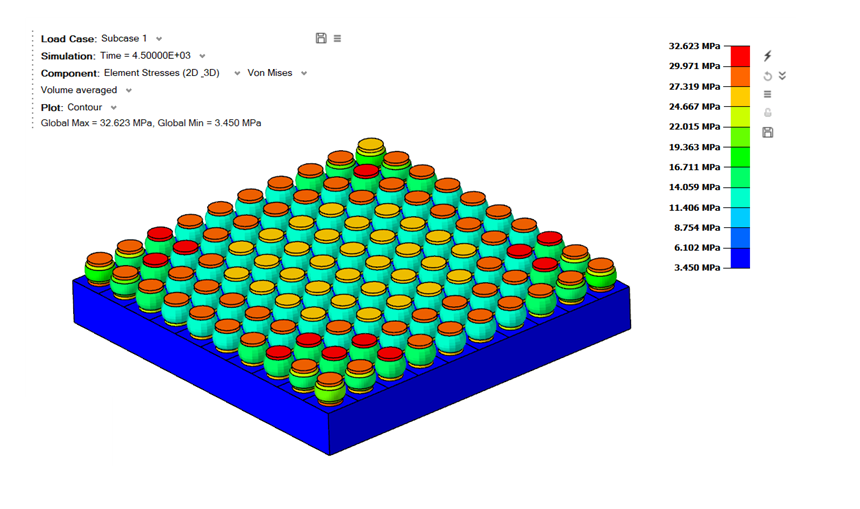
Average Method
![]()
Introduction
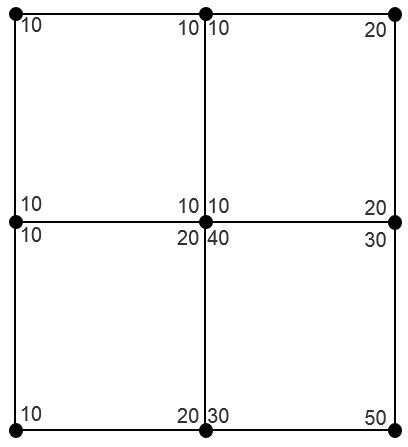
Not Averaged
Not averaged contours are displayed as element nodal contours that varies discontinuously even across element boundaries. The contours are unaffected by surrounding elements (that is, no nodal averaging is performed).
Average Method
