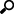Creating Solace Input Data Source
The Solace connector allows connection to Solace’s message bus on a real time streaming basis. Specifically, the connector allows Panopticon Streams to subscribe to messages that are published in particular topics in Solace and consequently, perform operational analytics.
Steps:
1. In the New Data Source page, select Input > Solace in the Connector drop-down list.
2. Enter the connection details including:
|
Property |
Description |
|
Host |
Solace host address. |
|
VPN Name |
Message VPN name. Default is default. |
|
User Id |
The user Id that will be used to connect to Solace. |
|
Password |
The password that will be used to connect to Solace. |
3. Enter the Topic or the queue physical name.
4. Select the Message Type. This will specify the format of the data within the message.
Aside from the Fix, Json, Text, and XML message types, Protobuf is also supported in Solace.
If Protobuf is selected, confirm the Decimal Separator, and enter the Schema Name and Type Name.
Then
click  to
select the File Descriptor (.desc
file) in the Open
dialog.
to
select the File Descriptor (.desc
file) in the Open
dialog.
|
Property |
Description |
|
Schema Name |
The Protobuf schema. |
|
Type Name |
The message of Protobuf type that will be sent to Kafka. |
|
File Descriptor |
The FileDescriptorSet which: · is an output of the protocol compiler. · represents a set of .proto files, using the --descriptor_set_out option. |
5. Select either the period (.) or comma (,) as the Decimal Separator.
|
NOTE |
Prepend 'default:' for the elements falling under default namespace. |
6. Click  to
the fetch the schema based on the connection details. This populates
the list of columns with the data type found from inspecting the first
‘n’ rows of the input data source.
to
the fetch the schema based on the connection details. This populates
the list of columns with the data type found from inspecting the first
‘n’ rows of the input data source.
7. You can opt
to click  to
add columns to the Solace connection that represent sections of the
message. Then enter or select:
to
add columns to the Solace connection that represent sections of the
message. Then enter or select:
|
Property |
Description |
|
Name |
The column name of the source schema. |
|
Type/JsonPath/Column Index/XPath |
The SDTMap Type/JsonPath/Text Column Index/XPath of the source schema. |
|
Type |
The data type of the column. Can be a Text, Numeric, or Time |
|
Date Format |
The format when the data type is Time. NOTE: To parse and format times with higher than millisecond precision, the format string needs to end with a period followed by sequence of upper case S. There can be no additional characters following them. For example: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS |
|
Filter |
Defined parameters that can be used as filter. Only available for JSON, Text, and XML message types. |
|
Enabled |
Determines whether the message field should be processed. |
To
delete a column, check its  or
all the column entries, check the topmost
or
all the column entries, check the topmost  ,
then click
,
then click  .
.
8. To create a new Timestamp field, enter a new Timestamp Name and then select the valid Date/Time from either a single Date or Time field, or a compound column created from Date and Time fields.
9. Define the Real-time Settings.
10. Click . The
new data source is added in the Data Sources list.