Create preview 3D
Introduction
- Verify that the 3D skewed geometry generated by the extrusion performed by Flux Skew and the corresponding physical description are correct.
- Create sensors before solving the actual users' scenarios. In Flux Skew,
this procedure allows a faster evaluation of the sensors when compared with
sensors created after solving. Note: Remind that this is a specificity of Flux Skew. In all other modules (Flux 2D and 3D), sensors may be created before solving a scenario without any special command.
How to preview the geometry in 3D
To create the PREVIEW3D scenario:
- While in pre-processing, go to the Solving menu.
- Then, select the Create preview 3D command.
- Flux Skew will then ask for a project name for saving it. The user may choose a new name for that project or overwrite it by providing the current project name.
- At this point, Flux Skew will build a scenario called PREVIEW3D,
which becomes automatically active. The user can then explore the skewed
design in 3D and eventually create sensors. Attention: The dummy PREVIEW3D scenario is considered solved, but contains no results. Consequently, several post-processing actions do not make sense in this context and must not be invoked. Further details are provided in the next section.
Allowed post-processing actions within the PREVIEW3D scenario
The most important actions that are allowed in the PREVIEW3D scenario are summarized in Table 1 below. The availability of the same actions in the regular 2D context of Flux Skew (before solving) and in a proper scenario (after solving) are also shown in that table, for the sake of comparison.
| Context in Flux Skew | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Possible actions | 2D view (before solving) | PREVIEW3D scenario | Regular solved scenario |
| Create sensors |
 |
 |
 |
| Change 2D geometry and physics |  |
 |
 |
| Check skewed geometry |  |
 |
 |
| Create new scenario |  |
 |
 |
Transitioning between the pre-processing (2D view), preview 3D and post-processing contexts (Regular solved scenario) of a project in Flux Skew
Figure 1 below illustrates the different states of a Flux Skew project and the actions required to transit between them.
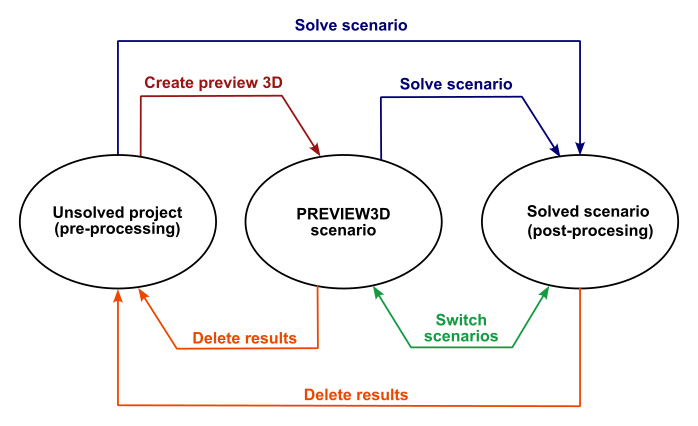
Figure 1. Possible transitions between the different states of a Flux Skew project.