In the averaging method, nodal values are directly averaged and the contours are continuous within the element boundary and in the surrounding elements.
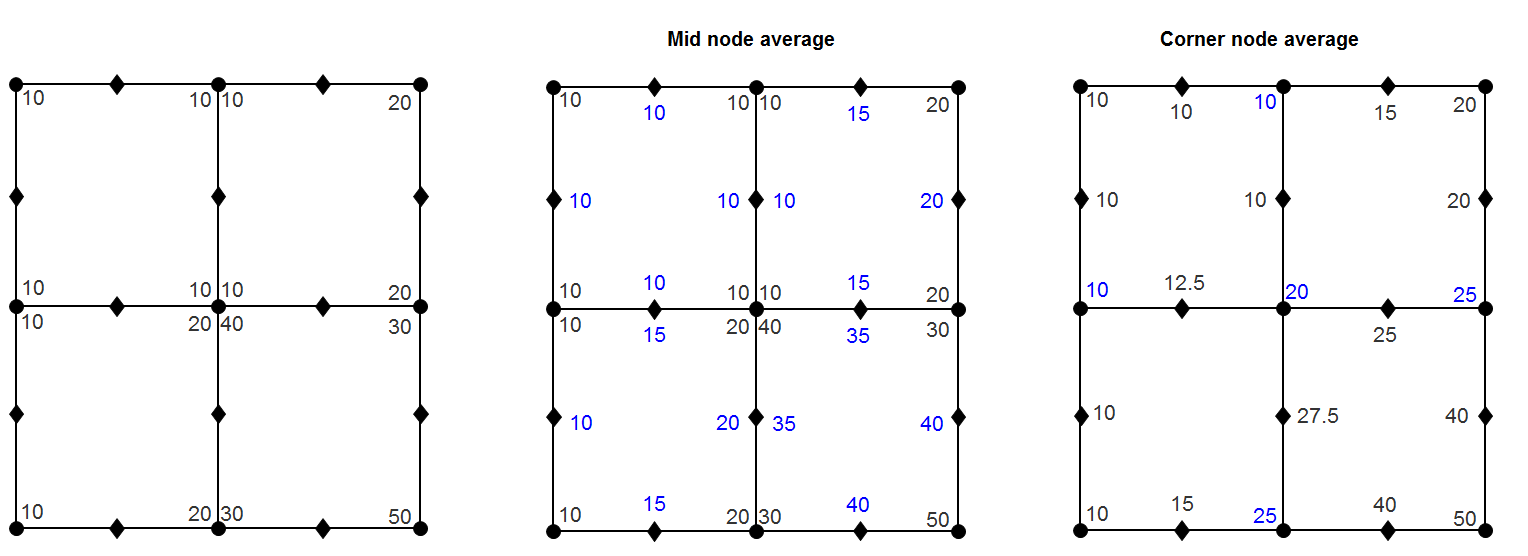
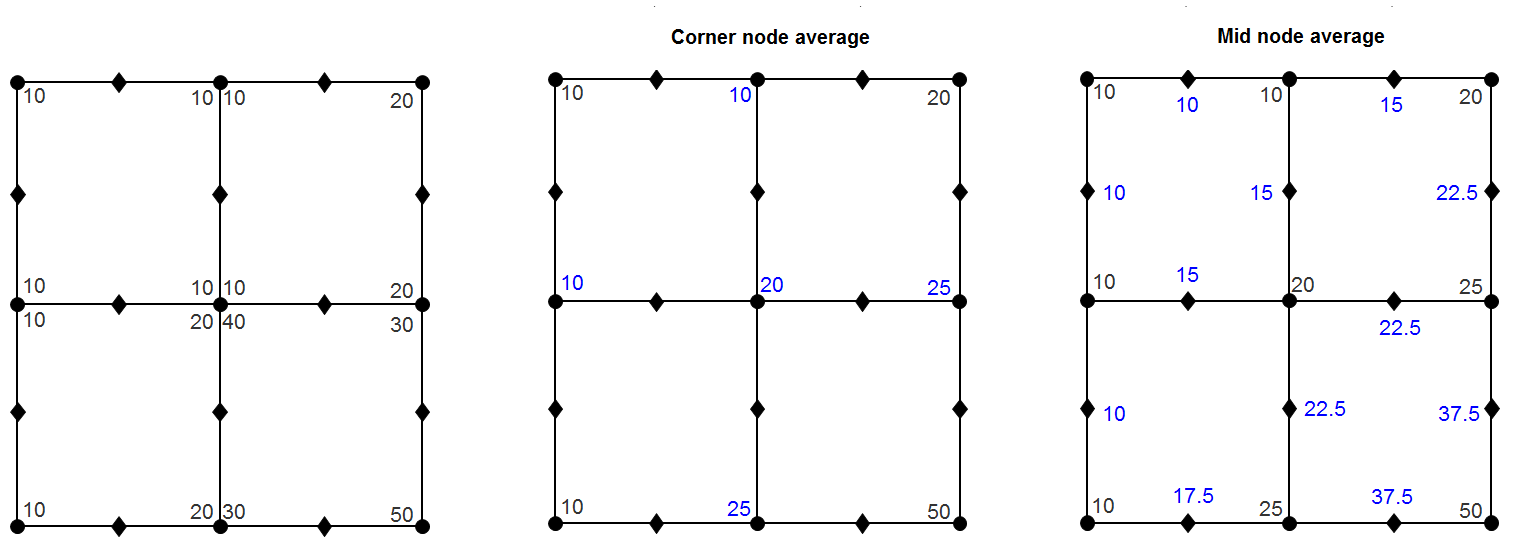
For the higher order elements, the mid node results are obtained by taking average of the corner node results.
There are two ways to calculate the mid node results from the corner nodes.
