DSHUFFLE
Bulk Data Entry Defines parameters for the generation of composite shuffling design variables.
Format
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSHUFFLE | ID | ETYPE | EID1 | EID2 | EID3 | EID4 | EID5 | EID6 | |
| + | EID7 | etc | |||||||
| + | MAXSUCC | MANGLE | MSUCC | VSUCC | |||||
| + | |||||||||
| + | PAIR | PANGLE1 | PANGLE2 | POPT | |||||
| + | CORE | CREP | CANG1 | CANG2 | CANG3 | CANG4 | CANG5 | CANG6 | |
| + | CANG7 | etc | |||||||
| + | COVER | VREP | VANG1 | VANG2 | VANG3 | VANG4 | VANG5 | VANG6 | |
| + | VANG7 | etc | |||||||
| + | RANGE | PIDSTA | PIDEND |
Definitions
| Field | Contents | SI Unit Example |
|---|---|---|
| ID | Unique identification
number. No default (Integer > 0) |
|
| ETYPE | Entity type for which this
DSHUFFLE card is defined.
No default |
|
| EID# | Entity identification
numbers. List of entities of type ETYPE for which
this DSHUFFLE card is defined. No default (Integer > 0) |
|
| MAXSUCC | Indicates that the "maximum number of successive plies" constraint is applied. Multiple MAXSUCC constraints are allowed. 1 | |
| MANGLE | Ply orientation, in
degrees, to which the MAXSUCC constraint is
applied. No default (Real or ALL) |
|
| MSUCC | Maximum number of
successive plies for the MAXSUCC constraint. No default (Integer > 0) |
|
| VSUCC | Allowable percentage
violation for the MAXSUCC constraint. 0.0
indicates that this constraint cannot be violated. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
|
| PAIR | Indicates that a pairing constraint is applied. 2 | |
| PANGLE1 | First ply orientation, in
degrees, to which the PAIR constraint is
applied. No default (Real, only 45.0 allowed at this time) |
|
| PANGLE2 | Second ply orientation, in
degrees, to which the PAIR constraint is
applied. No default (Real, only -45.0 allowed at this time) |
|
| POPT | Pairing option.
|
|
| CORE | Indicates that a ply sequence for the core layer is defined. Only one CORE sequence is allowed. 3 | |
| CREP | Number of times the core
ply sequence should be repeated. Default = 1 (Integer > 0) |
|
| CANG# | Ply orientations, in
degrees, defining the core. No default (Real) |
|
| COVER | Indicates that a ply sequence for the cover layer is defined. Only one COVER sequence is allowed. 3 | |
| VREP | Number of times the cover
ply sequence should be repeated. Default = 1 (Integer > 0) |
|
| VANG# | Ply orientations, in
degrees, defining the cover. No default (Real) |
|
| RANGE | Indicates that starting
and ending ply identification numbers are defined in the following
fields to specify the range of plies to be shuffled. OptiStruct will only shuffle plies between
PIDSTA and PIDEND.
Note: The ply sequence is respected for RANGE
and the range is not a numerical range from one integer to
another. 5 Multiple DSHUFFLE entries can be created to define different ply ranges. |
|
| PIDSTA | The ply identification
number (starting ply) in the stacking sequence defined in
STACK Bulk Data Entry that defines the first
ply in the range to be shuffled. No default (Integer > 0) |
|
| PIDEND | The ply identification
number (ending ply) in the stacking sequence defined in
STACK Bulk Data Entry that defines the last
ply in the range to be shuffled. No default (Integer > 0) |
Comments
- The MAXSUCC constraint
indicates that the stacking sequence should contain no sections with more than a
given number of successive plies with the same orientation. In the case of
symmetrical laminates, this constraint accounts for the mirrored successive plies on
both sides of the symmetry plane.
Figure 1. . (a) shows invalid and valid sequences for a non-symmetrical stack, and (b) shows invalid and valid sequences for a symmetrical stack, both for MAXSUCC=3
- The
PAIR constraint indicates that 45° and -45° plies should be
paired together. The POPT option specifies how the pairing should
be accomplished.
Figure 2.
- The CORE and
COVER constraints specify stacking sequences for the core
and cover layers, respectively. Plies are listed from the bottom surface upward,
in respect to the element's normal direction. In the example below, the sequence
for the core is (0°, 0°, 90°, and 90°) while the sequence for the cover is
defined as (90°, 90°, 0°, and 0°).
Figure 3.
Note: For non-symmetrical laminates, COVER corresponds to the bottom cover, whereas CORE corresponds to the upper cover. At this point, it is not possible to create an actual core for non-symmetrical stacks. - For a more detailed description and an example, refer to Optimization of Composite Structures in the User Guide.
- The RANGE
constraint considers the stacking sequence besides the starting and ending ply
ID numbers. These ply ID numbers are purely used to identify the starting and
ending ply IDs in the laminate, between which the plies are to be shuffled. They
are not a numerical range of ply IDs. If any ply, which is not supposed to be
shuffled, is located in the middle of the shuffling plies, multiple
RANGE constraints are required.In the following example, to exclude ply# 5101 from the shuffling process, two RANGE constraints are specified.
DSHUFFLE 1 STACK 1 + RANGE 1101 3101 + RANGE 3201 4301Figure 4. 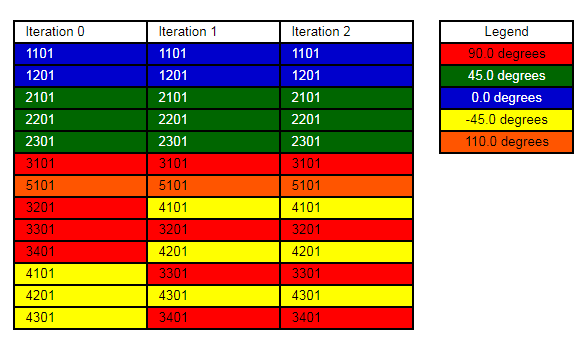
- This card is represented as an optimization design variables in HyperMesh.


