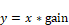
Block Category: Arithmetic
Inputs: Real or complex scalars, vectors, or matrices
Description: The gain block multiplies the input signal by the gain amount. You can enter a value in the dialog; you can alternatively double-click the gain block to enter a value.
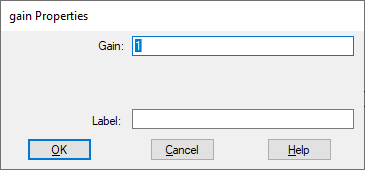
Gain: Indicates the constant multiplier of the input signal. The default is 1. You can enter a value in hexadecimal notation or as a C expression or complex number.
Label: Indicates a user-defined block label that appears when View > Block Labels is activated.
1. Gain of a scalar
Consider the equation y(t) = 3 sin(t), which can be realized as:
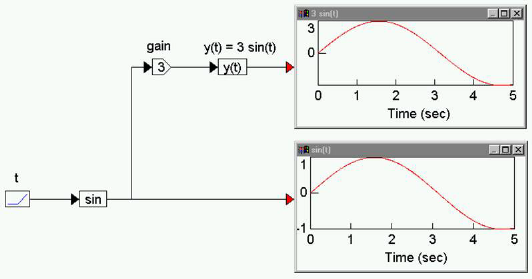
A ramp block is used to access simulation time t, a sin block generates sin(t), a gain block amplifies sin(t) to 3 sin(t). Both sin(t) and y(t) are shown in plot blocks for comparison.
2. Gain of a vector
Consider the equation:
z = 7 x
where x = [-1 5.6 4]. This equation can be realized as:
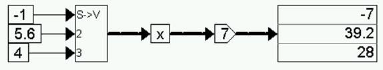
The gain block performs an element-by-element gain operation on the incoming vector.
3. Gain of a matrix
Consider the equation:
Z = 4.2 X
where 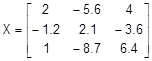
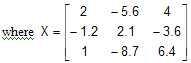
This equation can be realized as:
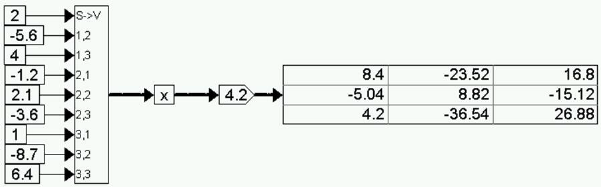
The gain block performs an element-by-element gain operation on the incoming matrix.