Connector for Apache Kafka
Allows Panopticon to subscribe to Kafka topics on an external cluster.
|
NOTE |
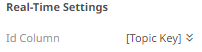
The key provided from the Kafka subscription is automatically selected as the Id Column.
|
Steps:
1. Enter the connection details:
|
Property |
Description |
|
Bootstrap Server |
List of host/port pairs of Kafka servers used to bootstrap connections to a Kafka cluster. By default, the value is localhost:9092. However, this can be overridden by specifying another bootstrap server in the External Settings text box (as specified in step 4). |
|
Schema Registry Host |
Where the Schema Registry is located. This can be in a different location from the Kafka cluster. |
|
Schema Registry Port |
The port number of the schema registry which provides the serving layer for the metadata. Default is 8081. |
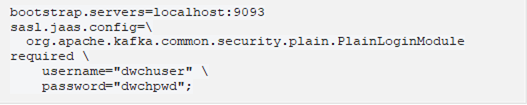
2. Enter the External Settings to support authentication (i.e., username and password). Note that if the bootstrap server is not secure, then there is no need to authenticate, and you may leave this text box blank.
Below is an example of system settings for an SASL authentication:
3. Click  .The first topic in the Topic drop-down list is selected and the
schema is displayed.
.The first topic in the Topic drop-down list is selected and the
schema is displayed.
By default, the Hide Internal Topics toggle button is enabled, and the Avro message type is selected.
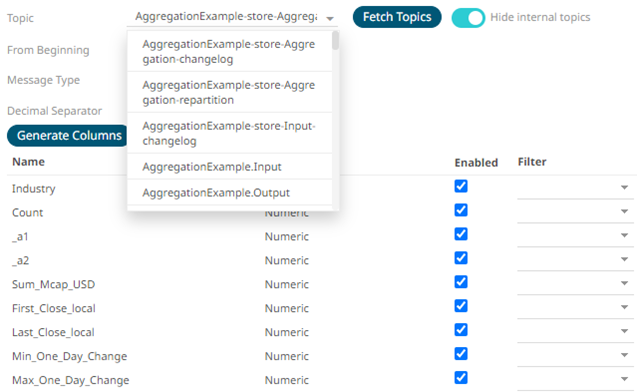
Tap the slider to turn it off. The internal Kafka topics are also displayed in the drop-down list.
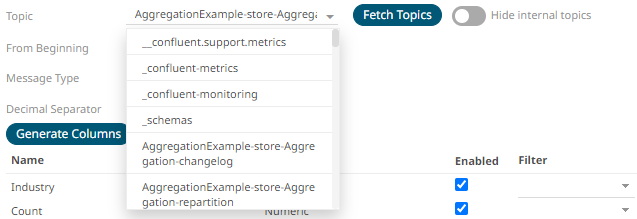
4. Click the drop-down list to search and select the desired topic.
For non-Avro topics, select the Message Type: Fix, JSON, Text, XML, or Protobuf.
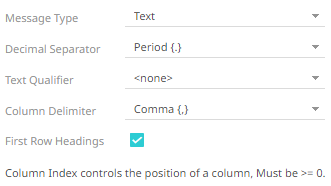
· If Text is selected, confirm the Decimal Separator, Text Qualifier, Column Delimiter, and if the first row of the message includes column headings.
|
Property |
Description |
|
Text Qualifier |
Specifies if fields are enclosed by text qualifiers, and if present to ignore any column delimiters within these text qualifiers. |
|
Column Delimiter |
Specifies the column delimiter to be used when parsing the text file. |
|
First Row Headings |
Determines if the first row should specify the retrieved column headings, and not be used in data discovery. |
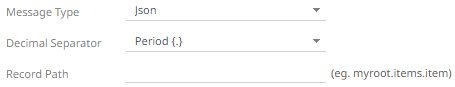
· If JSON is selected, enter the Record Path which allows the identification of multiple records within the JSON document (e.g., myroot.items.item).
|
Property |
Description |
|
Record Path |
The record path that will be queried by the connector’s path (e.g., myroot.items.item). |
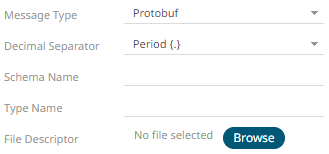
· If Protobuf is selected, confirm the Decimal Separator, and enter the Schema Name and Type Name.
Then click  to select the File Descriptor
(.desc
file) in the Open dialog.
to select the File Descriptor
(.desc
file) in the Open dialog.
|
Property |
Description |
|
Schema Name |
The Protobuf schema. |
|
Type Name |
The message of Protobuf type that will be sent to Kafka. |
|
File Descriptor |
The FileDescriptorSet which: · is an output of the protocol compiler. · represents a set of .proto files, using the --descriptor_set_out option. |
5. Check the From Beginning box to subscribe from the beginning to the latest messages.
If un-checked, you will only be subscribed to the latest messages.
6. Select either the dot (.) or comma (,) as the Decimal Separator.
|
NOTE |
Prepend 'default:' for the elements falling under default namespace. |
7. Click  to fetch the schema based on the
connection details. Consequently, the list of columns with the data
type found from inspecting the first ‘n’ rows of the input data source
is populated and the Save button is enabled.
to fetch the schema based on the
connection details. Consequently, the list of columns with the data
type found from inspecting the first ‘n’ rows of the input data source
is populated and the Save button is enabled.
This also populates the Id Column with the set of columns, of arbitrary type, that can be concatenated to form a unique row identifier.
8. You can also opt to load or save a copy of the column definition.
9. For non-Avro message types, except Protobuf, click ![]() to add columns to the Kafka connection
that represent sections of the message. Then enter or select:
to add columns to the Kafka connection
that represent sections of the message. Then enter or select:
|
Property |
Description |
|
Name |
The column name of the source schema. |
|
Fix Tag/JsonPath/Text Column Index/XPath |
The Fix Tag/JsonPath/Text Column Index/XPath of the source schema. |
|
Type |
The data type of the column. Can be a Text, Numeric, or Time |
|
Date Format |
The format when the data type is Time. |
|
Filter |
Defined parameters that can be used as filter. Only available for Avro, JSON, Text, and XML message types. |
|
Enabled |
Determines whether the message field should be processed. |
|
NOTE |
To parse and format times with higher than millisecond precision, the format string needs to end with a period followed by sequence of upper case S. There can be no additional characters following them. For example: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS |
10. Date/Time values of output data and Date/Time inputs, where supported, is by default unchanged.
You can opt to define the Show in Timezone and Source Timezone settings.
11. For this section:
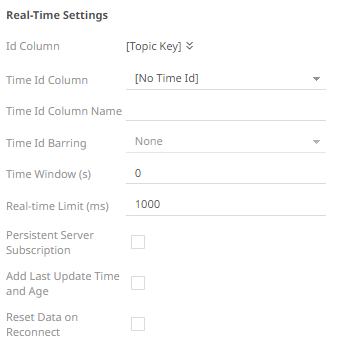
Refer to Define Real-Time Settings for more information.