Connector for JDBC
JDBC connector is the new version of JDBC Legacy and is the recommended connector for any new JDBC connectivity for better performance and configuration UI. Just like the JDBC Legacy connector, it also allows the retrieval and processing of data from virtually any database, that has a JDBC driver.
- On the Connection tab, set either of the following connection settings:
- JNDI Name

Enter the JNDI resource name to be used.
NOTE: The JNDI resource name needs to be on the form: jdbc/[resourcename]
- URL
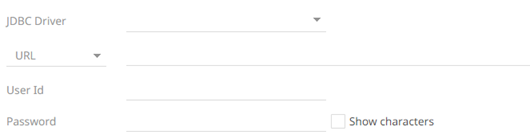
Select the JDBC Driver then enter its specific URL, and the User Id and Password.
Select the Show Characters checkbox to display the entered characters.
- JNDI Name
- Adjust the Timeout, if needed. Default is 60.
- Query definition and execution can be done, using either the query builder or freeform SQL. To use the query builder, select the Query Builder tab. Otherwise, proceed to step 13.
The Use Query Builder option is turned on by default.
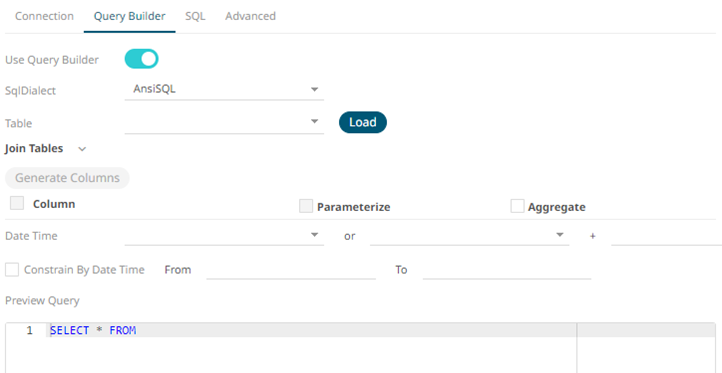
- Select the appropriate SQL Dialect in the drop-down list to be able to generate the correct SQL for the required data repository.
- On the Table field, click
 to populate the drop-down list with tables. Select a table.
to populate the drop-down list with tables. Select a table.
The SQL query is generated and displayed in the Preview Query text box.
Also, expanding the Join Tables displays the list of tables that you can join.
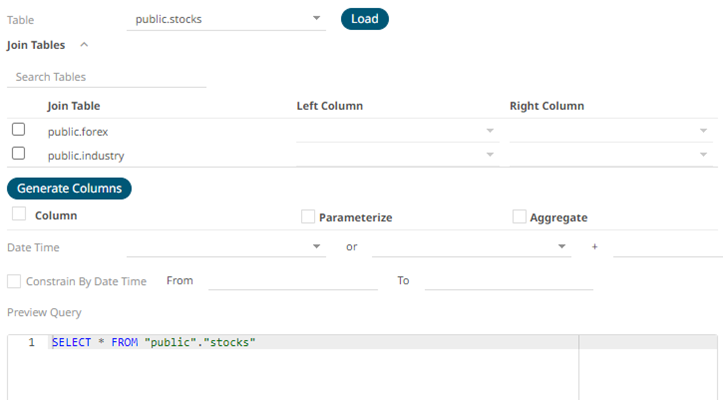
Use Search Tables to filter the list.
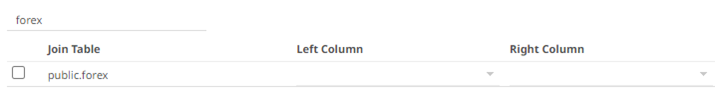
- Perform a join by checking one or more tables in the list.
The Left Column and Right Column fields are automatically filled out with the common fields.
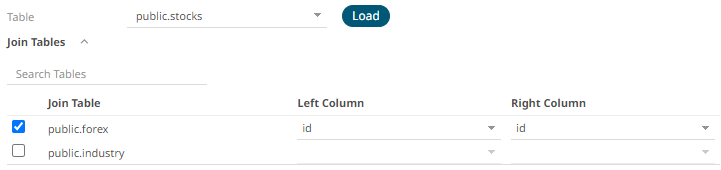
You can also opt to select other common fields.
The SQL query is generated and displayed in the Preview Query text box.
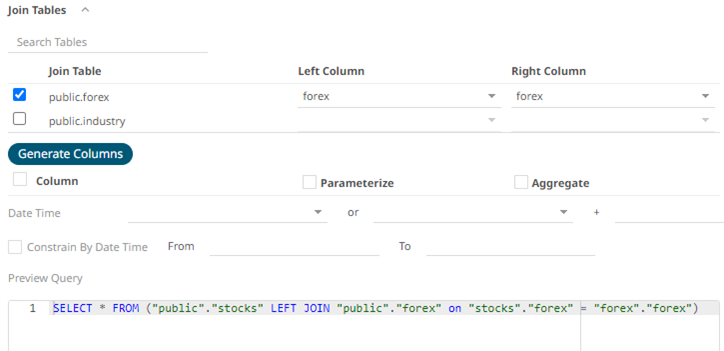
- Click
 . The columns populate the Output Column section.
