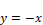
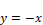
Block Inputs: Scalar, vector, or matrix.
The -X block negates the input signal.
1. Negation of a scalar
Consider the equation y(t) = - sin(t), which can be realized as shown below.
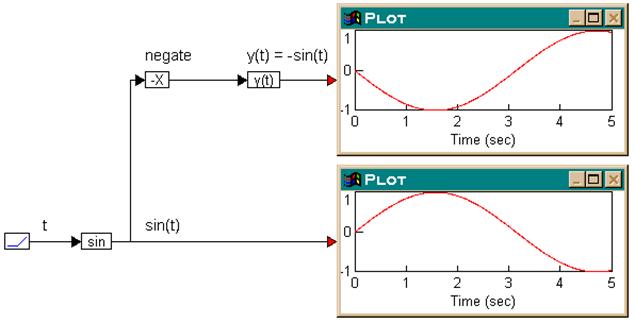
A ramp block is used to access simulation time t, a sin block generates sin(t), and a -X block converts sin(t) to -sin(t). Both sin(t) and y(t) are plotted for comparison.
2. Negation of a vector
Consider the equation:
z = -x
where x = [-1 5.6 4]. This equation can be realized as:
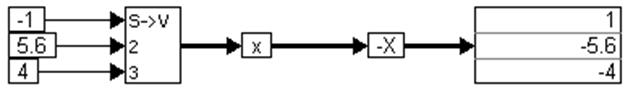
A scalarToVector block creates a three-element vector from the constant values -1, 5.6, and 4. When the simulation runs, the –X block performs an element-by-element negate operation on the incoming vector.
3. Negation of a matrix
Consider the equation:
Z = -X
where
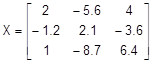
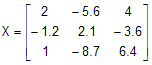
This equation can be realized as:
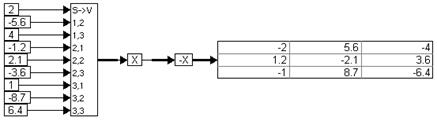
When the simulation runs, the –X block performs an element-by-element negate operation on the incoming matrix.