporting to NASTRAN format did not include the original triangular objects, only triangulated polygons.
- Some .dxf files exported from WallMan may not be compatible with Altair SimLab. If this happens, the objects should first be triangulated before exporting to a .dxf file.
- Corrected an issue where converting urban building vectors, the UTM zone is now correctly set (Northern or Southern hemisphere) if the option UTM Zone automatically determined is selected and the setting is kept when the option is changed to UTM zone manually defined.
Application Programming Interface
Feature
- Added support in the API for beam steering in 5G networks based on phased array antennas, where the antenna array forms a focused beam in the desired direction and can track the movement of users.
Resolved Issues
- Resolved an issue where, for a disabled trajectory, WinPropCLI might have ended with an error message while reading the result files.
- Resolved issues that could have occurred when using WinPropCLI, resulting in errors.
- Resolved an issue where converting .tda topography files using the API resulted in an error Error (0): Values for columns in file are negative but only positive values are allowed! Error during conversion.
WRAP 2025.1 Release Notes
The most notable extensions and improvements to WRAP are listed by component.
General
Features
- Updated the Propagation model advice dialog to include ITU-R P.684.
- Support for import of Ofcom WTR Database added.
- A license pool for API licenses has been added. A single license is checked out at start of WRAP. At exit , WRAP will check in all of the licenses that have been checked out. Using the license pool will let the API calls execute immediately, without any lengthy license check out, if a license is available.
- Review date has been added to allotments. Option is available while creating and editing allotments. The review date is included in allotment searches both from GUI and API.
- Disconnection from License server is managed as follows: In case WRAP is not being used as an API server, when WRAP is disconnected from the license server, it will show a pop-up window for the user. In case WRAP is being used as an API server (at least one message is sent), if the license server is disconnected until timeout, no pop-up window is shown. Instead, WRAP will wait for the next message and will try checking out new license. If it fails again, it will return an error message and will close after returning the results of any running calculations.
- The ability to create, modify, delete, use, get, link stations in read-only databases via the API has been added. The ability to perform calculations using stations in read-only databases has also been added.
- The calculation speed, when using area patches with a lot of objects, has been improved.
- Filters and Circulators made searchable via API.
- Area patches in Shapefile format may now use coordinate systems other than Lat-Long WGS84, if a standard project file (*.prj) is supplied. The British National Grid has also been added to the recognized coordinate systems.
- 'Review Date' has been added for all types of Equipment and included in their associated search functions.
- Added unit conversion between m and feet and between km and NM to the Radio Calculator dialog.
- More stringent controls added on the antenna diagram to avoid problems when an antenna creation message is sent into the API.
- Ability to log information, especially error information, when saving wpr/wpe project files has been added.
- When a status request is sent to the standard port (1234 by default), an error message is sent back stating "Status Message on Standard Port".
- Resolved the issue with Export Allotment function not exporting the review date.
- Added the possibility to save associated mobile on a station through API.
- The format of SMADEF has evolved and with that the structure in the SMIR database. The SMADEF43 version in WRAP has been updated to support version 4.3.3.
Resolved Issues
- Resolved issues in Coverage calculations, when the mobile height type is above ground level and building or above surface.
- Min and Max values in the statistics of Coverage results are now in correct order.
- When loading geo data in unprojected format, the created internal terrain rasters had lower resolution than they should have had. For very large areas the terrain resolution sometimes was reported as 0 meters. These issues have been resolved.
- SFAF Message contents are now read from Item 005 onwards. In Item 363/463, S is interpreted as M-Mixed. All supplementary details under Item 520 are now concatenated.
- Administrative change 'A' SFAF messages will now try to create a new station instead of calling an unimplemented function.
- Resolved an assertion failure when saving equipment and allotments with an invalid review date. It is now possible to copy equipment from read-only to writeable database.
- Resolved an issue with selection of 'Time' Radio Button within Resolution setting in Edit Trajectory Dialog.
- Resolved an issue for database column sort when the column data contained " - ".
- Resolved the issue in Coverage calculations, when the altitude type in trajectory is 'Above surface'.
- TEmissionClasses within API for Allotment has been extended with a choice of TDesignationOfEmission to complement the TClassOfEmission.
- Option 'Volume Above Sea Level' has been disabled for Mobile Field Strength calculation in Coverage dialog. Also resolved issue related to mobile field strength calculation in Coverage.
- The character '*' can now be used as wildcard in the 'Area' field within Allotment search.
- Resolved an issue with the visibility of Comment field in Allotment Search Dialog.
- Resolved an issue when changing geo class might result in unexpected graphic effects.
- Fixed bugs in Coverage, Interference, and Spectrum Viewer when typical stations are involved in the calculation.
- The return message of TStationCable now follows the same pattern as the input.
- Empty API message no longer hangs WRAP.
- Resolved the issue of removing databases from LocalDB instances within ChangeDB.
- Added the feature to allow the user to save allotments, stations and equipment to read-only databases using the API.
- Error messages returned from API calls could have the incorrect spelling "Unkown" in them. That has been corrected to "Unknown".
- Fixed a problem that might lead to a crash when loading large area maps with very high resolution.
- Fixed a problem when sending an API message to create antenna with wrong DBGUID which might lead to a crash.
- Fixed a problem that caused X and Y to be reversed in the area parameters dialog of the Raster Conversion tab, when using geo classes with different projections.
- Corrected an error in the definition of type TStation in API schema.
- Added an error message when non-status messages are sent on the status port.
- Resolved an issue where WRAP might hang if the Socket Communicator is closed before the calculations are finished.
- Fixed an error when converting height values in vector files into raster files. The handling of empty attribute fields of a polygon has been improved.
- Number of decimals used has been increased to reduce the rounding error in conversion back and forth between foot and meter.
- Dates that are used in SQL queries have internally been changed to use a specified format and not the localized date format which might not be compatible with SQL Server.
- Resolved an issue with copying equipment from read-only to writable database.
- Resolved the issue of WRAP crashing when editing multiple stations, with SFAF connected.
- Resolved the issue for name/area search function for MapInfo files that stopped working after the first search.
- More checks in place to identify illegal date entry in Review Date field.
- Resolved issues in API to allow the use of mobiles and allotments in readable database.
- Resolved an issue with tilt angles on multiple antennas at same station. Now tilt angle of the first antenna does not follow that of the primary.
- Resolved an issue in API function for Cost and Coverage Optimiser.