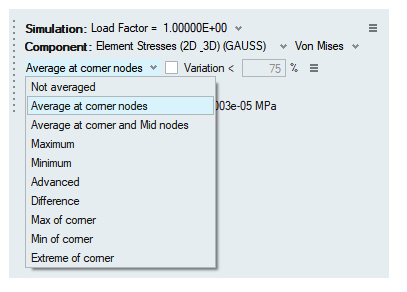
- Average at Corner Nodes
- Average at Corner and Mid Nodes
In this method, invariants are first computed for both the corner and mid-nodes. Then, values for the mid-nodes are calculated by averaging the values of corner nodes for each element, Finally, the average value for each node is calculated by considering all of its connected elements.
Average at Corner and Mid Nodes
In this method, the average value of corner nodes is calculated by considering all its connected elements. Then, the average value of the mid-nodes is obtained by averaging the value of the corner nodes. Finally, the stress invariants are computed using the averaged values of the corner and mid-nodes.
Few other averaging methods are listed below.
- Maximum
- Minimum
- Advanced
- Difference
Maximum
Maximum averaging extracts the maximum values from the adjacent elements connected to a node.
For tensor and vector result component, invariants are computed for each element (or corner) prior to averaging to a node. (e.g.) For tensor it is Principal, Vonmises, etc. and for Vector is Resultant.
Minimum
Minimum averaging extracts the minimum values from the adjacent elements connected to a node.
For tensor and vector result component, invariants are computed for each element (or corner) prior to averaging to a node. (e.g.) For tensor it is Principal, Vonmises, etc. and for Vector is Resultant.
Advanced
Advanced averaging, nodal values are averaged based on the surrounding elements.
For tensor result component, invariants are computed for each element (or corner) with the averaged nodal results value. (e.g.) For tensor it is Principal, Vonmises, etc. and for Vector is Resultant.
Difference
The nodal difference is the difference between the maximum and minimum result value at a node.
The sign of a value is considered in the difference calculation. For example, the difference for the values, 200, 400, -100, and -500 is 900.
For tensor result component, invariants are computed for each element (or corner) prior to averaging to a node. (e.g.) For tensor it is Principal, Vonmises, etc. and for Vector is Resultant.
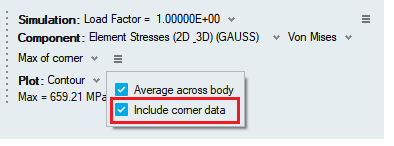
These three averaging methods are displayed in the Results Panel only when the “Include Corner Data” toggle is ON.
- Max of corner
- Min of corner
- Extreme of corner
Max of Corner
Max of corner averaging means that the maximum value from all the corners of an element is extracted and the value is shown at the centroid of the element.
Min of Corner
Min of corner averaging means that the minimum value from all the corners of an element is extracted and the value is shown at the centroid of the element.
Extreme of Corner
Extreme of corner averaging means that the extreme value from all the corners of an element is extracted and the value is shown at the centroid of the element.
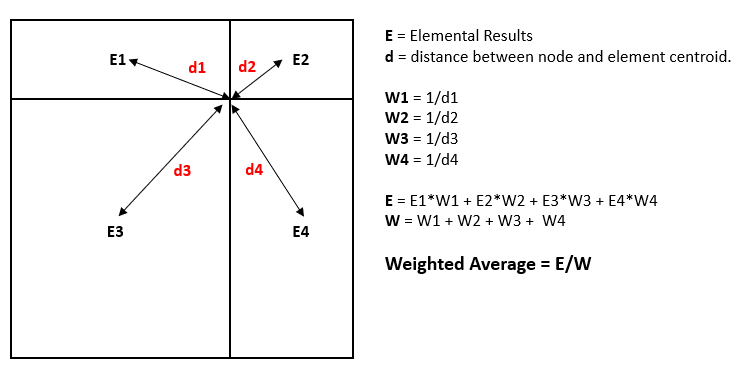
Weighted AverageThis averaging is supported only for EFlow solutions. It is calculated by the weight of the connected elements.
Volume Averaged
This averaging method is supported for Optistruct results and is shown only when the results are available at the element centroid. This method performs averaging across each connected volume of elements within a body.