DiscreteIntegral
This block implements a discrete integrator. The output is the integral of the input signal.
![]()
Library
Activate/Dynamical
Description
The DiscreteIntegral block implements a discrete integrator. The output is an approximation of the integral of the input signal. Various integration methods are supported.
Forward Euler method is given by
x(k) = x(k-1) + step*u(k-1)
Backward Euler method is given by
x(k) = x(k-1) + step*u(k)
Heun (Trapezoidal) method is given by
x(k) = x(k-1) + step*[u(k-1)+u(k)]/2
This block supports double and complex data types.
Parameters
| Name | Label | Description | Data Type | Valid Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
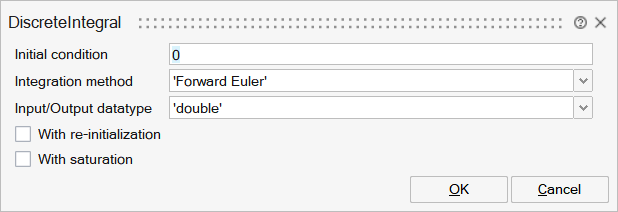
x0 | Initial condition | Initial state of the integrator. Only datatype double is supported. | Matrix | |
method | Integration method | Integration method. Default: Forward-Euler. | String | 'Forward |
typ | Input/Output datatype | Specifies the data type of the input and output.Supported types are: double, complex, int32, int16, int8, uint32, uint16, uint8, inherit. | String | 'double' |
reinit | With re-initialization | Check this parameter to reset its state to the specified initial condition based on an external signal. | Number | 0 |
satur | With saturation | Check this parameter to limit the states to a value between the Lower saturation limit and Upper saturation limit parameters. | Number | 0 |
limit | Saturation limit | Structure | ||
limit/max | Upper limit | Real value. Active only if With Saturation parameter is active. | Cell of matrices | |
limit/min | Lower limit | Real value. Active only if With Saturation parameter is active. | Cell of matrices |
Ports
| Name | Type | Description | IO Type | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Port 1 | explicit | Integration result. | output | 1 |
Port 2 | explicit | Signal to be integrated. Must be double. | input | 1 |
Port 3 | explicit | input | reinit | |
Port 4 | activation | input | reinit+1 |
Advanced Properties
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
always active | no | |
direct-feedthrough | yes/no | The feedthrough property of the second input (if present) is always true. That of the first input depends on the choice of the method: it is false only in case of "forward Euler". |
zero-crossing | no | |
mode | no | |
continuous-time state | no | |
discrete-time state | yes |