. The columns populate the Output Column section.
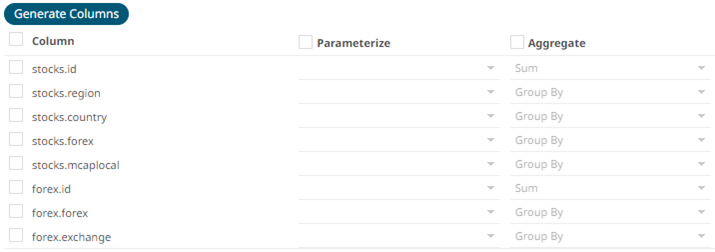
- Individual columns can be added by checking the corresponding Column box in the Output Column listing. To select all of the columns, check the topmost box.
The SQL query is generated and displayed in the Preview Query text box.
- If the data returned is to be aggregated, then the Aggregate checkbox should be selected. For each selected column, the possible aggregation methods are listed including:
- Text Columns: Last, First, Count, Group By
- Date Columns: Count, Min, Max, Group By
- Numeric Columns: Last, First, Sum, Count, Min, Max, Mean, Group By
- Select the Parameterize checkbox and match the parameter to the appropriate column. By default, they will be matched by name.
The appropriate SQL Query is updated in the Preview Query text box.
- If the data is filtered or aggregated on Date/Times, then a valid Date Time field needs to be selected from either a single Date/Time field, or a compound column created from a selected Date and a selected Time column.
- Select the Constrain by Date Time checkbox, and enter From and To Date/Time constraints that are assumed to be in this time zone for incorporation into the query.
If the query is to filter/constrain the results on Date/Time, the constrain sections are completed.
- To use freeform SQL, select the SQL tab and turn on the Use SQL toggle button.
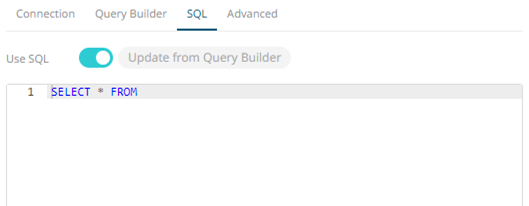
- Modify the SQL-like query language in the User Query text box.
NOTE:
- If you initially used the Query Builder then switched to the freeform SQL option, the content of Preview Query is copied to the User Query text box.
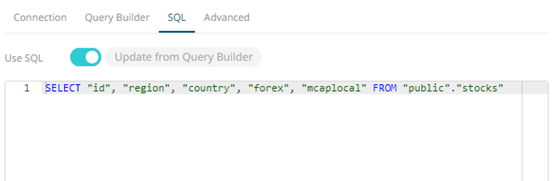
- Switching back to the Query Builder, the Preview Query is updated, keeping the User Query unmodified.
 is enabled when User Query is non-empty and different from Preview Query.
is enabled when User Query is non-empty and different from Preview Query.Click this button to update the User Query from the query builder.
- If you initially used the Query Builder then switched to the freeform SQL option, the content of Preview Query is copied to the User Query text box.
- Select the Advanced tab.
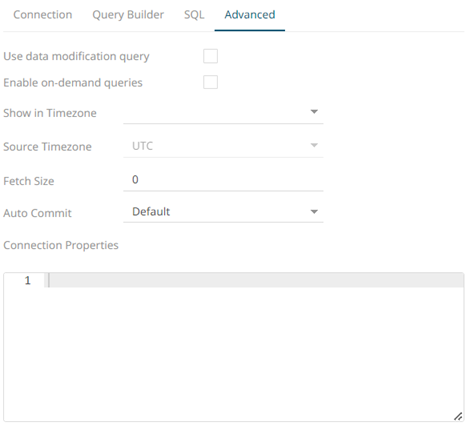
Set the following properties, if needed:
Property Description Use data modification query
Signals that the table is created for writing data. This property is also used for filtering out target data tables for further data update action configuration
Enable on-demand queries
On-demand queries provide ROLAP functionality to the Altair Visual Data Discovery products, where the aggregation and filtering tasks are largely offloaded to the underlying data repository.
Fetch Size
Sets the number of rows to fetch per iteration.
Auto Commit
Postgres ignores fetch size if auto commit is not set to False. You would need to explicitly set it to force when using fetch size.
Connection Properties
NOTE: This property is only applicable for URL connection.
Enter Java-style properties format which can consist of a series of lines (terminated by CRLF, CR, or LF) where each is a key-value pair, a comment, or a blank line.
You can opt to define the Show in Timezone and Source Timezone settings.
NOTE: The time zone transformation is not applied to Date columns.
(c) 2013-2025 Altair Engineering Inc. All Rights Reserved.