Adding a Python Transform Operator
A Python script can be executed as a data transformation step in the data pipeline.
- On the Application page, click
 and select Python Transform in the Add Operator pane.
and select Python Transform in the Add Operator pane.
The Python Transform node
 icon displays in the Graph pane, as well as the properties to be defined in the Operator Settings pane, and the preview of the data in the Schema pane.
icon displays in the Graph pane, as well as the properties to be defined in the Operator Settings pane, and the preview of the data in the Schema pane.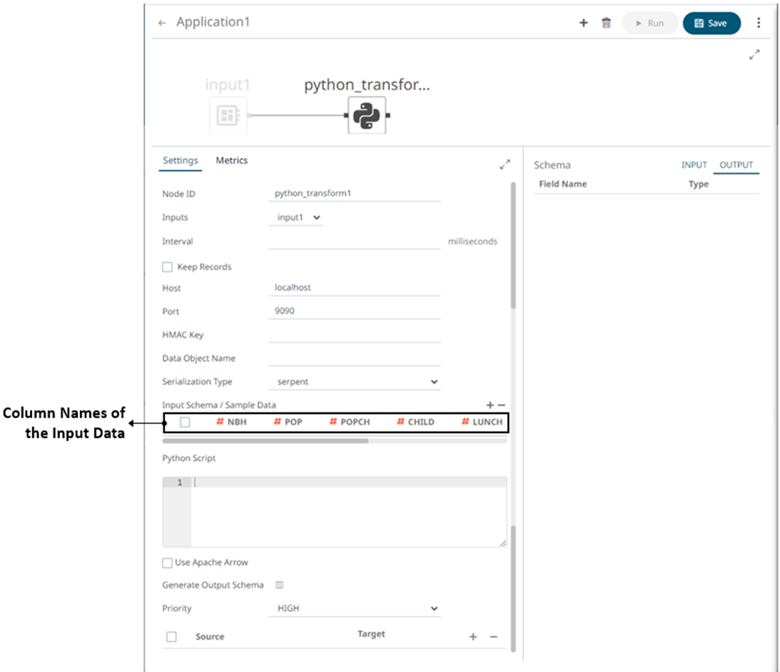
The right (outbound) edge allows you to connect to the other operators.
- In the Operator Settings pane, define or select the following required properties:
Property Description Node ID
The ID of the Python Transform operator.
Inputs
The stream of records or input you will be subscribed to.
Interval
The interval of which the data should be published to the output stream (in milliseconds).
Keep Records
Select to retain or not remove flushed elements. This means the entire set of records will be flushed at each interval.
Host
Host of the Python Pyro instance.
Port
Port of the Python Pyro instance.
HMAC Key
The HMAC key that will be used to connect to the Python Pyro instance.
Data Object Name
The data structure (array of dictionaries) that Panopticon will produce, and then will be utilized by the Python Script.
Serialization Type
The serialization type: Serpent or Pickle
-
Simple serialization library based on ast.literal_eval
-
Faster serialization but less secure
NOTE: The Host, Port, HMAC Key, and Serialization Type fields will be hidden if their corresponding properties are set in the Streams.properties file.
Role Corresponding Property in Streams.properties Host
connector.python.host
Port
connector.python.port
HMAC Key
connector.python.password
Serialization Type
connector.python.serializertype
-
- Enter the required Python Script to execute on the active Pyro instance.
- Select the Use Apache Arrow checkbox to enable fast serialization of data frames in the Python transform.
- In the Input Schema/Sample Data section, the column names of the Input data source are displayed. In cases where there are no rows from the input data source and the Python script is not handling zero rows, you can add sample data to ensure transform is applied.
To add or manage the sample data, you can use the following icons:
Button Description 
Add sample data for the input column names.
Select the checkbox of a sample data row and click
 to delete, or select the topmost check box and click
to delete, or select the topmost check box and click  to delete all of the sample data rows.
to delete all of the sample data rows.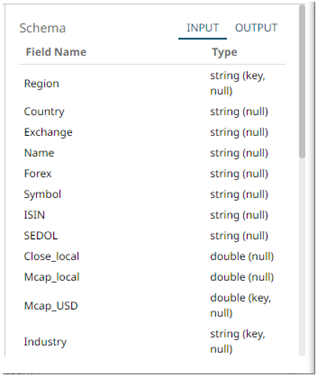
- In the Generate Output Schema section, click Generate Output Schema
 to fetch the schema of the output topic. This populates the list of columns, with the data type found from inspecting the first ‘n’ rows of the file.
to fetch the schema of the output topic. This populates the list of columns, with the data type found from inspecting the first ‘n’ rows of the file.
- Select the Priority of the node's startup:
Priority Description APPLICATION
Running and successful completion of the node is critical in the application startup.
HIGHEST
Highest priority but not critical.
HIGH (Default)
High priority but not critical.
STANDARD
Standard priority.
LOW
Low priority.
- You can also click the following icons:
Button Description 
Fetch the schema of the output topic. This populates the list of columns, with the data type found from inspecting the first ‘n’ rows of the file.
Add a new field entry.
Select the checkbox of a field entry and click
 to delete.
to delete. - Save the changes.
Example

(c) 2013-2025 Altair Engineering Inc. All Rights Reserved.